
Iodine oxidises sodium borohydride to give:
A) ${B_2}{H_6}$
B) Sodium hydride
C) $HI$
D) ${I_3}^{ - 1}$
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen borohydride is a minor reducing agent. It does selective reduction and it reduces substances by transfer of hydride ions (${H^ - }$).
Complete step by step solution:
-Sodium borohydride is an organic compound with molecular formula: $NaB{H_4}$. It is a salt consisting of a tetrahedral ($B{H_4}^ - $).
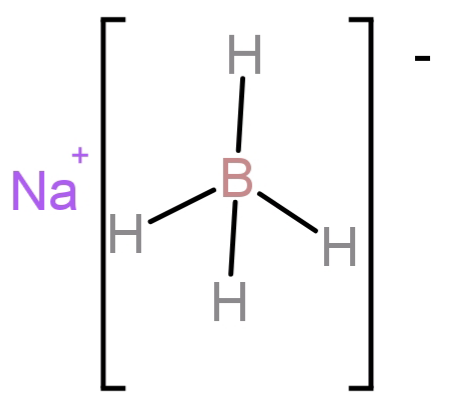
-It is an effective source of nucleophilic hydride ions in polar aprotic solvents like sulfolane, DMSO, DMF, HMPA or diglyme.
- So, it acts as a minor reducing agent and does selective reduction that is it reduces aldehydes and ketones to corresponding alcohols. It does not reduce double bonds. It reduces substance by transfer of the hydride ions.
-When one sodium borohydride molecule reacts with iodine, a borane ($B{H_3}$) molecule is produced along with sodium iodide ($NaI$) and hydrogen iodide ($HI$). Hydrogen iodide then reacts with another sodium borohydride molecule producing another borane and hydrogen iodide molecule. These 2 borane molecules thus do the bridging forming diborane (${B_2}{H_6}$). This is shown in the below reaction:
$NaB{H_4} + {I_2} \to B{H_3} + NaI + HI\xrightarrow{{NaB{H_4}}}B{H_3} + HI$
-This reaction takes place in the presence of Diglyme which acts as a catalyst.
-So, this reaction can also be written as:
$2NaB{H_4} + {I_2}\xrightarrow{{Diglyme}}2NaI + {B_2}{H_6} + {H_2}$
So, the correct option is: A) ${B_2}{H_6}$
Additional information: Diborane is found to be a rocket propellant because it is highly flammable. It undergoes a highly exothermic complete combustion. But it is unable to undergo complete combustion in a rocket engine and thus produces some amount of boron monoxide ($BO$).
Note: Before attempting read the question carefully about iodine oxidising sodium borohydride and not the other way round. And do not get confused between reducing agent (donates electron) and oxidising agent (accepts electron).
Complete step by step solution:
-Sodium borohydride is an organic compound with molecular formula: $NaB{H_4}$. It is a salt consisting of a tetrahedral ($B{H_4}^ - $).

-It is an effective source of nucleophilic hydride ions in polar aprotic solvents like sulfolane, DMSO, DMF, HMPA or diglyme.
- So, it acts as a minor reducing agent and does selective reduction that is it reduces aldehydes and ketones to corresponding alcohols. It does not reduce double bonds. It reduces substance by transfer of the hydride ions.
-When one sodium borohydride molecule reacts with iodine, a borane ($B{H_3}$) molecule is produced along with sodium iodide ($NaI$) and hydrogen iodide ($HI$). Hydrogen iodide then reacts with another sodium borohydride molecule producing another borane and hydrogen iodide molecule. These 2 borane molecules thus do the bridging forming diborane (${B_2}{H_6}$). This is shown in the below reaction:
$NaB{H_4} + {I_2} \to B{H_3} + NaI + HI\xrightarrow{{NaB{H_4}}}B{H_3} + HI$
-This reaction takes place in the presence of Diglyme which acts as a catalyst.
-So, this reaction can also be written as:
$2NaB{H_4} + {I_2}\xrightarrow{{Diglyme}}2NaI + {B_2}{H_6} + {H_2}$
So, the correct option is: A) ${B_2}{H_6}$
Additional information: Diborane is found to be a rocket propellant because it is highly flammable. It undergoes a highly exothermic complete combustion. But it is unable to undergo complete combustion in a rocket engine and thus produces some amount of boron monoxide ($BO$).
Note: Before attempting read the question carefully about iodine oxidising sodium borohydride and not the other way round. And do not get confused between reducing agent (donates electron) and oxidising agent (accepts electron).
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




