
If we use carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) in the Riemer - Tiemann reaction in place of chloroform, the product formed is:
A. Salicylaldehyde
B. Phenolphthalein
C. Salicylic Acid
D. Cyclohexanol
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: The Riemer-Tiemann reaction involves the ortho-formylation of phenol. It takes place in the presence of chloroform and a strong hydroxide base. Under such conditions, phenol is converted into salicylaldehyde.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The Riemer-Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction in which phenol gets converted to salicylaldehyde. This occurs when phenol is reacted with chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]) in the presence of a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (\[NaOH\]) or potassium hydroxide (\[KOH\]).
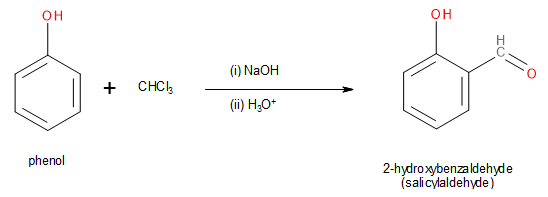
Image: Formation of Salicylaldehyde
However, the Riemer-Tiemann can be modified to produce phenolic acids such as salicylic acid by using carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) instead of chloroform.
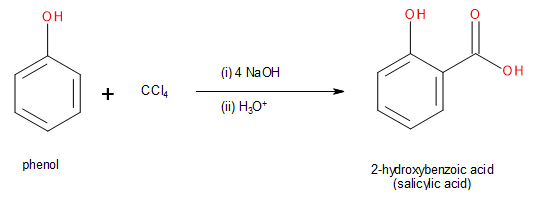
Image: Conversion of phenol into salicylic acid through Riemer-Tiemann reaction
The reaction proceeds in the following way.
First, the \[NaOH\] abstracts the acidic proton from phenol to give a phenoxide ion. The negative charge in the oxygen atom gets dispersed into the ring through the +R effect making the ring more nucleophilic.
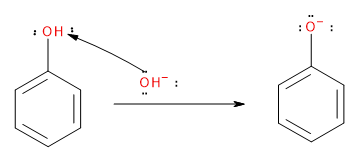
Image: Step 1: Abstraction of proton
The nucleophilic ring then attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of\[CC{l_4}\].
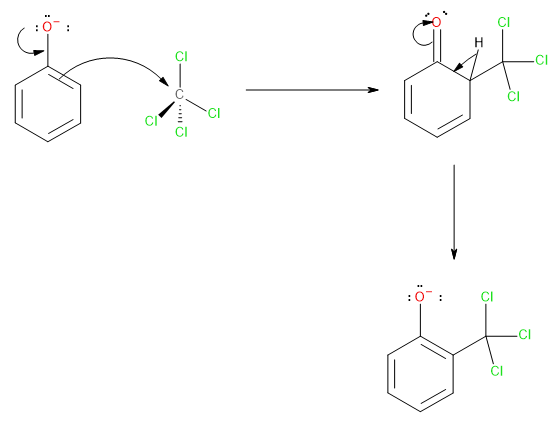
Image: Step 2
Each of the three chlorine atoms is removed by the sodium hydroxide leaving behind three hydroxyl groups attached to the carbon atom as shown here.
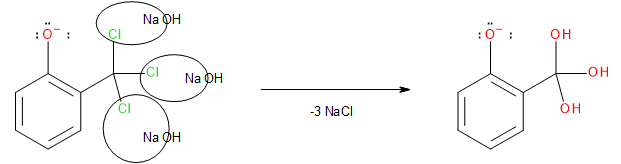
Image: Step 3
The product formed above undergoes spontaneous dehydration followed by acidic hydrolysis to give us the final product i.e., salicylic acid.
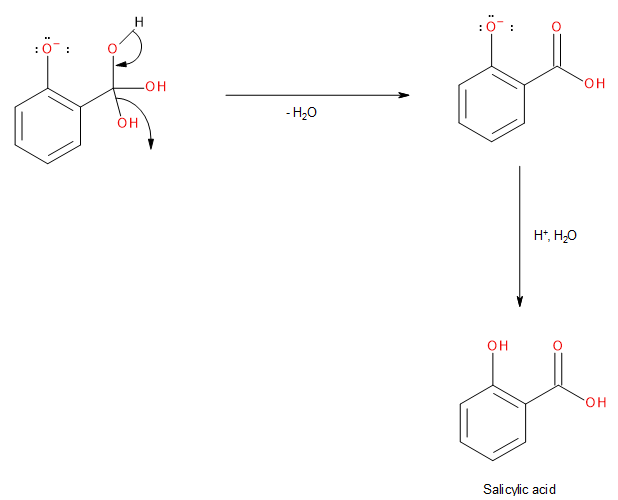
Image: Step 4
Thus, option C is the correct option.
Note: It must be remembered that the reaction mentioned above is only a variation of the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. The actual Riemer-Tiemann reaction leads to the formation of salicylaldehyde from phenol.
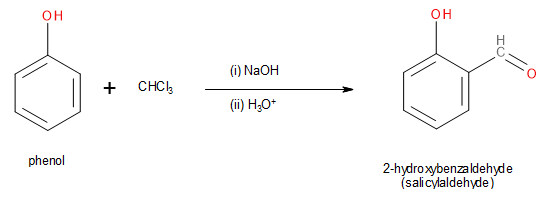
Image: Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The Riemer-Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction in which phenol gets converted to salicylaldehyde. This occurs when phenol is reacted with chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]) in the presence of a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (\[NaOH\]) or potassium hydroxide (\[KOH\]).

Image: Formation of Salicylaldehyde
However, the Riemer-Tiemann can be modified to produce phenolic acids such as salicylic acid by using carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) instead of chloroform.

Image: Conversion of phenol into salicylic acid through Riemer-Tiemann reaction
The reaction proceeds in the following way.
First, the \[NaOH\] abstracts the acidic proton from phenol to give a phenoxide ion. The negative charge in the oxygen atom gets dispersed into the ring through the +R effect making the ring more nucleophilic.

Image: Step 1: Abstraction of proton
The nucleophilic ring then attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of\[CC{l_4}\].

Image: Step 2
Each of the three chlorine atoms is removed by the sodium hydroxide leaving behind three hydroxyl groups attached to the carbon atom as shown here.

Image: Step 3
The product formed above undergoes spontaneous dehydration followed by acidic hydrolysis to give us the final product i.e., salicylic acid.

Image: Step 4
Thus, option C is the correct option.
Note: It must be remembered that the reaction mentioned above is only a variation of the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. The actual Riemer-Tiemann reaction leads to the formation of salicylaldehyde from phenol.

Image: Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




