
In which case, work is not done?
$\left( {\text{A}} \right)$ A girl swimming in pond
$\left( {\text{B}} \right)$ Windmill lifting water from a well
$\left( {\text{C}} \right)$ A standing man holding a suitcase in his hand
$\left( {\text{D}} \right)$ A sail boat moving in the direction of wind
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Here first we discuss the definition of work.
That is, Work is defined as the product of force and displacement in the direction of the force. If there is no displacement in the direction of applied force, work done will be zero.
Then we discuss the option one by one and then we conclude the required answer.
Complete answer:
Option A: Here, a girl is swimming in the pond.
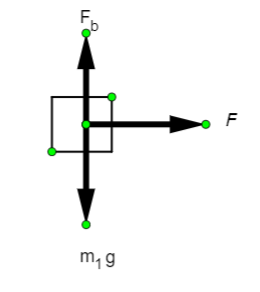
The girl is represented by a block of mass ${m_1}$. The free body diagram of the girl is as shown above. As we can see that the motion of the girl is in the direction of net applied force F. The vertical forces balance each other for a floating body. Now, since the displacement is in the direction of the applied force, we say that there is work done by the girl. Hence, Option A is not correct.
Option B: In this case, the windmill is lifting water from a well. So in this case the bucket which will be carrying water will be moving up and the windmill is applying a force in the upward direction to lift this bucket. Since there is displacement in the direction of the applied force, we say that work is done here. Hence option B is also not correct.
Option C: In this case, a man is holding a suitcase. The man will be applying a force in the upward direction to hold the suitcase, but the suitcase will be stationary, i.e. there is no displacement in the direction of applied force. Hence, the work done is zero. So, option C is correct.
Option D: A sailboat is moving in the direction of wind. So, there is displacement as well as the force applied by the wind. Hence there will be the work done. So, option D is not correct.
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: Do not confuse work with energy. In option C, the man is spending energy to hold the suitcase, but the work done is zero as displacement is zero. But, if it is asked that the man is lifting the suitcase, then there will be work done.
That is, Work is defined as the product of force and displacement in the direction of the force. If there is no displacement in the direction of applied force, work done will be zero.
Then we discuss the option one by one and then we conclude the required answer.
Complete answer:
Option A: Here, a girl is swimming in the pond.

The girl is represented by a block of mass ${m_1}$. The free body diagram of the girl is as shown above. As we can see that the motion of the girl is in the direction of net applied force F. The vertical forces balance each other for a floating body. Now, since the displacement is in the direction of the applied force, we say that there is work done by the girl. Hence, Option A is not correct.
Option B: In this case, the windmill is lifting water from a well. So in this case the bucket which will be carrying water will be moving up and the windmill is applying a force in the upward direction to lift this bucket. Since there is displacement in the direction of the applied force, we say that work is done here. Hence option B is also not correct.
Option C: In this case, a man is holding a suitcase. The man will be applying a force in the upward direction to hold the suitcase, but the suitcase will be stationary, i.e. there is no displacement in the direction of applied force. Hence, the work done is zero. So, option C is correct.
Option D: A sailboat is moving in the direction of wind. So, there is displacement as well as the force applied by the wind. Hence there will be the work done. So, option D is not correct.
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: Do not confuse work with energy. In option C, the man is spending energy to hold the suitcase, but the work done is zero as displacement is zero. But, if it is asked that the man is lifting the suitcase, then there will be work done.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




