
In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the nitro group is meta directing because it:
(A) Decreases electron density at meta position
(B) Increases electron density at meta position
(C) Increases electron density at ortho and para positions
(D) Decreases electron density at ortho and para positions
Answer
239.7k+ views
Hint: Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group (EWG). When it is directly bonded to the carbon atom of benzene, it can show resonance and inductive effect which directs the position of incoming electrophile
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us analyse this behaviour of the Nitro group in detail and see why it occurs.
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) requires the benzene ring to be nucleophilic, as benzene attacks the electrophile using sites where it holds a negative charge.
- Now, when a nitro group is attached to a benzene ring, it deactivates the benzene ring towards EAS, as it prevents a negative charge from even existing in the benzene ring and makes the ring positively charged due to its electron withdrawing nature by resonance effect. How positive charge shuffles across the benzene ring is shown in the following figure by resonating structures.
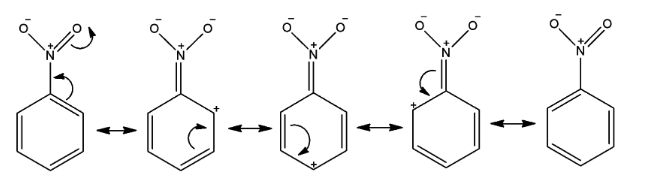
- We can see that the meta positions are less positively charged than the ortho/meta positions of the benzene ring and we need more electron density at a position at which the electrophile will connect. So, the carbon atom of meta position will attack the electrophile and as a result, a meta-substituted product will form.
- This is further proven as there is no full positive charge drawn on a meta position in the nitro group resonance forms.
- Therefore, nitro groups are meta directing, as only the meta positions can be nucleophilic enough to attack an electrophile. Remember that there is no increase in electron density at meta position.
- So, we can say that here, electron density at ortho and para position gets decreased by the nitro group and so that it is meta directing.
Note: Remember that not all EWG are meta directing. Halogens, despite being EWG, are ortho-para directors. The reason behind this is that they can donate electron density through resonance to the aromatic ring.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us analyse this behaviour of the Nitro group in detail and see why it occurs.
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) requires the benzene ring to be nucleophilic, as benzene attacks the electrophile using sites where it holds a negative charge.
- Now, when a nitro group is attached to a benzene ring, it deactivates the benzene ring towards EAS, as it prevents a negative charge from even existing in the benzene ring and makes the ring positively charged due to its electron withdrawing nature by resonance effect. How positive charge shuffles across the benzene ring is shown in the following figure by resonating structures.

- We can see that the meta positions are less positively charged than the ortho/meta positions of the benzene ring and we need more electron density at a position at which the electrophile will connect. So, the carbon atom of meta position will attack the electrophile and as a result, a meta-substituted product will form.
- This is further proven as there is no full positive charge drawn on a meta position in the nitro group resonance forms.
- Therefore, nitro groups are meta directing, as only the meta positions can be nucleophilic enough to attack an electrophile. Remember that there is no increase in electron density at meta position.
- So, we can say that here, electron density at ortho and para position gets decreased by the nitro group and so that it is meta directing.
Note: Remember that not all EWG are meta directing. Halogens, despite being EWG, are ortho-para directors. The reason behind this is that they can donate electron density through resonance to the aromatic ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26




