
If the distance of the point \[\left( {1, - 2,3} \right)\] from the plane \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\] measured parallel to the line, \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\] is \[\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{2}} \], then the value of \[\left| m \right|\] is equal to
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
In this question, we have to find the value of \[\left| m \right|\]. By using this direction cosines for the equation \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\] we find the coordinate points on the plane then finally we calculate the value of \[\left| m \right|\] by using the given distance and the substitution method.
Formula used:
The equation of line formula are given as
1. \[\left\langle {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right\rangle = \left\langle {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{b}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }}} \right\rangle \]
2. coordinates with direction cosines \[ = \left( {{x_1} + r\cos \alpha ,{y_1} + r\cos \beta ,{z_1} + r\cos \gamma } \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given plane is \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\] and a point anywhere is given \[\left( {1, - 2,3} \right)\] which is to be measured parallel to the line is \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\].
Firstly, we will rearrange the term of \[y\] by taking out minus as common in the line \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\], we get
\[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{y - 2}}{{ - m}} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\]
Now, we will draw the diagram and it looks like:
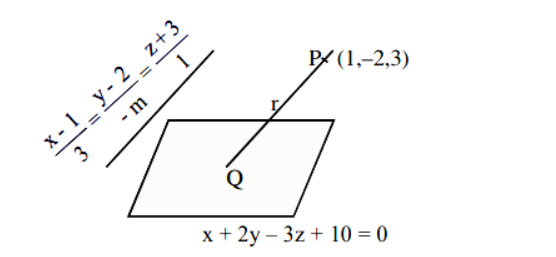
There is a plane satisfying \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\] and \[Q\] is the point on this plane and the distance between \[P\] and \[Q\] is \[r\].
Now, we will find the direction cosines using the formula \[\left\langle {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right\rangle = \left\langle {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{b}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }}} \right\rangle \] for the line \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{y - 2}}{{ - m}} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\] where \[a\] is \[3,b\] is \[ - m\] and \[c\] is \[1\], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}D.C. = \left\langle {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right\rangle \\D.C. = \left\langle {\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - m} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}} }},\dfrac{{ - m}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - m} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}} }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - m} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}} }}} \right\rangle \\D.C. = \left\langle {\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }},\dfrac{{ - m}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right\rangle \end{array}\]
If we have a point \[P\] whose points are \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)\]and there is another point \[Q\] at a distance \[r\] with direction cosines \[\left( {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right)\].
Now, we will find the coordinates of \[Q\]using the formula \[\left( {{x_1} + r\cos \alpha ,{y_1} + r\cos \beta ,{z_1} + r\cos \gamma } \right)\]where \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 2,3} \right)\]and \[r\] is \[\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{2}} \], we get
\[Q = \left( {1 + \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}, - 2 + \dfrac{{ - mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }},3 + \dfrac{r}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right)\]
As we know, \[Q\] is lie on the plane so its coordinate must satisfy the equation \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}1 + \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} + 2\left( { - 2 + \dfrac{{ - mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right) - 3\left( {3 + \dfrac{r}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right) + 10 = 0\\1 + \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - 4 - \dfrac{{2mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - 9 - \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} + 10 = 0\\\dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - \dfrac{{2mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - 2 = 0\end{array}\]
Further, we will taking out the common factor, we get
\[\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{r}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}\left( {3 - 2m - 3} \right) = 2\\\dfrac{{ - 2mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} = 2\\\dfrac{{ - mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} = 1\end{array}\]
Furthermore, we will squaring both sides, we get
\[\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{{{m^2}{r^2}}}{{{m^2} + 10}} = 1\\{m^2}{r^2} = {m^2} + 10\\{m^2}\left( {{r^2} - 1} \right) = 10\end{array}\]
As we are given that the distance is \[r = \sqrt {\dfrac{7}{2}} \], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}{m^2}\left( {\dfrac{7}{2} - 1} \right) = 10\\\dfrac{5}{2}{m^2} = 10\\{m^2} = 4\\m = \pm 2\end{array}\]
We have to find the value of \[\left| m \right|\] so we neglect the negative value and we get \[\left| m \right| = 2\]
Hence, the value of \[\left| m \right|\] is equal to \[2\]
Note
In these types of questions, we should remember the formulas of direction of cosines or we can also solve it by assuming the line \[\dfrac{{x - {x_1}}}{a} = \dfrac{{y - {y_{_1}}}}{b} = \dfrac{{z - {z_1}}}{c} = \lambda \] and substitute the values of \[\left( {x,y,z} \right)\]in the given plane.
In this question, we have to find the value of \[\left| m \right|\]. By using this direction cosines for the equation \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\] we find the coordinate points on the plane then finally we calculate the value of \[\left| m \right|\] by using the given distance and the substitution method.
Formula used:
The equation of line formula are given as
1. \[\left\langle {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right\rangle = \left\langle {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{b}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }}} \right\rangle \]
2. coordinates with direction cosines \[ = \left( {{x_1} + r\cos \alpha ,{y_1} + r\cos \beta ,{z_1} + r\cos \gamma } \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given plane is \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\] and a point anywhere is given \[\left( {1, - 2,3} \right)\] which is to be measured parallel to the line is \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\].
Firstly, we will rearrange the term of \[y\] by taking out minus as common in the line \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{2 - y}}{m} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\], we get
\[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{y - 2}}{{ - m}} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\]
Now, we will draw the diagram and it looks like:

There is a plane satisfying \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\] and \[Q\] is the point on this plane and the distance between \[P\] and \[Q\] is \[r\].
Now, we will find the direction cosines using the formula \[\left\langle {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right\rangle = \left\langle {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{b}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }},\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} }}} \right\rangle \] for the line \[\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3} = \dfrac{{y - 2}}{{ - m}} = \dfrac{{z + 3}}{1}\] where \[a\] is \[3,b\] is \[ - m\] and \[c\] is \[1\], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}D.C. = \left\langle {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right\rangle \\D.C. = \left\langle {\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - m} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}} }},\dfrac{{ - m}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - m} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}} }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - m} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}} }}} \right\rangle \\D.C. = \left\langle {\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }},\dfrac{{ - m}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right\rangle \end{array}\]
If we have a point \[P\] whose points are \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)\]and there is another point \[Q\] at a distance \[r\] with direction cosines \[\left( {\cos \alpha ,\cos \beta ,\cos \gamma } \right)\].
Now, we will find the coordinates of \[Q\]using the formula \[\left( {{x_1} + r\cos \alpha ,{y_1} + r\cos \beta ,{z_1} + r\cos \gamma } \right)\]where \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 2,3} \right)\]and \[r\] is \[\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{2}} \], we get
\[Q = \left( {1 + \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}, - 2 + \dfrac{{ - mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }},3 + \dfrac{r}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right)\]
As we know, \[Q\] is lie on the plane so its coordinate must satisfy the equation \[x + 2y - 3z + 10 = 0\], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}1 + \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} + 2\left( { - 2 + \dfrac{{ - mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right) - 3\left( {3 + \dfrac{r}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}} \right) + 10 = 0\\1 + \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - 4 - \dfrac{{2mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - 9 - \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} + 10 = 0\\\dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - \dfrac{{2mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - \dfrac{{3r}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} - 2 = 0\end{array}\]
Further, we will taking out the common factor, we get
\[\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{r}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }}\left( {3 - 2m - 3} \right) = 2\\\dfrac{{ - 2mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} = 2\\\dfrac{{ - mr}}{{\sqrt {10 + {m^2}} }} = 1\end{array}\]
Furthermore, we will squaring both sides, we get
\[\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{{{m^2}{r^2}}}{{{m^2} + 10}} = 1\\{m^2}{r^2} = {m^2} + 10\\{m^2}\left( {{r^2} - 1} \right) = 10\end{array}\]
As we are given that the distance is \[r = \sqrt {\dfrac{7}{2}} \], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}{m^2}\left( {\dfrac{7}{2} - 1} \right) = 10\\\dfrac{5}{2}{m^2} = 10\\{m^2} = 4\\m = \pm 2\end{array}\]
We have to find the value of \[\left| m \right|\] so we neglect the negative value and we get \[\left| m \right| = 2\]
Hence, the value of \[\left| m \right|\] is equal to \[2\]
Note
In these types of questions, we should remember the formulas of direction of cosines or we can also solve it by assuming the line \[\dfrac{{x - {x_1}}}{a} = \dfrac{{y - {y_{_1}}}}{b} = \dfrac{{z - {z_1}}}{c} = \lambda \] and substitute the values of \[\left( {x,y,z} \right)\]in the given plane.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




