
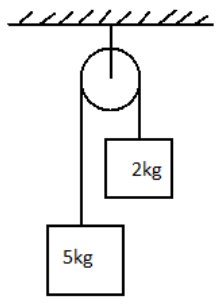
In the arrangement shown, what is the normal reaction between the block $A$ (mass $ = 5kg$ ) and ground?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: For a system to be in equilibrium, all the forces on each body have to balance each other otherwise the equilibrium would be destroyed. We can either draw free body diagrams for individual weights to mark all the forces on the diagram and balance it individually. Since the normal force is for block $A$ therefore we only draw the normal force for $A$.
Formula used:
${F_g} = mg$
Where ${F_g}$ is the force due to gravity on the blocks due to which it gets pulled downward, $m$ is the mass of the body and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
$T$ is the tension in the string which keeps the string taut.
$N$ is the normal on the block acting in the same direction as tension.
Complete step by step solution:

In the diagram,
$T$ is the tension in the string, $N$ is the normal on the block, ${m_1} = 5kg$ , ${m_2} = 2kg$ , and $g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
To balance forces in string $A$ ,
$T + N = {m_1}g$
$ \Rightarrow T + N = 5 \times 9.8$
$ \Rightarrow T + N = 49N$ $...\left( 1 \right)$
To balance forces in string $B$
$T = {m_2}g$
$ \Rightarrow T = 2 \times 9.8$
$ \Rightarrow T = 19.6N$ $...\left( 2 \right)$
Using $...\left( 1 \right)$ and $...\left( 2 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 19.6 + N = 49N$
$ \Rightarrow N = 49 - 19.6$
$ \Rightarrow N = 29.4N$
Therefore the normal force acting on block $A$ is $29.4N$.
Note: In systems such as this, it is important to mark all forces so as to avoid any silly mistakes. Write units with every data and if required, draw free body diagrams for individual bodies. The string and the pulley are considered massless since information is not provided to suggest otherwise. In ideal pulleys, the tension in both ends of the string is equal. Thus, it becomes simpler to balance tension and force of gravity along a normal reaction and find out either of the quantities.
Formula used:
${F_g} = mg$
Where ${F_g}$ is the force due to gravity on the blocks due to which it gets pulled downward, $m$ is the mass of the body and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
$T$ is the tension in the string which keeps the string taut.
$N$ is the normal on the block acting in the same direction as tension.
Complete step by step solution:

In the diagram,
$T$ is the tension in the string, $N$ is the normal on the block, ${m_1} = 5kg$ , ${m_2} = 2kg$ , and $g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
To balance forces in string $A$ ,
$T + N = {m_1}g$
$ \Rightarrow T + N = 5 \times 9.8$
$ \Rightarrow T + N = 49N$ $...\left( 1 \right)$
To balance forces in string $B$
$T = {m_2}g$
$ \Rightarrow T = 2 \times 9.8$
$ \Rightarrow T = 19.6N$ $...\left( 2 \right)$
Using $...\left( 1 \right)$ and $...\left( 2 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 19.6 + N = 49N$
$ \Rightarrow N = 49 - 19.6$
$ \Rightarrow N = 29.4N$
Therefore the normal force acting on block $A$ is $29.4N$.
Note: In systems such as this, it is important to mark all forces so as to avoid any silly mistakes. Write units with every data and if required, draw free body diagrams for individual bodies. The string and the pulley are considered massless since information is not provided to suggest otherwise. In ideal pulleys, the tension in both ends of the string is equal. Thus, it becomes simpler to balance tension and force of gravity along a normal reaction and find out either of the quantities.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




