




How is the Potential Energy of an Electric Dipole Calculated?
The potential energy of an electric dipole in an external electric field is a key concept in electrostatics. It describes the energy stored due to the orientation of the dipole with respect to the uniform electric field and is vital for understanding the stability and dynamics of dipoles in physical systems.
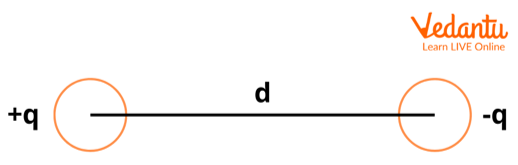
Definition of Electric Dipole and Its Potential Energy
An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. The dipole moment $\vec{p}$ is defined as the product of charge magnitude $q$ and the separation vector $2\vec{a}$. The potential energy is the work required to rotate the dipole in a uniform field.
The potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field depends upon the dipole’s orientation relative to the field direction. This energy determines the equilibrium positions and rotational behavior of the dipole.
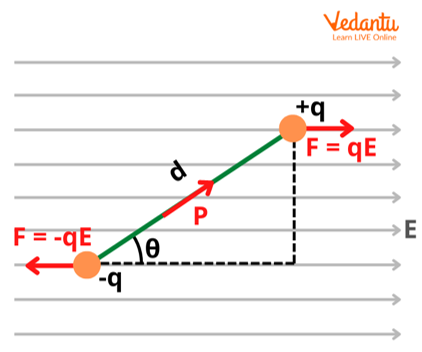
Derivation of Potential Energy of an Electric Dipole in an External Electric Field
The torque $\vec{\tau}$ experienced by a dipole of moment $\vec{p}$ in a uniform electric field $\vec{E}$ is given by $\vec{\tau} = \vec{p} \times \vec{E}$. Its magnitude is $\tau = pE\sin\theta$, where $\theta$ is the angle between $\vec{p}$ and $\vec{E}$.
When the dipole is rotated through an infinitesimal angle $d\theta$ against the torque, the work done $dW$ is $dW = \tau d\theta = pE\sin\theta d\theta$. This work is accumulated as the dipole’s potential energy.
To find the total work done in rotating the dipole from an initial angle $\theta_1$ to a final angle $\theta_2$, integrate:
$W = \int_{\theta_1}^{\theta_2} pE\sin\theta d\theta = -pE [\cos\theta]_{\theta_1}^{\theta_2}$
$W = -pE(\cos\theta_2 - \cos\theta_1)$
This work is stored as the change in potential energy $U$ of the dipole, thus:
$U = -pE\cos\theta +$ constant
By setting the potential energy zero when the dipole is perpendicular to the field ($\theta = 90^\circ$), the constant is zero, and the formula becomes $U = -pE\cos\theta$ or $U = -\vec{p} \cdot \vec{E}$.
Physical Significance and Orientation Dependence
The potential energy $U = -pE\cos\theta$ reflects the alignment between dipole moment and electric field. Lower (more negative) energy represents a more stable orientation, while higher (positive) energy indicates instability relative to the field.
This principle governs dipole behavior in materials science, molecular orientation, and various practical applications. It also forms the foundation for advanced topics like field-induced alignment and polarization. Refer to Properties of Solids and Liquids for related molecular phenomena.
Summary Table: Potential Energy at Key Orientations
| Orientation of Dipole (θ) | Potential Energy U |
|---|---|
| $0^\circ$ (parallel to field) | $-pE$ (minimum, stable) |
| $90^\circ$ (perpendicular) | $0$ |
| $180^\circ$ (antiparallel) | $+pE$ (maximum, unstable) |
Key Points: Potential Energy of Electric Dipole in Electric Field
- Potential energy depends on dipole orientation
- Formula: $U = -pE\cos\theta$
- Energy minimum when aligned with field
- Energy maximum when oppose to field
- Zero energy at perpendicular orientation
- Work done equals the change in potential energy
Application in Electrostatics and Related Concepts
Understanding dipole potential energy is essential for analyzing the response of materials in external fields, work by electric fields, and capacitor behavior. For related explanations, visit Electrostatics Overview and Electric Potential.
The mathematical structure is analogous to gravitational potential energy, enabling comparison of field effects on dipoles and masses. This concept is fundamental in solving JEE and board-level physical questions dealing with electric fields and work.
Potential Energy of Electric Dipole: Formula Recap
In summary, for a dipole of moment $p$ in uniform field $E$, making angle $\theta$ with $\vec{E}$:
$U = -pE\cos\theta$ or $U = -\vec{p} \cdot \vec{E}$
Here, $U$ is in joules (SI unit), $p$ is in coulomb-metre, and $E$ in newton per coulomb. Orientation determines stability, which is critical in applied physics and advanced electrostatics. For more about electric field direction, visit Electric Field Intensity.
This understanding interconnects with electrostatic potential, capacitance, and the difference between electric and magnetic fields. For further comparative analysis, see Difference Between Electric Field and Magnetic Field and Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance.
FAQs on Understanding the Potential Energy of an Electric Dipole
1. What is the potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field?
The potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is the work required to rotate the dipole from alignment with the field to a specific angle.
- It is calculated as U = –p · E · cosθ, where:
• p is the dipole moment
• E is the electric field strength
• θ is the angle between p and E
- The potential energy is minimum (most negative) when the dipole is aligned with the electric field and maximum when anti-aligned.
- This concept is important in physics, chemistry, and competitive exams, reflecting how dipoles interact with external fields.
2. How do you derive the expression for the potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field?
The potential energy expression for an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is derived by calculating the work done in rotating the dipole.
Steps involved:
1. Consider a dipole with moment p in an electric field E.
2. Torque acting on the dipole is τ = p × E.
3. Work done against this torque to rotate the dipole by an angle dθ is dW = τ dθ = pE sinθ dθ.
4. Integrate from initial angle θ₁ to final angle θ₂:
• W = –∫ (pE sinθ) dθ
5. Final expression: U = –p · E · cosθ
3. What is the formula for the potential energy of an electric dipole in an electric field?
The formula for the potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is:
- U = –p · E · cosθ
• U: potential energy
• p: electric dipole moment
• E: electric field strength
• θ: angle between p and E
4. In which orientation does an electric dipole have the least potential energy in a uniform electric field?
An electric dipole has the least (most negative) potential energy when it is aligned with the electric field.
- When θ = 0° (dipole moment parallel to field), U = –pE (minimum).
- Stable equilibrium occurs in this alignment.
- This concept is key in electrostatics and CBSE-level problem solving.
5. What is the significance of potential energy of a dipole in an external electric field?
The potential energy of a dipole in an electric field determines its stability and tendency to align with the field direction.
- Lower (more negative) potential energy means more stable alignment.
- Dipoles experience torque, trying to reach the minimum energy orientation.
- Important for understanding molecular, atomic, and physical phenomena in chemistry and physics.
6. How does the potential energy of an electric dipole change with angle?
The potential energy of an electric dipole varies with the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
- U = –pE cosθ
- U is minimum when θ = 0° (aligned).
- U is zero when θ = 90° (perpendicular).
- U is maximum when θ = 180° (opposite direction).
7. What happens to the potential energy if the electric field strength is doubled?
If the electric field strength is doubled, the potential energy of the dipole also doubles in magnitude.
- Since U = –pE cosθ, when E becomes 2E:
• U' = –p (2E) cosθ = 2(–pE cosθ)
- Thus, the potential energy increases (more negative if aligned).
8. Can the potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field be positive?
Yes, the potential energy of a dipole can be positive if it is oriented opposite to the electric field direction.
- For θ = 180°: U = +pE (maximum value).
- In this configuration, the dipole is in unstable equilibrium.
- The potential energy is positive, highest, and the system tends to rotate back to lower energy position.
9. What do you mean by electric dipole moment?
Electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a system.
- Defined as p = q × 2a, where
• q: magnitude of charge
• 2a: distance between charges
- It is a vector pointing from negative to positive charge.
- SI unit: Coulomb-metre (C·m).
- Indicates strength and orientation of a dipole in an electric field.
10. Why is the concept of potential energy of a dipole important in physics?
The concept of potential energy of a dipole is essential for understanding the behaviour of molecules and atoms in external fields.
- Explains molecular alignment in electric fields.
- Helps in studying dielectric properties of materials.
- Crucial for exam concepts under electrostatics (CBSE, NEET, JEE), and real-world applications like sensors and devices.
























