
If two soaps bubbles of equal radii $r$coalesce, then the radius of curvature of interface between two bubble will be:
A. $r$
B. $0$
C. Infinity
D. $\dfrac{r}{2}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The radius of curvature is defined as the approximate circle's radius at a given location. It is equal to the radius of the circular arc that, at that moment, most closely resembles the curve for a curve. As the curve advances, the radius shifts. The radius of curvature, denoted by $R$.
Formula used:
Excess pressure in a soap bubble is calculated using the formula:
$P=\dfrac {4T}{r}$ Where,
r- The radius of the soap bubble
T-The surface tension
Complete answer:
Here, we have given a situation that a radii of the two soaps bubbles are equal, We need to determine the radius of curvature of interface between the two bubble.
Let $R$be the radius of curvature and, $T$ be the surface tensions. In order to know that the radius of curvature is the diameter of a circle that contacts a curve at a particular place and shares its tangent and curvature there.
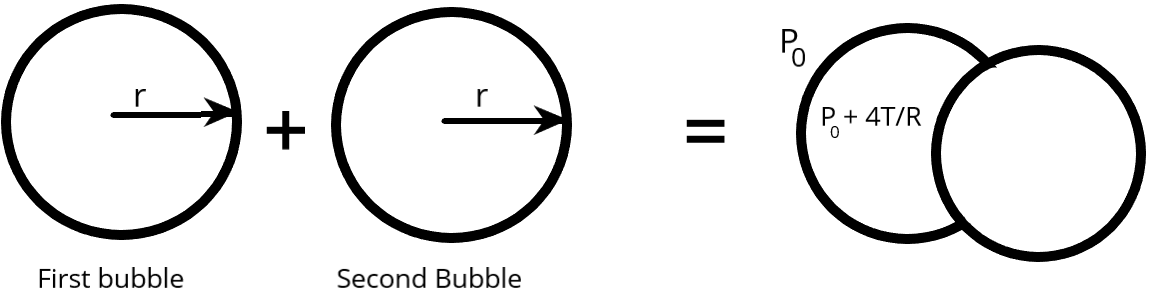
Use the formula of the excess pressure of the bubble $\dfrac{{4T}}{r}$,
From the above figure of the given situation, we have:
The equation of the bubble $1$ is:
${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$.
The equation of the bubble $2$ is:
${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$,
Therefore, At the interface pressure from both sides should be same, then we obtain:
${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} = {P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{r} - \dfrac{1}{r}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = 0 $
$\Rightarrow R = \infty $
Thus, the correct option is (C) Infinity.
Note: It should be noted that the excess pressure of the first bubble is two times than the second bubble that’s why the equation of the first bubble is ${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$ instead of ${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$. And when the two bubble soaps' radii aren't equal, air moves from the smaller bubble into the larger one, which causes the larger bubble to expand and the smaller one to diminishes.
Formula used:
Excess pressure in a soap bubble is calculated using the formula:
$P=\dfrac {4T}{r}$ Where,
r- The radius of the soap bubble
T-The surface tension
Complete answer:
Here, we have given a situation that a radii of the two soaps bubbles are equal, We need to determine the radius of curvature of interface between the two bubble.
Let $R$be the radius of curvature and, $T$ be the surface tensions. In order to know that the radius of curvature is the diameter of a circle that contacts a curve at a particular place and shares its tangent and curvature there.

Use the formula of the excess pressure of the bubble $\dfrac{{4T}}{r}$,
From the above figure of the given situation, we have:
The equation of the bubble $1$ is:
${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$.
The equation of the bubble $2$ is:
${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$,
Therefore, At the interface pressure from both sides should be same, then we obtain:
${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} = {P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{r} - \dfrac{1}{r}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = 0 $
$\Rightarrow R = \infty $
Thus, the correct option is (C) Infinity.
Note: It should be noted that the excess pressure of the first bubble is two times than the second bubble that’s why the equation of the first bubble is ${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$ instead of ${P_0} + \dfrac{{4T}}{r}$. And when the two bubble soaps' radii aren't equal, air moves from the smaller bubble into the larger one, which causes the larger bubble to expand and the smaller one to diminishes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




