
$In coordination compound $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$which is false
A. show geometrical isomerism
B. Show optical isomerism
C. Show ionic isomerism
D.A octahedral complex
E.A cationic complex
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A coordination compound that consists of a central atom or ion, bonded to a set of atoms, ions, or molecules. Two or more coordination compounds with identical formulas but have different arrangements of bonded species show isomerism. Not all coordination complexes allow displacement of attached species or ligands bound to central metal.
Complete answer:Coordination compounds show the same type of isomers with identical chemical formulas but have different arrangements. These isomers have different chemical and physical properties. The coordination complex shows different kinds of isomerism for example ionic isomerism, coordination isomerism, linkage isomerism, and stereoisomerism.
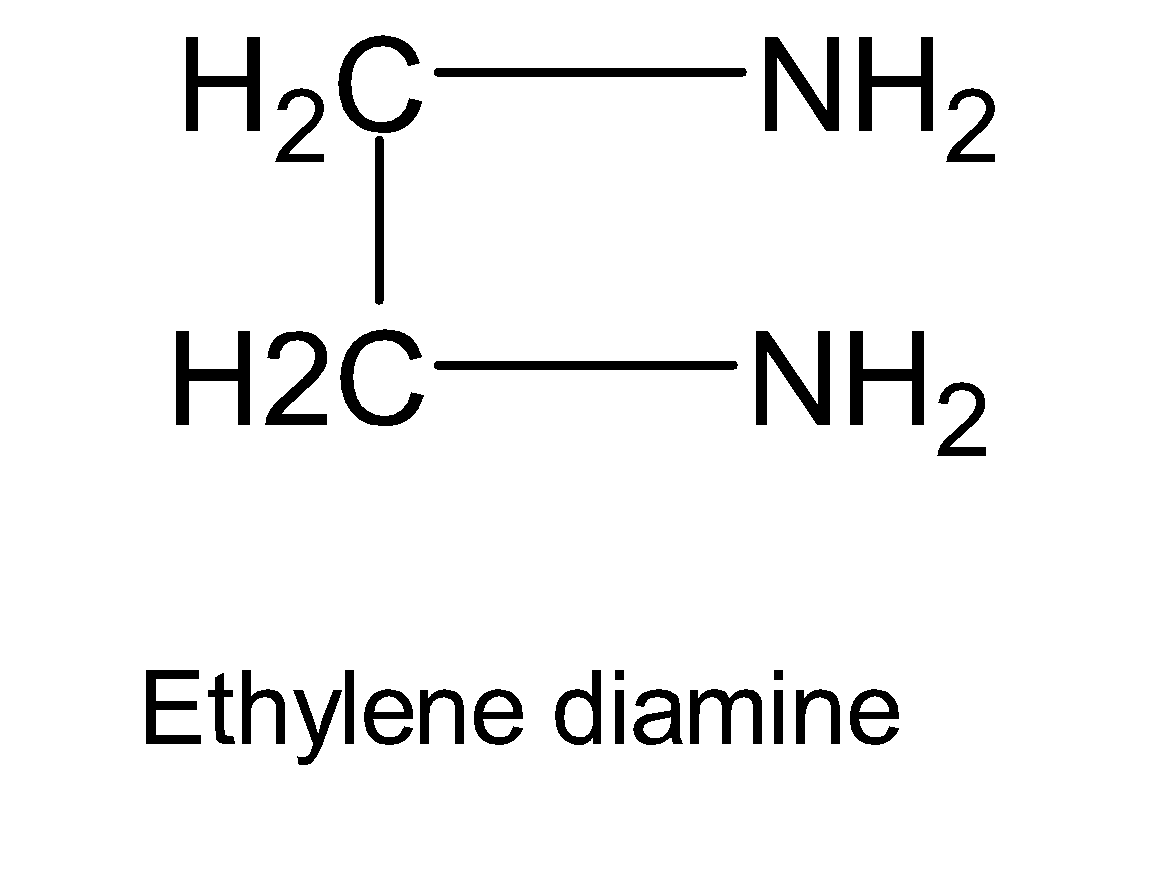
Here we have a coordination compound $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$. ‘en’ is ethylene diamine and the structure is shown below:
Let us check the isomerism present in this compound.
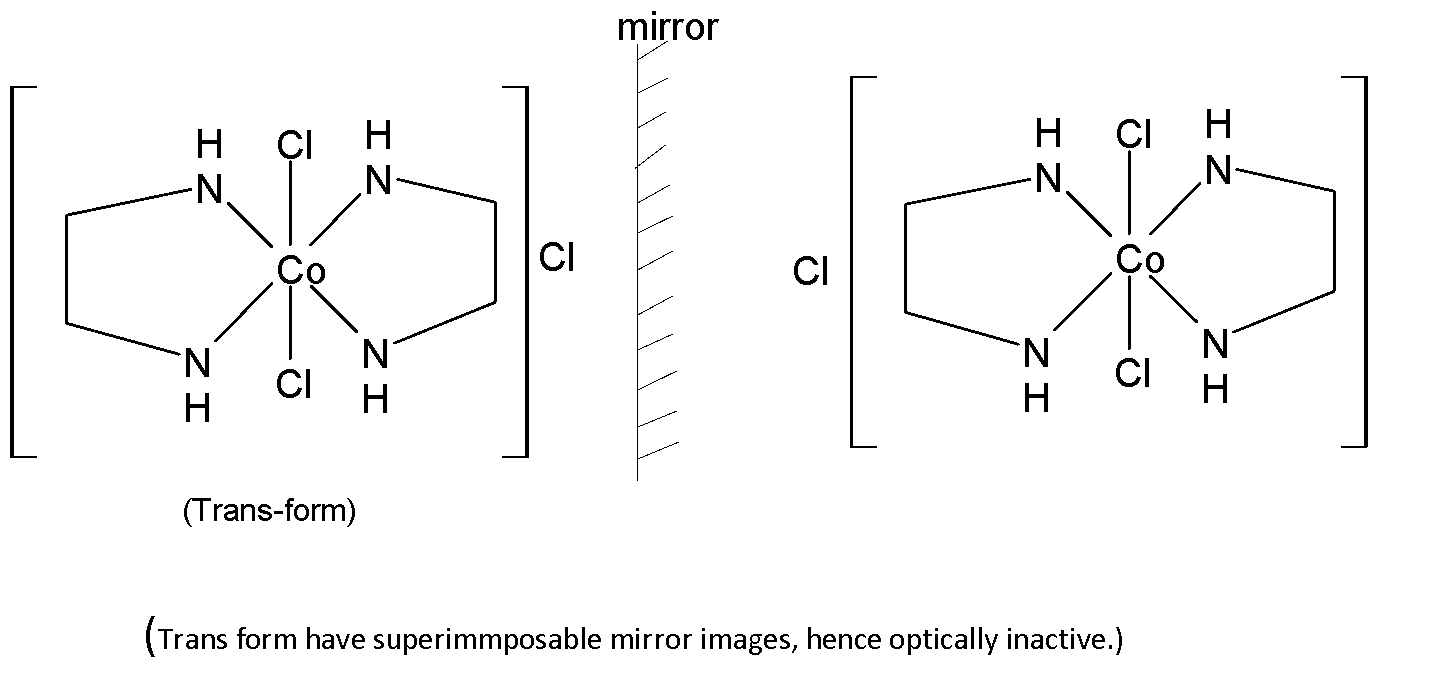
Stereoisomers are of two types; optical isomers and geometric isomers. $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$ has two geometric isomers; cis isomer and trans isomer. Hence this compound shows geometrical isomerism.

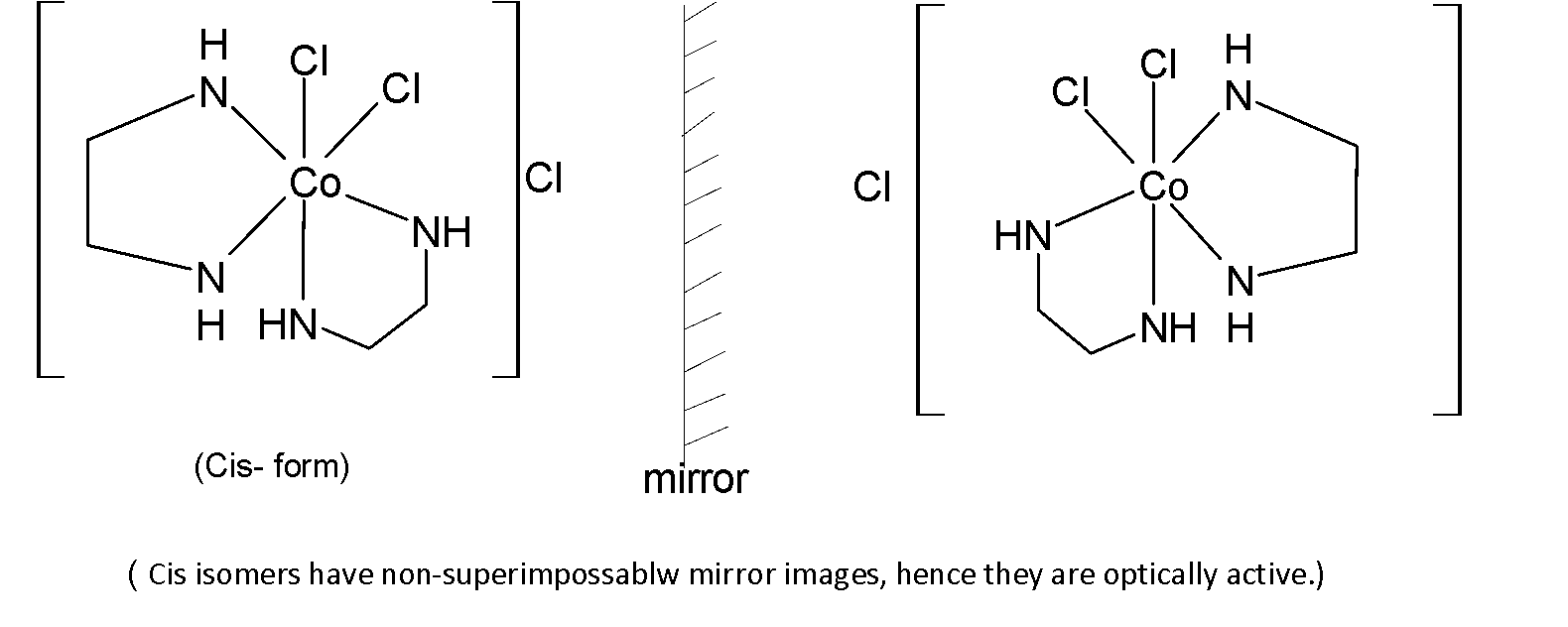
Also, the given compound has three optical isomers as cis isomers of this compound have non-superimposable mirror images. Hence this compound will show optical isomerism.
But $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$does not show ionization isomerism as this compound gives an identical ionic complex in solution. When compounds allow displacements of ligands attached to the metal with an anion or neutral molecule from outside the coordination complex and give different ionic compounds, it shows ionic isomerism.
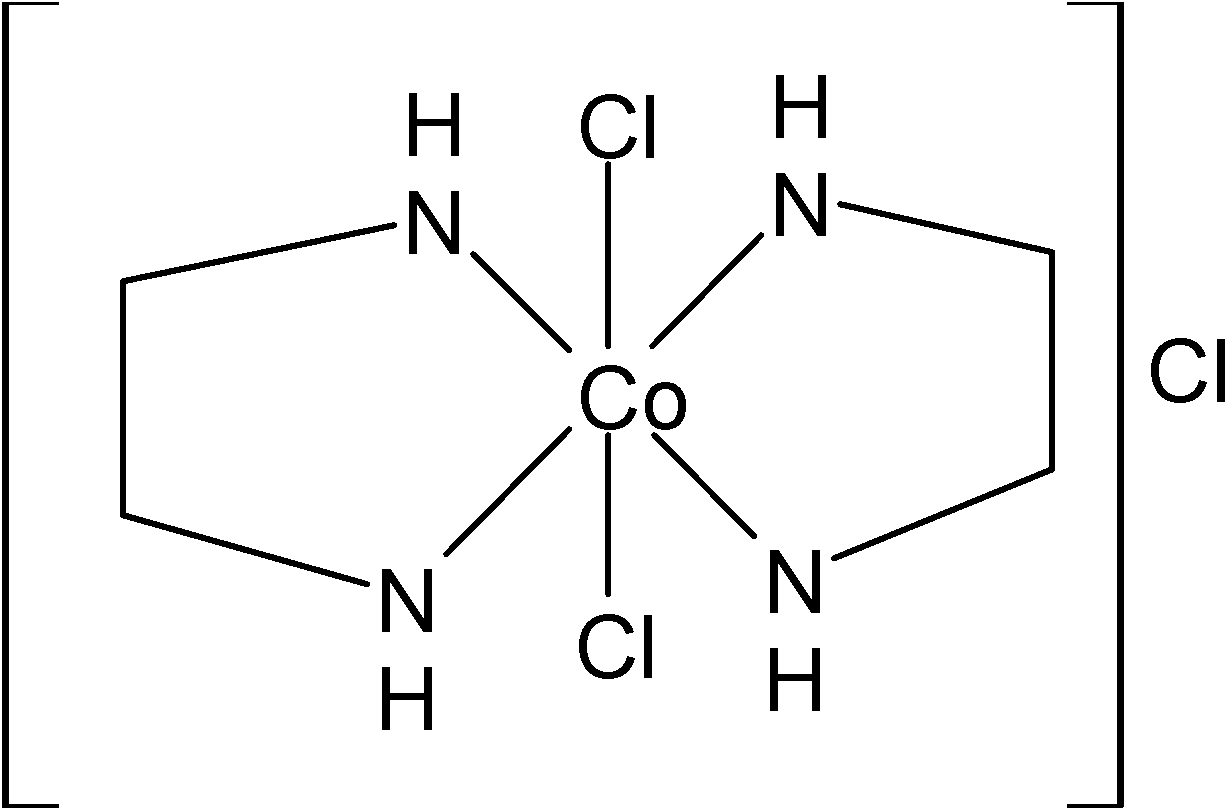
Also, the given compound is an octahedral complex with coordination number six. Here it is a bidentate ligand i.e, each en will make two bonds and each$Cl$will make one bond $Co$.
$[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$ the complex is carrying one net positive charge as ${{[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]}^{+}}$
$[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl\to {{[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}}$
Thus, it is a cationic complex.
Option (C) is correct.
Note:Coordination compounds do not completely ionize in aqueous solution They are partially ionizable. Generally in these compounds, a strong covalent is formed between transition metals and the ligands in the coordination sphere therefore it is hard to break these bonds in an aqueous solution.
Complete answer:Coordination compounds show the same type of isomers with identical chemical formulas but have different arrangements. These isomers have different chemical and physical properties. The coordination complex shows different kinds of isomerism for example ionic isomerism, coordination isomerism, linkage isomerism, and stereoisomerism.
Here we have a coordination compound $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$. ‘en’ is ethylene diamine and the structure is shown below:

Let us check the isomerism present in this compound.
Stereoisomers are of two types; optical isomers and geometric isomers. $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$ has two geometric isomers; cis isomer and trans isomer. Hence this compound shows geometrical isomerism.

Also, the given compound has three optical isomers as cis isomers of this compound have non-superimposable mirror images. Hence this compound will show optical isomerism.


But $[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$does not show ionization isomerism as this compound gives an identical ionic complex in solution. When compounds allow displacements of ligands attached to the metal with an anion or neutral molecule from outside the coordination complex and give different ionic compounds, it shows ionic isomerism.
Also, the given compound is an octahedral complex with coordination number six. Here it is a bidentate ligand i.e, each en will make two bonds and each$Cl$will make one bond $Co$.

$[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl$ the complex is carrying one net positive charge as ${{[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]}^{+}}$
$[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl\to {{[Co{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}}$
Thus, it is a cationic complex.
Option (C) is correct.
Note:Coordination compounds do not completely ionize in aqueous solution They are partially ionizable. Generally in these compounds, a strong covalent is formed between transition metals and the ligands in the coordination sphere therefore it is hard to break these bonds in an aqueous solution.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




