
\[PC{l_5}\] reacts with propanone, to give
A. Vicinal dichloride
B. Propanal
C. propane chloride
D. Gem-dichloride
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Phosphorus pentachloride is the name of the chemical compound PCl₅. It is a significant phosphorus chloride and is used as a chlorinating reagent. When this compound is treated with ketones, chlorination transpires at the carbonyl carbon.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound possessing the formula PCl5.
It is one of the considerably crucial phosphorus chlorides alongside\[PC{l_3}\] and\[POC{l_3}\].
\[PC{l_5}\] is utilised as a chlorinating reagent.
It has no colour and is sensitive to moisture and water.
Its structure is as follows:
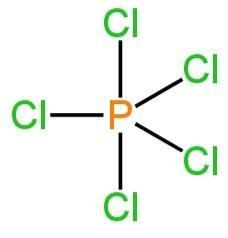
Image: Structure of phosphorus pentachloride
When it reacts with carbonyl groups like in ketones it leads to the conversion of C=O groups to \[CC{l_2}\]groups.
So, when it reacts with propanone it converts the C=O group to the CCl2 group.
Mechanism
1. The lone pair of oxygen in the carbonyl group attacks the phosphorus atom present in phosphorus pentachloride leading to the formation of a complex.
2. The complex formed when treated with a proton leads to the breaking of the carbon and oxygen bond. A carbocation is formed.
3. Carbocation is attacked by chloride ions present in the medium forming 2,2-dichloropropane and Phosphoryl chloride along with it which is a side product.
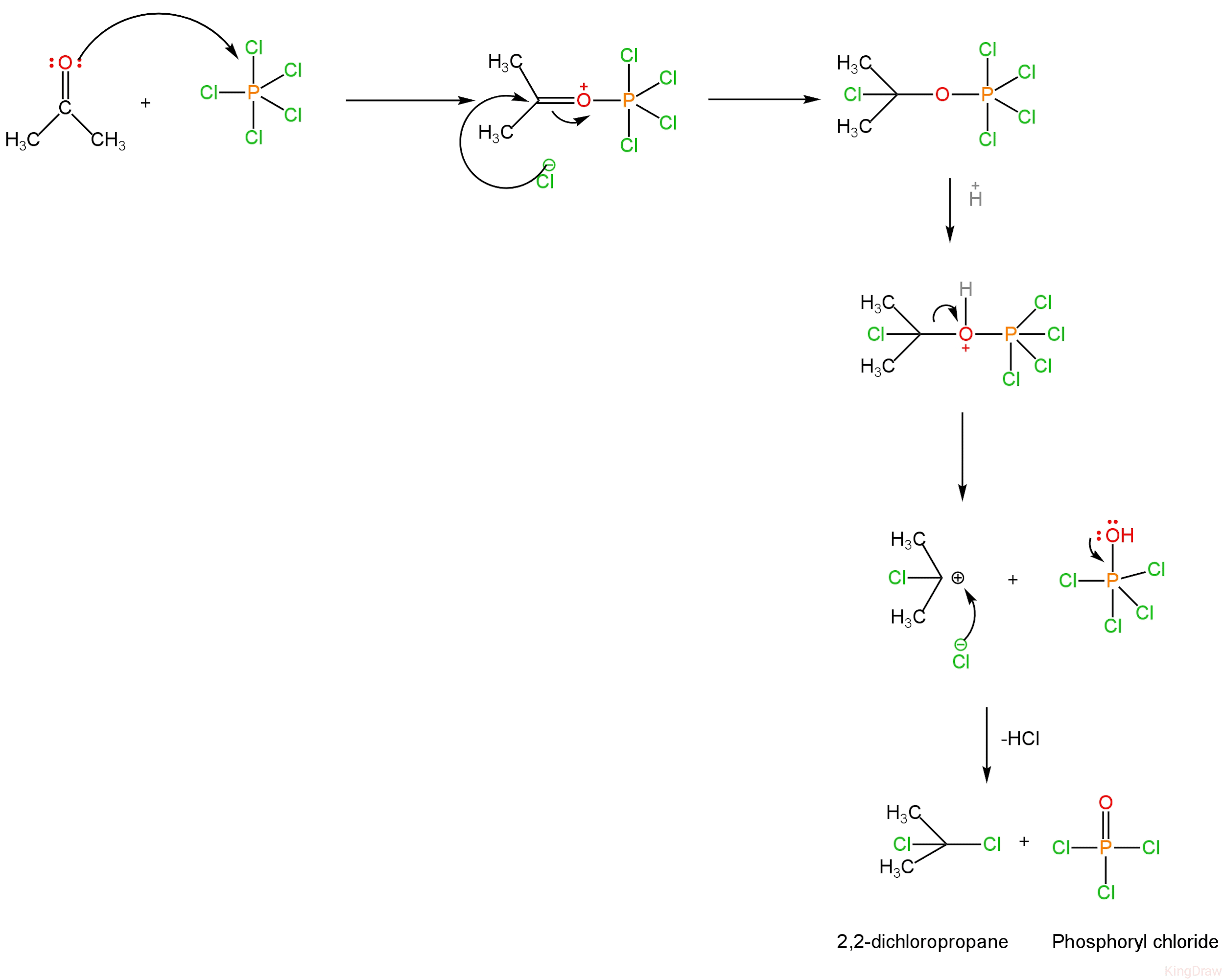
Image: Mechanism of chlorination of propanone.
As we know, 2,2-dichloropropane is a gem-dichloride. So, D is correct.
So, option D is correct.
Note: Phosphorus pentachloride also transforms alcohols into alkyl chlorides. This reaction is used in the preparation of alkyl chlorides. But thionyl chloride is more generally utilised in the laboratory as the resultant sulphur dioxide is a gas, and hence is more effortlessly isolated from the organic products than \[POC{l_3}\].
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound possessing the formula PCl5.
It is one of the considerably crucial phosphorus chlorides alongside\[PC{l_3}\] and\[POC{l_3}\].
\[PC{l_5}\] is utilised as a chlorinating reagent.
It has no colour and is sensitive to moisture and water.
Its structure is as follows:

Image: Structure of phosphorus pentachloride
When it reacts with carbonyl groups like in ketones it leads to the conversion of C=O groups to \[CC{l_2}\]groups.
So, when it reacts with propanone it converts the C=O group to the CCl2 group.
Mechanism
1. The lone pair of oxygen in the carbonyl group attacks the phosphorus atom present in phosphorus pentachloride leading to the formation of a complex.
2. The complex formed when treated with a proton leads to the breaking of the carbon and oxygen bond. A carbocation is formed.
3. Carbocation is attacked by chloride ions present in the medium forming 2,2-dichloropropane and Phosphoryl chloride along with it which is a side product.

Image: Mechanism of chlorination of propanone.
As we know, 2,2-dichloropropane is a gem-dichloride. So, D is correct.
So, option D is correct.
Note: Phosphorus pentachloride also transforms alcohols into alkyl chlorides. This reaction is used in the preparation of alkyl chlorides. But thionyl chloride is more generally utilised in the laboratory as the resultant sulphur dioxide is a gas, and hence is more effortlessly isolated from the organic products than \[POC{l_3}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




