
In a reaction, if half of the double bond is broken and two new bonds are formed, this is a case of
A. Elimination
B. Addition
C. Displacement
D. Rearrangement
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Addition reaction is a chemical reaction in which two or more reactants react to form an individual product. Elimination, displacement, or rearrangement reactions do not include the breaking of half of the double bonds and the formation of two new bonds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here in this question, we have to find out a reaction in which half of the double bond is broken and two new bonds are formed.
A. Elimination
Elimination reaction involves the elimination of a couple of atoms or a group of atoms in the presence of a suitable reagent giving rise to unsaturated compounds.
These reactions are utilised to convert saturated compounds to unsaturated compounds.
So, these types of reactions do involve double bonds but lead to the formation of double bonds.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Addition
An addition reaction is a chemical reaction in which two or more reactants react to form an individual product.
Chemical compounds comprising multiple bond characters can undergo these types of reactions.
Double or triple bonds are usually broken down to create single bonds.
It is the opposite of an elimination reaction.
For example, the conversion of ethene to 1,2-dibromoethane.
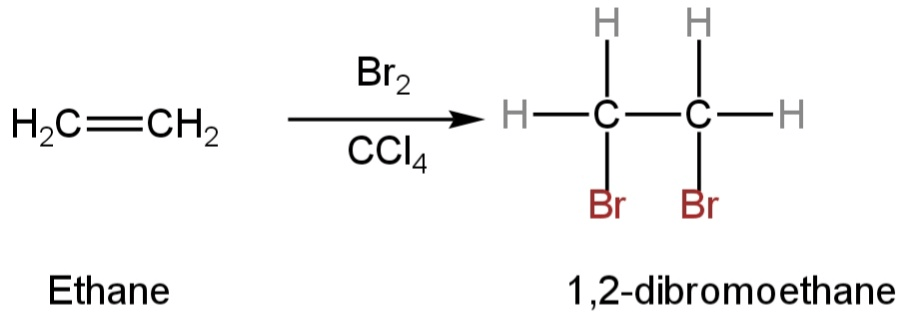
The double bond is broken and two new bonds are formed.
So, B is correct.
C. Displacement
A displacement reaction or a single replacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which one element is displaced by another in a compound.
It can be depicted as:
\[A + BC \to AC{\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}B\]
where
A and B are different metals and C is an anion.
Or
A, and B are halogens and C is a cation.
D. Rearrangement
A rearrangement reaction is a category of organic reactions involving the carbon skeleton of a molecule that is rearranged to provide a structural isomer of the actual molecule.
It mainly involves the moving of the substituent from one atom to another atom in one molecule.
So, these reactions are mainly intramolecular.
So, D is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Addition reactions are restricted to chemical compounds that possess multiple bonds like molecules with carbon-carbon double bonds or alkenes or with triple bonds or alkynes and compounds that possess rings. Molecules comprising carbon—hetero double bonds, for example, carbonyl (\[{\rm{C = O}}\]) groups, or imine (\[{\rm{C = N}}\]) groups, can go through addition due to double-bond character.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here in this question, we have to find out a reaction in which half of the double bond is broken and two new bonds are formed.
A. Elimination
Elimination reaction involves the elimination of a couple of atoms or a group of atoms in the presence of a suitable reagent giving rise to unsaturated compounds.
These reactions are utilised to convert saturated compounds to unsaturated compounds.
So, these types of reactions do involve double bonds but lead to the formation of double bonds.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Addition
An addition reaction is a chemical reaction in which two or more reactants react to form an individual product.
Chemical compounds comprising multiple bond characters can undergo these types of reactions.
Double or triple bonds are usually broken down to create single bonds.
It is the opposite of an elimination reaction.
For example, the conversion of ethene to 1,2-dibromoethane.

The double bond is broken and two new bonds are formed.
So, B is correct.
C. Displacement
A displacement reaction or a single replacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which one element is displaced by another in a compound.
It can be depicted as:
\[A + BC \to AC{\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}B\]
where
A and B are different metals and C is an anion.
Or
A, and B are halogens and C is a cation.
D. Rearrangement
A rearrangement reaction is a category of organic reactions involving the carbon skeleton of a molecule that is rearranged to provide a structural isomer of the actual molecule.
It mainly involves the moving of the substituent from one atom to another atom in one molecule.
So, these reactions are mainly intramolecular.
So, D is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Addition reactions are restricted to chemical compounds that possess multiple bonds like molecules with carbon-carbon double bonds or alkenes or with triple bonds or alkynes and compounds that possess rings. Molecules comprising carbon—hetero double bonds, for example, carbonyl (\[{\rm{C = O}}\]) groups, or imine (\[{\rm{C = N}}\]) groups, can go through addition due to double-bond character.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




