
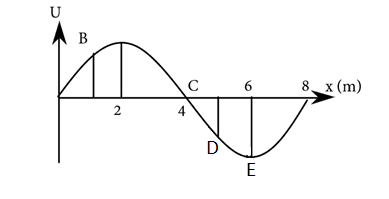
Potential energy curve is shown in figure. Point at unstable equilibrium is:
(A) \[x = 6\]
(B) \[x = 4\]
(C) \[x = 2\]
(D) \[x = 3\]
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: An object is in equilibrium when the net force on it is zero. The force on a body can be given as the negative of the gradient of the potential energy. Unstable equilibrium occurs when a slight displacement will cause a decrease in potential energy.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}}\], where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[U\] is the potential energy of the body, and \[x\] is the position of the body.
\[\dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}}\] signifies an instantaneous rate of change of potential energy with distance (called gradient).
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
A graph of potential energy with distance is given, and we are to find the point of unstable equilibrium.
Generally, we know that equilibrium exists where the sum of the forces acting on a body is zero. Hence we need first to identify the point of zero net force.
The force acting on a body can be given as
\[F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}}\], where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[U\] is the potential energy of the body, and \[x\] is the position of the body.
Hence, if \[F\] is zero, then \[\dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}} = 0\] i.e. the slope of the graph given is zero.
This occurs at a point where the tangent to the curve would be horizontal. And this occurs at point 2 and 6 in the curve given.
Now, the point of unstable equilibrium occurs at the maximum point of the curve (where the gradient is zero) which corresponds with point 2.
Hence, the correct option is C
Note: For clarity, unstable equilibrium corresponds to the maximum point because although the force at such point may be zero, any slight displacement will tend to reduce the potential energy of the body and hence the body continues to move (which is the description for unstable equilibrium). And generally, the potential energy of the body in any field whatsoever always tends towards the minimum.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}}\], where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[U\] is the potential energy of the body, and \[x\] is the position of the body.
\[\dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}}\] signifies an instantaneous rate of change of potential energy with distance (called gradient).
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
A graph of potential energy with distance is given, and we are to find the point of unstable equilibrium.
Generally, we know that equilibrium exists where the sum of the forces acting on a body is zero. Hence we need first to identify the point of zero net force.
The force acting on a body can be given as
\[F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}}\], where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[U\] is the potential energy of the body, and \[x\] is the position of the body.
Hence, if \[F\] is zero, then \[\dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}} = 0\] i.e. the slope of the graph given is zero.
This occurs at a point where the tangent to the curve would be horizontal. And this occurs at point 2 and 6 in the curve given.
Now, the point of unstable equilibrium occurs at the maximum point of the curve (where the gradient is zero) which corresponds with point 2.
Hence, the correct option is C
Note: For clarity, unstable equilibrium corresponds to the maximum point because although the force at such point may be zero, any slight displacement will tend to reduce the potential energy of the body and hence the body continues to move (which is the description for unstable equilibrium). And generally, the potential energy of the body in any field whatsoever always tends towards the minimum.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Exam Dates, Session 2 Updates, City Slip, Admit Card & Latest News

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 - Units And Measurements - 2025-26

Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurement - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26




