
Poly\[ - \beta - \]hydroxybutyrate-co\[ - \beta - \]hydroxy valerate (PHBV) is a copolymer of:
A. \[3 - \]hydroxybutanoic acid and \[4 - \]hydroxypentanoic acid
B. \[2 - \] hydroxybutanoic acid and \[3 - \]hydroxypentanoic acid
C. \[3 - \] hydroxybutanoic acid and \[2 - \]hydroxypentanoic acid
D. \[3 - \] hydroxybutanoic acid and \[3 - \]hydroxypentanoic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Polymer is a substance or material made up of very large molecules or macromolecules made up of numerous repeating subunits. Natural and manmade polymers both play important parts in our daily lives due to their broad spectrum. Polymers are crucial to biological structure and function, ranging from synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural polymers and natural biopolymers such as protein and DNA.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
PHBV stands for Poly\[ - \beta - \]hydroxybutyrate-co\[ - \beta - \]hydroxyvalerate. It is a polyhydroxyalkanoate polymer of some sort. It is a non-toxic natural biodegradable plastic made by bacteria that can be utilised as an alternative to synthetic polymers.
The structure of PHBV is as follows:
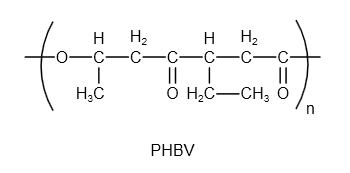
Image: Structure of PHBV
Two (or more) types of monomer units are used to make a copolymer. Two (or more) types of monomer units can be found in the copolymer's repeating structural unit.
PHBV is prepared by the reaction as follows:
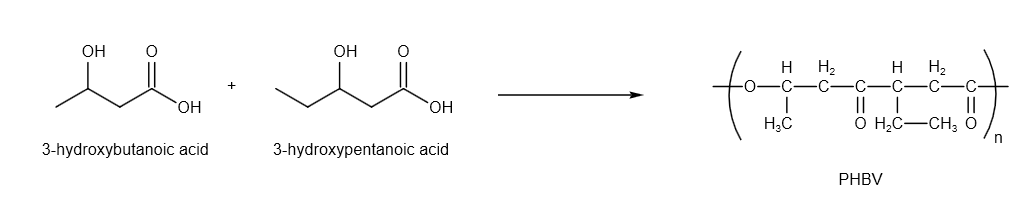
Image: Reaction to prepare PHBV
Therefore, PHBV is a copolymer of \[3 - \] hydroxybutanoic acid and \[3 - \]hydroxypentanoic acid.
Additional Information: Many bacteria, such as Paracoccus denitrificans, generate it naturally, and many genetically altered plants can also produce it. PHBV is a brittle thermoplastic polymer with poor elongation at break and limited impact resistance.
Note: Because of the geometry of the f-orbitals, the elements near the bottom of the group have f-subshell electrons that are diffused. They successfully shelter the s-electrons from the nucleus's attraction and render them bonding inactive.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
PHBV stands for Poly\[ - \beta - \]hydroxybutyrate-co\[ - \beta - \]hydroxyvalerate. It is a polyhydroxyalkanoate polymer of some sort. It is a non-toxic natural biodegradable plastic made by bacteria that can be utilised as an alternative to synthetic polymers.
The structure of PHBV is as follows:

Image: Structure of PHBV
Two (or more) types of monomer units are used to make a copolymer. Two (or more) types of monomer units can be found in the copolymer's repeating structural unit.
PHBV is prepared by the reaction as follows:

Image: Reaction to prepare PHBV
Therefore, PHBV is a copolymer of \[3 - \] hydroxybutanoic acid and \[3 - \]hydroxypentanoic acid.
Additional Information: Many bacteria, such as Paracoccus denitrificans, generate it naturally, and many genetically altered plants can also produce it. PHBV is a brittle thermoplastic polymer with poor elongation at break and limited impact resistance.
Note: Because of the geometry of the f-orbitals, the elements near the bottom of the group have f-subshell electrons that are diffused. They successfully shelter the s-electrons from the nucleus's attraction and render them bonding inactive.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




