
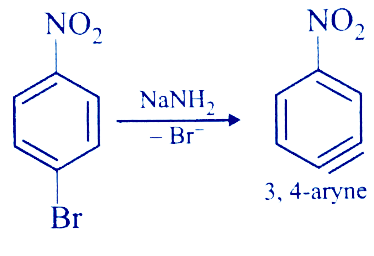
p-Nitrobromobenzene can be converted to p-nitroaniline by using NaNH2. The reaction proceeds through the intermediate named
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: NaNH2 is an effective base. When its strong basicity doesn't have negative effects, it can occasionally be a great nucleophile. It is employed in elimination reactions as well as the deprotonation of weak acids. Alkynes, alcohols, and a variety of other functional groups with acidic protons, such as esters and ketones, will all be deprotonated by NaNH2.
Complete step by step solution:
Firstly, when NaNH2 reacts with p-Nitrobromobenzene, NaNH2 being a base will attack the most acidic hydrogen of p-Nitrobromobenzene. The carbon attached to Br will leave producing a carbanion.
In the next step, the bromine-carbon bond of p-Nitrobromobenzene will break and attach to the Na+ of NaNH2, leaving a positive charge on that carbon i.e, an empty orbital.
Now, two adjacent carbon having a positive and a negative charge creates instability and thus the carbon containing an electron pair will donate its electron pair to the adjacent carbon containing an empty orbital.
After this, a triple bond is formed between the two carbon atoms. The intermediate now formed is called benzyne. The nomenclature of the compound formed is 3,4-aryne.
The correct answer is Benzyne.
Note: Because bases give up their electrons to form new covalent bonds, they are less likely to share them if they are more attracted to them. As a result we see that electronegativity is related to basicity. The greater the electronegativity of an atom, the less it is willing to share its electrons. Electronegativity is important to consider when comparing atoms in the same row of the periodic table.
Complete step by step solution:
Firstly, when NaNH2 reacts with p-Nitrobromobenzene, NaNH2 being a base will attack the most acidic hydrogen of p-Nitrobromobenzene. The carbon attached to Br will leave producing a carbanion.
In the next step, the bromine-carbon bond of p-Nitrobromobenzene will break and attach to the Na+ of NaNH2, leaving a positive charge on that carbon i.e, an empty orbital.
Now, two adjacent carbon having a positive and a negative charge creates instability and thus the carbon containing an electron pair will donate its electron pair to the adjacent carbon containing an empty orbital.
After this, a triple bond is formed between the two carbon atoms. The intermediate now formed is called benzyne. The nomenclature of the compound formed is 3,4-aryne.

The correct answer is Benzyne.
Note: Because bases give up their electrons to form new covalent bonds, they are less likely to share them if they are more attracted to them. As a result we see that electronegativity is related to basicity. The greater the electronegativity of an atom, the less it is willing to share its electrons. Electronegativity is important to consider when comparing atoms in the same row of the periodic table.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




