
Why in the tetrahedral splitting, terms e and \[{t_2}\] are used, whereas, in octahedral splitting, terms as \[{e_g}\] and \[{t_{2g}}\] are used?
(A) Due to the approach of the ligands from the axis
(B) Due to the approach of the ligands in between the axis
(C) Due to the symmetry present in the octahedral system
(D) Due to the symmetry present in the tetrahedral system
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: If any system is symmetric or has centre of inversion symmetry, it is called gerade orbital, symbolised by g. while if no such symmetry exists, the g term is removed. Octahedral is a symmetric system while tetrahedral is not symmetric.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In an octahedral complex, six ligands are attached to the central transition metal. The d-orbital splits into two different levels. The bottom three energy levels are named as \[{d_{xy}}, {d_{yz}},{d_{xz}}\] and collectively referred to as \[{t_{2g}}\]. The two upper energy levels are named as \[{d_{{z^2}}}, {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\], and collectively referred to as \[{e_g}\].
In a tetrahedral complex, four ligands are attached to the central metal. The d orbitals too split into two different energy levels. The top three consist of the \[{d_{xy}}, {d_{yz}}, {d_{xz}}\] orbitals and collectively referred as \[{t_2}\]. The bottom two consist of the \[{d_{{z^2}}}, {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbitals and are collectively referred to as e. The reason for this is due to poor orbital overlap between the metal and the ligand orbitals. The orbitals are directed on the axes, while the ligands are not as per the tetrahedral structure.
This difference in ‘g’ terms in both the structure is due to their symmetry. The word g stands for gerade which means symmetry, it is a German word. If the sign of the lobes remains the same, we call it a gerade orbital and if the signs are changed, the orbital is ungerade. In gerade, the centre of inversion symmetry is present.
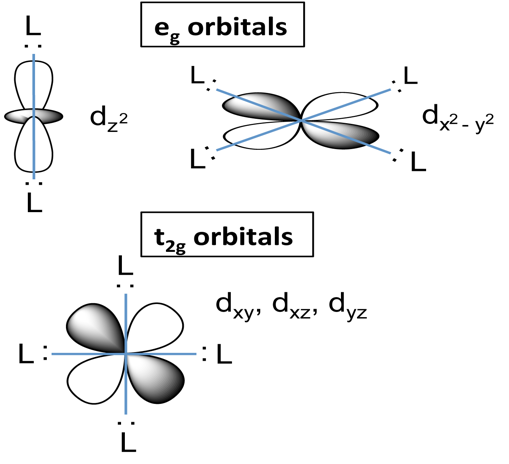
Tetrahedral complexes have no centre of symmetry and thus its orbital do not have g term in it. While in an octahedral system, g term is included because it is symmetric. Therefore, in the tetrahedral splitting, terms e and \[{t_2}\] are used, whereas, in octahedral splitting, terms as \[{e_g}\] and \[{t_{2g}}\] are used.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: This can also be understood by Laporte selection rule which states that for a coordination complex that contains a centre of symmetry, only transitions which involve a change in parity of lobes are allowed. That is why octahedral is symmetric, hence allowed and vice versa for tetrahedral.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In an octahedral complex, six ligands are attached to the central transition metal. The d-orbital splits into two different levels. The bottom three energy levels are named as \[{d_{xy}}, {d_{yz}},{d_{xz}}\] and collectively referred to as \[{t_{2g}}\]. The two upper energy levels are named as \[{d_{{z^2}}}, {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\], and collectively referred to as \[{e_g}\].
In a tetrahedral complex, four ligands are attached to the central metal. The d orbitals too split into two different energy levels. The top three consist of the \[{d_{xy}}, {d_{yz}}, {d_{xz}}\] orbitals and collectively referred as \[{t_2}\]. The bottom two consist of the \[{d_{{z^2}}}, {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbitals and are collectively referred to as e. The reason for this is due to poor orbital overlap between the metal and the ligand orbitals. The orbitals are directed on the axes, while the ligands are not as per the tetrahedral structure.
This difference in ‘g’ terms in both the structure is due to their symmetry. The word g stands for gerade which means symmetry, it is a German word. If the sign of the lobes remains the same, we call it a gerade orbital and if the signs are changed, the orbital is ungerade. In gerade, the centre of inversion symmetry is present.

Tetrahedral complexes have no centre of symmetry and thus its orbital do not have g term in it. While in an octahedral system, g term is included because it is symmetric. Therefore, in the tetrahedral splitting, terms e and \[{t_2}\] are used, whereas, in octahedral splitting, terms as \[{e_g}\] and \[{t_{2g}}\] are used.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: This can also be understood by Laporte selection rule which states that for a coordination complex that contains a centre of symmetry, only transitions which involve a change in parity of lobes are allowed. That is why octahedral is symmetric, hence allowed and vice versa for tetrahedral.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




