
In Young's double slit experiment, in an interference pattern second minimum is observed exactly in front of one slit. The distance between the two coherent sources is ′d′ and the distance between source and screen is ′D′. The wavelength of light source used is :
(A) $\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D}$
(B) $\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{2D}}$
(C) $\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{3D}}$
(D) $\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{4D}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: As this is the case of young double slit experiment and minima is formed so the condition of minima is used in the required formula of the path difference i.e. $Y = \left( {n + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$, Y is the position of second minima in front of one slit i.e. $Y = \dfrac{d}{2}$, here n is order of fringe and for second minima n=1, then substitute the values and we will get the value of wavelength.
Diagram:
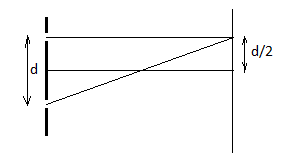
Complete step by step solution:
Minima is produced when the crust of one wave falls on the trough of another wave. Here, a second minima is produced in front of one slit so we use the condition of dark fringes.
The position of second minima just in front of one slit $Y = \dfrac{d}{2}$
The formula for minima is $Y = \left( {n + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$…………………………(1)
Where, λ is the wavelength of light used
D is the distance of screen from the slit
D isn the distance between the slits
n is the order of fringes
For second minimum n=1 then put these values in equation (1) we get,
⇒ $\dfrac{d}{2} = \left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d} = \dfrac{{3\lambda D}}{{2d}}$
⇒ $\lambda = \dfrac{{2{d^2}}}{{6D}} = \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{3D}}$
This the required value of wavelength used. Hence, C option is correct.
Note: As here we are talking about the second minima so just remember that for second minima n is equal to 1. And we must use the correct formula that the position of the fringe is equal to the odd multiple of fringe width. i.e. $Y = \left( {n + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$, where $\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$ is the fringe width which is the distance between the two crust and trough.
Diagram:

Complete step by step solution:
Minima is produced when the crust of one wave falls on the trough of another wave. Here, a second minima is produced in front of one slit so we use the condition of dark fringes.
The position of second minima just in front of one slit $Y = \dfrac{d}{2}$
The formula for minima is $Y = \left( {n + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$…………………………(1)
Where, λ is the wavelength of light used
D is the distance of screen from the slit
D isn the distance between the slits
n is the order of fringes
For second minimum n=1 then put these values in equation (1) we get,
⇒ $\dfrac{d}{2} = \left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d} = \dfrac{{3\lambda D}}{{2d}}$
⇒ $\lambda = \dfrac{{2{d^2}}}{{6D}} = \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{3D}}$
This the required value of wavelength used. Hence, C option is correct.
Note: As here we are talking about the second minima so just remember that for second minima n is equal to 1. And we must use the correct formula that the position of the fringe is equal to the odd multiple of fringe width. i.e. $Y = \left( {n + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$, where $\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$ is the fringe width which is the distance between the two crust and trough.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




