
In reversible isochoric change
A. $\Delta W = 0$
B. $\Delta Q = 0$
C. $\Delta T = 0$
D. $\Delta U = 0$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In this problem, to find out the correct option for a reversible isochoric change; we have to first find out the specific condition for the isochoric process and then analyze that condition with respect to different parameters such as work done, internal energy, temperature, etc., to give a correct result.
Complete answer:
Isochoric process in thermodynamics is a process during which the volume of a system remains constant that’s why it is also referred to as a constant-volume process.
A reversible process in thermodynamics is a process in which both the system and the surroundings return to their original state without any external effect on the universe.
According to the question, An Isochoric change to be reversible, the system must be maintained in thermal equilibrium and heat must be supplied in a quasi-static manner.
Also, we know that Pressure-Volume Work in thermodynamics is defined as: -
At constant pressure, $Workdone = W = P\Delta V$ … (1)
Graphically, an isochoric process can be represented as: -
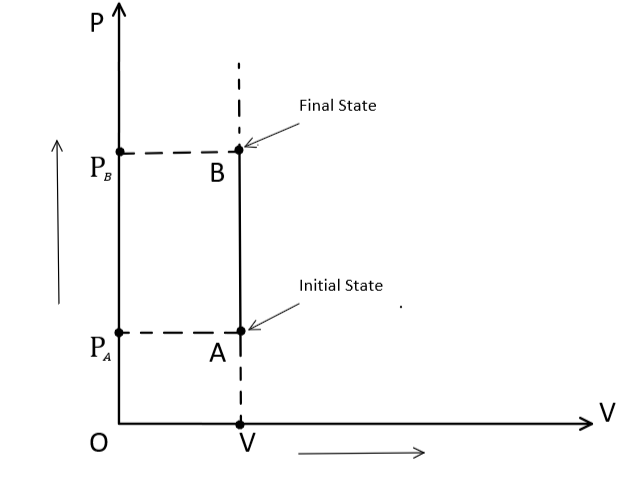
Also, By definition of an isochoric process, $\Delta V = 0$
So, from eq. (1), we get
$ \Rightarrow W = P\Delta V = 0$
Thus, In a reversible isochoric change $\Delta W = 0$. Hence, the correct option is (A) $\Delta W = 0$
Note: It is crucial to carefully consider all the given possibilities i.e., work done, internal energy, temperature, etc., in order to provide a comprehensive explanation because this is a theoretical conceptual problem. Always keep in mind to give specific justifications with the help of graphs in support of your explanation while writing an answer for this type of conceptual problem.
Complete answer:
Isochoric process in thermodynamics is a process during which the volume of a system remains constant that’s why it is also referred to as a constant-volume process.
A reversible process in thermodynamics is a process in which both the system and the surroundings return to their original state without any external effect on the universe.
According to the question, An Isochoric change to be reversible, the system must be maintained in thermal equilibrium and heat must be supplied in a quasi-static manner.
Also, we know that Pressure-Volume Work in thermodynamics is defined as: -
At constant pressure, $Workdone = W = P\Delta V$ … (1)
Graphically, an isochoric process can be represented as: -

Also, By definition of an isochoric process, $\Delta V = 0$
So, from eq. (1), we get
$ \Rightarrow W = P\Delta V = 0$
Thus, In a reversible isochoric change $\Delta W = 0$. Hence, the correct option is (A) $\Delta W = 0$
Note: It is crucial to carefully consider all the given possibilities i.e., work done, internal energy, temperature, etc., in order to provide a comprehensive explanation because this is a theoretical conceptual problem. Always keep in mind to give specific justifications with the help of graphs in support of your explanation while writing an answer for this type of conceptual problem.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




