
What is the physical meaning of cross-product?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: For a resultant vector, the cross product is known as the vector product of the two vectors and can be written as A x B. This resultant vector illustrates a cross-product between two vectors on a plane surface.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that A vector is a quantity with magnitude and direction used to locate one location in space in relation to another. It can be visualized as an arrow or a line segment with the direction in a geometrical representation.
Mathematically, the cross product of two non-zero vectors \[\overrightarrow a \] and \[\overrightarrow b \] , is
\[\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b = |\overrightarrow a ||\overrightarrow b |sin\,\theta \widehat {\,n}\]
Where \[\theta \] is the angle between \[\overrightarrow a \] and \[\overrightarrow b \] , \[0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \pi \] . Also, \[\widehat n\] is a unit vector perpendicular to both \[\overrightarrow a \] and \[\overrightarrow b \] such that \[\overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow b \] and \[\widehat {\,n}\] form a right-handed system.
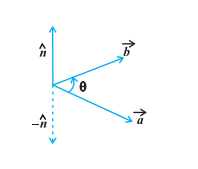
Image: cross product of two vectors
Hence, the physical meaning of cross product is a vector that is perpendicular to the two vectors is the cross product of any two vectors. It has magnitude as well as direction. The resultant vector has the same magnitude as the parallelogram, whose side lengths are the same as the magnitudes of the two provided vectors.
Note: Students should remember the right-hand thumb rule in which you stretch your right hand so that the index finger of the right hand is in the direction of the first vector and the middle finger is in the direction of the second vector. Then, the thumb of the right hand indicates the direction vector.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that A vector is a quantity with magnitude and direction used to locate one location in space in relation to another. It can be visualized as an arrow or a line segment with the direction in a geometrical representation.
Mathematically, the cross product of two non-zero vectors \[\overrightarrow a \] and \[\overrightarrow b \] , is
\[\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b = |\overrightarrow a ||\overrightarrow b |sin\,\theta \widehat {\,n}\]
Where \[\theta \] is the angle between \[\overrightarrow a \] and \[\overrightarrow b \] , \[0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \pi \] . Also, \[\widehat n\] is a unit vector perpendicular to both \[\overrightarrow a \] and \[\overrightarrow b \] such that \[\overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow b \] and \[\widehat {\,n}\] form a right-handed system.

Image: cross product of two vectors
Hence, the physical meaning of cross product is a vector that is perpendicular to the two vectors is the cross product of any two vectors. It has magnitude as well as direction. The resultant vector has the same magnitude as the parallelogram, whose side lengths are the same as the magnitudes of the two provided vectors.
Note: Students should remember the right-hand thumb rule in which you stretch your right hand so that the index finger of the right hand is in the direction of the first vector and the middle finger is in the direction of the second vector. Then, the thumb of the right hand indicates the direction vector.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




