
Mark the element which can displace the other three halogens from their compounds.
(A) Fluorine
(B) Chlorine
(C) Bromine
(D) Iodine
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: All the given elements are halogens. Halogens are very reactive as they contain seven electrons in the valence shell and thus require only one electron to complete their octet. For an element to displace another element, it should have higher reactivity.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
As the order of reactivity of halogens is:
Fluorine > Chlorine > Bromine > Iodine
This means fluorine is the most reactive of all the halogens. The reason for the higher reactivity of fluorine is its small size and higher electronegativity. Hence, fluorine is the element that can displace the other three halogens from their compounds.
Fluorine can displace chlorine from sodium chloride ($NaCl$) to form sodium fluoride ($NaF$).
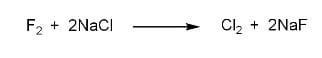
Similarly, it can displace bromine from sodium bromide ($NaBr$) to form sodium fluoride ($NaF$).
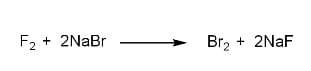
Also, it can displace iodine from sodium iodide ($NaI$) to form sodium fluoride ($NaF$).

Correct Option: (A) Fluorine
Additional Information: Due to the smallest size of fluorine among halogens, its melting and boiling points are very low. Also, the ionisation energy, that is the energy required to remove an electron from the valence shell of fluorine, is very high.
Note: Fluorine (${{F}_{2}}$) and chlorine ($C{{l}_{2}}$) are gases; bromine ($B{{r}_{2}}$) is a liquid; and iodine (${{I}_{2}}$) is a solid. The halogens can form metal halides, hydrogen halides, organohalogens, interhalogen compounds, and polyhalogenated compounds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
As the order of reactivity of halogens is:
Fluorine > Chlorine > Bromine > Iodine
This means fluorine is the most reactive of all the halogens. The reason for the higher reactivity of fluorine is its small size and higher electronegativity. Hence, fluorine is the element that can displace the other three halogens from their compounds.
Fluorine can displace chlorine from sodium chloride ($NaCl$) to form sodium fluoride ($NaF$).

Similarly, it can displace bromine from sodium bromide ($NaBr$) to form sodium fluoride ($NaF$).

Also, it can displace iodine from sodium iodide ($NaI$) to form sodium fluoride ($NaF$).

Correct Option: (A) Fluorine
Additional Information: Due to the smallest size of fluorine among halogens, its melting and boiling points are very low. Also, the ionisation energy, that is the energy required to remove an electron from the valence shell of fluorine, is very high.
Note: Fluorine (${{F}_{2}}$) and chlorine ($C{{l}_{2}}$) are gases; bromine ($B{{r}_{2}}$) is a liquid; and iodine (${{I}_{2}}$) is a solid. The halogens can form metal halides, hydrogen halides, organohalogens, interhalogen compounds, and polyhalogenated compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




