
Let the plane \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ax + by + cz + d}& = &0
\end{array}\]bisects the line joining the points (4, -3, 1) and (2, 3, -5) at the right angles. If a, b, c, and d are the integers, then the minimum value of \[({a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2} + {d^2})\] is
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First of all, find the equation of the plane. When we find the equation of the plane, then we compare the equation of the plane with the given equation of the plane. After comparing, we will get the value of the a, b, c, and c respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume that p, q, and r are the direction ratios respectively.
Here, according to the question, we have given the equation of the plane that is,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ \Rightarrow ax + by + cz + d}& = &0
\end{array}\]…………. (a)
Here, a line bisects the plane normally whose coordinates are (4, -3, 1) and (2, 3, -5). And the midpoint of this line will lie in the plan.
Now, we will draw a figure accordingly,
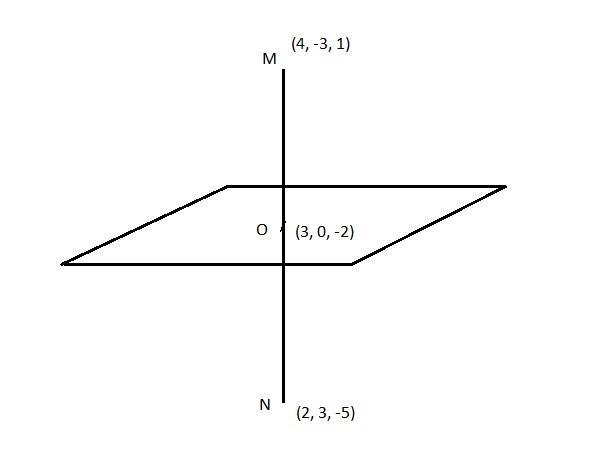
Image: Plane perpendicular to a line
Now, we will have to find the direction ratio, for that purpose, we will find the difference between the coordinates between the M(4, -3, 1) and O(2, 3, -5). Therefore, the direction ratio is,
\[ \Rightarrow \](1, -3, 3).
Now we got the direction ratios that is.
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ \Rightarrow p}& = &1
\end{array}\], \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
q& = &{ - 3}
\end{array}\] and \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
r& = &3
\end{array}\]
Now, we know that the equation of the plane when the plane coordinates and the direction ratios are given,
Therefore, we Can write.
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{p(x - {x_1}) + q(y - {y_1}) + r(z - {z_1})}& = &0
\end{array}\]
Now,
\[ \Rightarrow \begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{1(x - 3) - 3(y - 0) + 3(z + 2)}& = &0
\end{array}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{x - 3y - 3z + 3}& = &0
\end{array}\] …………………. (b)
Now compare the equation (a) and (b). we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow \begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
a& = &1
\end{array}\], \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
b& = &{ - 3}
\end{array}\] \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
c& = &{ - 3}
\end{array}\] and \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
d& = &3
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the minimum of \[{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2} + {d^2}\]will be,
\[ \Rightarrow {(1)^2} + {( - 3)^2} + {( - 3)^2} + {(3)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 28\]
Hence correct answer is 28.
Note: The first point to keep in mind is that the midpoint of the line lies in the plan. And with the help of the midpoint of the line and point M, we can determine the direction ratio. After that, we can find the equation of the plane with the help of the midpoint of the line which lies on the plane and the direction ratio.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume that p, q, and r are the direction ratios respectively.
Here, according to the question, we have given the equation of the plane that is,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ \Rightarrow ax + by + cz + d}& = &0
\end{array}\]…………. (a)
Here, a line bisects the plane normally whose coordinates are (4, -3, 1) and (2, 3, -5). And the midpoint of this line will lie in the plan.
Now, we will draw a figure accordingly,

Image: Plane perpendicular to a line
Now, we will have to find the direction ratio, for that purpose, we will find the difference between the coordinates between the M(4, -3, 1) and O(2, 3, -5). Therefore, the direction ratio is,
\[ \Rightarrow \](1, -3, 3).
Now we got the direction ratios that is.
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ \Rightarrow p}& = &1
\end{array}\], \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
q& = &{ - 3}
\end{array}\] and \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
r& = &3
\end{array}\]
Now, we know that the equation of the plane when the plane coordinates and the direction ratios are given,
Therefore, we Can write.
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{p(x - {x_1}) + q(y - {y_1}) + r(z - {z_1})}& = &0
\end{array}\]
Now,
\[ \Rightarrow \begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{1(x - 3) - 3(y - 0) + 3(z + 2)}& = &0
\end{array}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{x - 3y - 3z + 3}& = &0
\end{array}\] …………………. (b)
Now compare the equation (a) and (b). we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow \begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
a& = &1
\end{array}\], \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
b& = &{ - 3}
\end{array}\] \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
c& = &{ - 3}
\end{array}\] and \[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
d& = &3
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the minimum of \[{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2} + {d^2}\]will be,
\[ \Rightarrow {(1)^2} + {( - 3)^2} + {( - 3)^2} + {(3)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 28\]
Hence correct answer is 28.
Note: The first point to keep in mind is that the midpoint of the line lies in the plan. And with the help of the midpoint of the line and point M, we can determine the direction ratio. After that, we can find the equation of the plane with the help of the midpoint of the line which lies on the plane and the direction ratio.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




