
If true enter ${ 1 } $, else enter ${ 0 } $.
Covalent bonds are directional and ionic bonds are non-directional
(a) ${ 1 }$
(b) ${ 0 } $
(c) Both
(d) None of these
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Covalent bond is defined as the bond which is formed by mutual sharing of electrons. Ionic bond is defined as the bond which is formed by the transfer of electrons from metal to non-metal. It occurs between oppositely charged ions.
Complete step-by-step solution:
> Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.So, the direction of overlapping gives direction of bonds,i.e, a shared pair of electron/ electrons are localized between two atoms. Hence, covalent bond is a directional bond.
> In ionic compounds, there is no overlapping of atomic orbitals. Each ion has its influence in all the directions. It means it is surrounded by a number of oppositely charged ions with no definite direction. Thus, ionic bonds are non-directional.
Figure:- Showing Lewis structure of covalent and ionic compounds
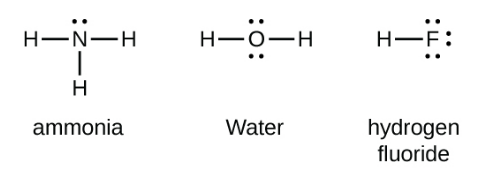
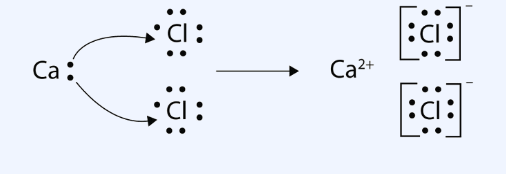
Hence, the above statement is true.Therefor answer is (A)
Additional Information: Polar Bonding:- A covalent bond formed between two different atoms, with different electronegativities is known as Polar covalent bond.
Non-polar bonding:- A covalent bond formed between two like atoms is known as Non-Polar bond. Here, the electronegativity difference is zero.
Note: The possibility for the mistake is that you can choose the option (b). You may think covalent bonds are non-directional and ionic bonds are directional. But it’s not true because in covalent bonds both sigma and pi bonding occurs and its directional while in ionic, an ion has the same attraction from all directions.
Complete step-by-step solution:
> Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.So, the direction of overlapping gives direction of bonds,i.e, a shared pair of electron/ electrons are localized between two atoms. Hence, covalent bond is a directional bond.
> In ionic compounds, there is no overlapping of atomic orbitals. Each ion has its influence in all the directions. It means it is surrounded by a number of oppositely charged ions with no definite direction. Thus, ionic bonds are non-directional.
Figure:- Showing Lewis structure of covalent and ionic compounds


Hence, the above statement is true.Therefor answer is (A)
Additional Information: Polar Bonding:- A covalent bond formed between two different atoms, with different electronegativities is known as Polar covalent bond.
Non-polar bonding:- A covalent bond formed between two like atoms is known as Non-Polar bond. Here, the electronegativity difference is zero.
Note: The possibility for the mistake is that you can choose the option (b). You may think covalent bonds are non-directional and ionic bonds are directional. But it’s not true because in covalent bonds both sigma and pi bonding occurs and its directional while in ionic, an ion has the same attraction from all directions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




