
Increase order of acidic strength of given compounds is :
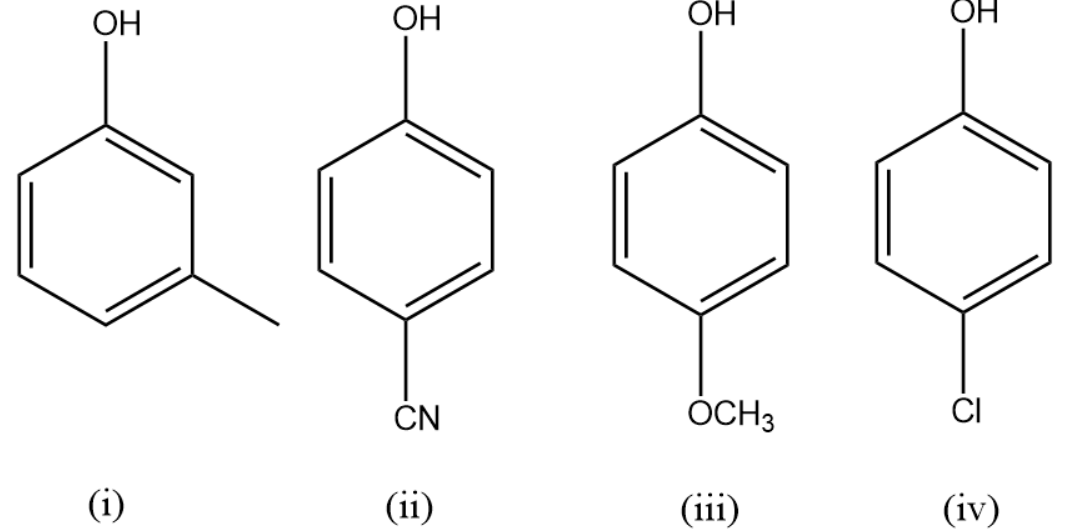
(A) (ii) < (i) < (iv) < (iii)
(B) (i) < (iii) < (iv) < (ii)
(C) (i) < (iii) < (ii) < (iv)
(D) (iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii)
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The four organic compounds have the hydroxyl group in common. The acidic strength of the compounds can be determined by the stability of the conjugate base formed. Only when the conjugate base formed is stable, the hydrogen ion will be released easily. The groups attached will contribute to either stabilizing or destabilizing the negative charge after deprotonation.
Complete step by step solution:
Electronic factors are the factor that influences carious organic reactions and rearrangements. Electronic effects are significantly observed in organic aromatic compounds.
Electronic factors are:
- Inductive effect
- Resonance
- Mesomeric effect
- Electromeric effect
- Hyperconjugation.
We will now identify at which position of the aromatic ring, the following effect is observed.
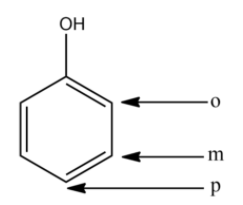
In the above compound,
- o stands for ortho-position
- m stands for meta-position
- p stands for para-position
In compound (i) the anion of the compound or the conjugate base is destabilised only by inductive effect as the methyl group is attached at the meta position.
In compound (ii) the conjugate base is stabilised by the cyanide or nitrile group attached at the para position as it withdraws electrons from the benzene ring
In compound (iii) the conjugate base is destabilised by the ether group attached at para-position as the oxygen atom increases electron density in the ring making it unstable.
In compound (iv) the conjugate base is mildly stabilised by the halogen atom attached at the para position.
Therefore, the increasing order of acidic strength of the given compounds is (iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii).
The correct answer is option (D).
Note: Resonance effect is mainly observed in the ortho and para position of the aromatic ring and the only significant electronic effect observed at meta position is the inductive effect. Resonance has much more priority than inductive effect while determining the acidic strength of phenols or carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step solution:
Electronic factors are the factor that influences carious organic reactions and rearrangements. Electronic effects are significantly observed in organic aromatic compounds.
Electronic factors are:
- Inductive effect
- Resonance
- Mesomeric effect
- Electromeric effect
- Hyperconjugation.
We will now identify at which position of the aromatic ring, the following effect is observed.

In the above compound,
- o stands for ortho-position
- m stands for meta-position
- p stands for para-position
In compound (i) the anion of the compound or the conjugate base is destabilised only by inductive effect as the methyl group is attached at the meta position.
In compound (ii) the conjugate base is stabilised by the cyanide or nitrile group attached at the para position as it withdraws electrons from the benzene ring
In compound (iii) the conjugate base is destabilised by the ether group attached at para-position as the oxygen atom increases electron density in the ring making it unstable.
In compound (iv) the conjugate base is mildly stabilised by the halogen atom attached at the para position.
Therefore, the increasing order of acidic strength of the given compounds is (iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii).
The correct answer is option (D).
Note: Resonance effect is mainly observed in the ortho and para position of the aromatic ring and the only significant electronic effect observed at meta position is the inductive effect. Resonance has much more priority than inductive effect while determining the acidic strength of phenols or carboxylic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




