
In the experiment on the photoelectric effect, the graph between \[\mathop E\nolimits_K (\max )\] and \[\nu \] is found to be a straight line as shown in fig. The threshold frequency and Planck's constant according to this graph are:
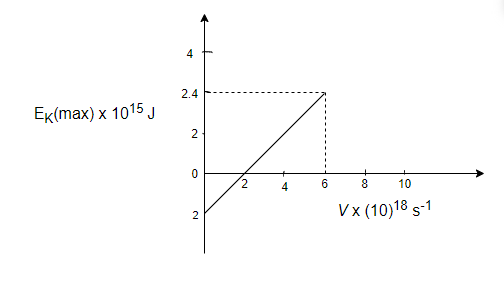
A) \[3.33 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} \]$s^{-1}$, \[6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} \]J-s
B) \[6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} \] $s^{-1}$, \[6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} \] J-s
C) \[2.66 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} \] $s^{-1}$, \[4 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} \] J-s
D) \[4 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} \] $s^{-1}$, \[3 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} \] J-s
Answer
241.2k+ views
Hint: This given problem can be solved by Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Einstein explained the various laws of photoelectric emission on the basis of Planck’s quantum theory. According to Planck’s quantum theory, the energy of a photon is given by \[E = h\nu \].
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
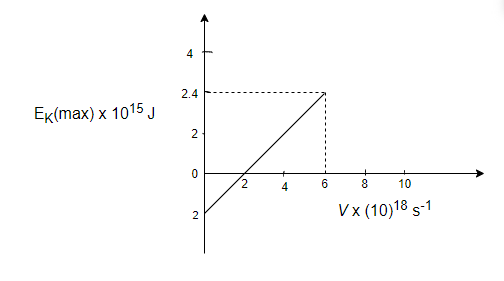
Einstein assumed that one photoelectron is ejected from a metal surface if one photon of suitable light radiation falls on it.
Let us consider a photon of light of frequency \[\nu \], incident on a photosensitive metal surface. The energy of the photon is \[h\nu \], spent in two ways:
A part of the energy of the photon will be used in liberating the electron from the metal surface which is equal to the work function \[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 \] of the metal.
The rest of the energy of the photon will be used in imparting the maximum kinetic energy \[\mathop K\nolimits_{\max } \] to the emitted photoelectron.
So, from above two points, we will get-
\[h\nu = \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 + \mathop K\nolimits_{\max } \].................(1)
This equation (1) is known as Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Step 2: Now from the equation (1) –
\[h\nu = \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 + \mathop K\nolimits_{\max } \]; where \[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 = \]work function of metal, \[h = \]Planck’s constant, and \[\nu = \]frequency of incident photon
If we rearrange the equation (1) in the form of \[\mathop K\nolimits_{\max } = h\nu + \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 \] and this equation can be compared with the \[y = mx + c\] .
So, the slope of the given line will be \[h\] and the intercept will be \[ - \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 \].
So, from the graph, \[h = \dfrac{{\mathop K\nolimits_{\max } }}{{\mathop \nu \nolimits_2 - \mathop \nu \nolimits_1 }}\]
\[h = \dfrac{{2.4 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 15} }}{{\left( {6 - 2} \right) \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} }}\]
\[h = 6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} \]J-s
And \[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 = 2 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 15} \]J
\[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 = h\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 \]; where \[\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 = \] threshold frequency
\[\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 = \dfrac{{\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 }}{h} = \dfrac{{2 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 15} }}{{6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} }}\]
\[\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 = 3.33 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} \]$s^{-1}$
So, the correct option is (A).
Note: If \[\nu < \mathop \nu \nolimits_0 \] , then maximum K.E. will be negative, which is not possible. So, Photoelectric emission does not occur if the frequency of incident radiation is less than the threshold frequency.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
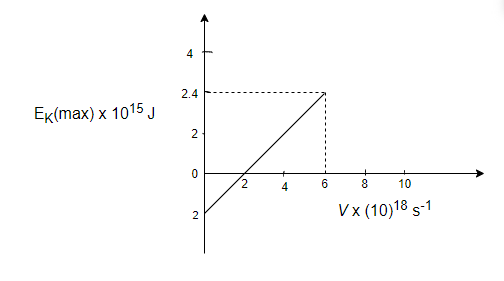
Einstein assumed that one photoelectron is ejected from a metal surface if one photon of suitable light radiation falls on it.
Let us consider a photon of light of frequency \[\nu \], incident on a photosensitive metal surface. The energy of the photon is \[h\nu \], spent in two ways:
A part of the energy of the photon will be used in liberating the electron from the metal surface which is equal to the work function \[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 \] of the metal.
The rest of the energy of the photon will be used in imparting the maximum kinetic energy \[\mathop K\nolimits_{\max } \] to the emitted photoelectron.
So, from above two points, we will get-
\[h\nu = \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 + \mathop K\nolimits_{\max } \].................(1)
This equation (1) is known as Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Step 2: Now from the equation (1) –
\[h\nu = \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 + \mathop K\nolimits_{\max } \]; where \[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 = \]work function of metal, \[h = \]Planck’s constant, and \[\nu = \]frequency of incident photon
If we rearrange the equation (1) in the form of \[\mathop K\nolimits_{\max } = h\nu + \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 \] and this equation can be compared with the \[y = mx + c\] .
So, the slope of the given line will be \[h\] and the intercept will be \[ - \mathop \phi \nolimits_0 \].
So, from the graph, \[h = \dfrac{{\mathop K\nolimits_{\max } }}{{\mathop \nu \nolimits_2 - \mathop \nu \nolimits_1 }}\]
\[h = \dfrac{{2.4 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 15} }}{{\left( {6 - 2} \right) \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} }}\]
\[h = 6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} \]J-s
And \[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 = 2 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 15} \]J
\[\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 = h\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 \]; where \[\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 = \] threshold frequency
\[\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 = \dfrac{{\mathop \phi \nolimits_0 }}{h} = \dfrac{{2 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 15} }}{{6 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{ - 34} }}\]
\[\mathop \nu \nolimits_0 = 3.33 \times \mathop {10}\nolimits^{18} \]$s^{-1}$
So, the correct option is (A).
Note: If \[\nu < \mathop \nu \nolimits_0 \] , then maximum K.E. will be negative, which is not possible. So, Photoelectric emission does not occur if the frequency of incident radiation is less than the threshold frequency.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




