
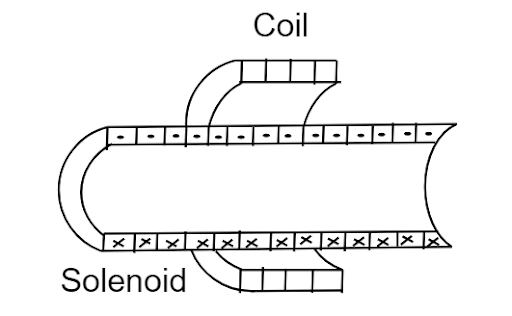
In Figure, a 120- turn coil of radius 1.8 cm and resistance \[5.3\Omega \] is coaxial with a solenoid of 220 turns/cm and diameter of \[3.2cm\]. The solenoid current drops from \[1.5A\]to zero in the time interval \[\Delta t = 25ms\]. What current is induced in the coil during \[\Delta t\]?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Before we proceed with the problem let’s see what is given. They have given the number of turns in the coil, resistance, solenoid turns, the diameter of the solenoid, and change in current and flux. Using these data first we need to find induced emf using the formula and then by ohm’s law the current can be calculated.
Formula Used:
The formula to find the total induced emf is given by,
\[e = - N\dfrac{{d{\varphi _B}}}{{dt}}\]……… (1)
Where, \[N\] is the number of turns in coil and \[\dfrac{{d{\varphi _B}}}{{dt}}\] is change of magnetic flux wrt to t.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider equation (1)
\[e = - N\dfrac{{d{\varphi _B}}}{{dt}}\]……… (2)
By the definition flux,
\[{\varphi _B} = BA\]
So, substituting the value of value of flux in equation (2) we obtain,
\[e = - N\dfrac{{d\left( {BA} \right)}}{{dt}}\]
Here, we know that, \[B = {\mu _0}ni\] and substitute this value in above equation
\[e = - NA\dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {{\mu _0}ni} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow e = - N{\mu _0}nA\left( {\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}} \right)\]……… (3)
Then, area of the coil is,
\[A = \pi {r^2}\],
\[\Rightarrow N = 120\],
\[\Rightarrow n = \dfrac{{220turns}}{{cm}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow n = \dfrac{{2200turns}}{m}\]
\[\Rightarrow di = 1.5A - 0 = 1.5A\]
\[\Rightarrow \Delta t = dt = 25 \times {10^{ - 3}}s\]
\[\Rightarrow d = 3.2cm\]\[ \Rightarrow r = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 2}}m\]
Substitute these values in equation (3) we get,
\[e = - 120 \times 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}} \times 2200 \times \left( {\pi {r^2}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1.5}}{{2.5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow e = - 120 \times 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}} \times 2200 \times 3.142 \times {\left( {1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{1.5}}{{2.5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow e = - 0.16V\]
We have found the value of induced emf, now using this find the value of current.By ohm’s law, we know that,
\[i = \dfrac{V}{R}\]
Since V is the potential difference, nothing but emf, so replacing V by e and taking its magnitude, we get,
\[i = \dfrac{{\left| e \right|}}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{0.16}}{{5.3}}\]
\[\therefore i = 0.031\,A\]
Therefore, the current which is induced in the coil is \[0.031\,A\].
Note:Solenoid depends on the strength of the current, number of turns in the coil and permeability of the material. Its function is to produce a regulated magnetic field through a coil twisted into a compact helix. The solenoid is a sort of electromagnet.
Formula Used:
The formula to find the total induced emf is given by,
\[e = - N\dfrac{{d{\varphi _B}}}{{dt}}\]……… (1)
Where, \[N\] is the number of turns in coil and \[\dfrac{{d{\varphi _B}}}{{dt}}\] is change of magnetic flux wrt to t.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider equation (1)
\[e = - N\dfrac{{d{\varphi _B}}}{{dt}}\]……… (2)
By the definition flux,
\[{\varphi _B} = BA\]
So, substituting the value of value of flux in equation (2) we obtain,
\[e = - N\dfrac{{d\left( {BA} \right)}}{{dt}}\]
Here, we know that, \[B = {\mu _0}ni\] and substitute this value in above equation
\[e = - NA\dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {{\mu _0}ni} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow e = - N{\mu _0}nA\left( {\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}} \right)\]……… (3)
Then, area of the coil is,
\[A = \pi {r^2}\],
\[\Rightarrow N = 120\],
\[\Rightarrow n = \dfrac{{220turns}}{{cm}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow n = \dfrac{{2200turns}}{m}\]
\[\Rightarrow di = 1.5A - 0 = 1.5A\]
\[\Rightarrow \Delta t = dt = 25 \times {10^{ - 3}}s\]
\[\Rightarrow d = 3.2cm\]\[ \Rightarrow r = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 2}}m\]
Substitute these values in equation (3) we get,
\[e = - 120 \times 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}} \times 2200 \times \left( {\pi {r^2}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1.5}}{{2.5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow e = - 120 \times 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}} \times 2200 \times 3.142 \times {\left( {1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{1.5}}{{2.5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow e = - 0.16V\]
We have found the value of induced emf, now using this find the value of current.By ohm’s law, we know that,
\[i = \dfrac{V}{R}\]
Since V is the potential difference, nothing but emf, so replacing V by e and taking its magnitude, we get,
\[i = \dfrac{{\left| e \right|}}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{0.16}}{{5.3}}\]
\[\therefore i = 0.031\,A\]
Therefore, the current which is induced in the coil is \[0.031\,A\].
Note:Solenoid depends on the strength of the current, number of turns in the coil and permeability of the material. Its function is to produce a regulated magnetic field through a coil twisted into a compact helix. The solenoid is a sort of electromagnet.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




