
In the circuit shown in the figure:
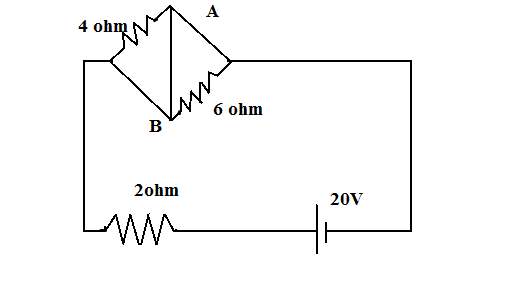
A) Power supplied by the battery is $200W$.
B) Current flowing the circuit is $5A$.
C) Potential difference across $4\Omega $ is equal to the potential difference across $6\Omega $ resistance.
D) Current in wire $AB$ is zero.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: After determining the circuital validity of the $4\Omega $ and $6\Omega $ resistor arrangement, we will determine the current in the circuit. That value will help us determine the power supplied by it.
Formula Used:
Current supplied by the battery: $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$.
Where $V$ is the voltage supplied and is expressed in Volt $(V)$, $R$ is the resistance value and is expressed in Ohms $(\Omega )$ and $I$ is the current value of the battery and is expressed in Ampere $(A)$.
Power supplied by the battery $P = EI$
Where $P$ is the power valueof the battery and is expressed in Watts $(W)$ and $E$ is the emf value of the cell and is expressed in Volt $(V)$.
Complete step by step answer:
The arrangement of the $4\Omega ,6\Omega $ is short circuited due to the negligibly low equivalent resistance value of its arrangement.
This means that the voltage difference across its end is zero. That is the potential difference across $4\Omega ,6\Omega $ is the same which is equal to $0$. Which means that no current passes through it.
But, current passes through the internally connected wire. In this case, this wire is $AB$. The value of this current is equal to the current passing through the entire circuit via the battery.
Therefore, the current passing through the battery we use the expression $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$.
Substituting the values we get,
$
I = \dfrac{{20}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow I = 10A \\
$
As we have the current value through the battery we will be able to calculate the power supplied by the same by substituting the values of $E$ and $I$ in $P = EI$.
We get,
$
P = EI = 20 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow P = 200W \\
$
In conclusion, the correct options are A and C.
Note: The resistance values of $4\Omega $ and $6\Omega $ are not to be considered while calculating the current in the battery. Also, it is a short circuited arrangement but current passes through the middle wire.
Formula Used:
Current supplied by the battery: $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$.
Where $V$ is the voltage supplied and is expressed in Volt $(V)$, $R$ is the resistance value and is expressed in Ohms $(\Omega )$ and $I$ is the current value of the battery and is expressed in Ampere $(A)$.
Power supplied by the battery $P = EI$
Where $P$ is the power valueof the battery and is expressed in Watts $(W)$ and $E$ is the emf value of the cell and is expressed in Volt $(V)$.
Complete step by step answer:
The arrangement of the $4\Omega ,6\Omega $ is short circuited due to the negligibly low equivalent resistance value of its arrangement.
This means that the voltage difference across its end is zero. That is the potential difference across $4\Omega ,6\Omega $ is the same which is equal to $0$. Which means that no current passes through it.
But, current passes through the internally connected wire. In this case, this wire is $AB$. The value of this current is equal to the current passing through the entire circuit via the battery.
Therefore, the current passing through the battery we use the expression $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$.
Substituting the values we get,
$
I = \dfrac{{20}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow I = 10A \\
$
As we have the current value through the battery we will be able to calculate the power supplied by the same by substituting the values of $E$ and $I$ in $P = EI$.
We get,
$
P = EI = 20 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow P = 200W \\
$
In conclusion, the correct options are A and C.
Note: The resistance values of $4\Omega $ and $6\Omega $ are not to be considered while calculating the current in the battery. Also, it is a short circuited arrangement but current passes through the middle wire.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




