
If $f(x) = \dfrac{1}{2} - \tan \left( {\dfrac{{\pi x}}{2}} \right), - 1 < x < 1$ and $g(x) = \sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2}$ , then find the domain of $(f + g)$ .
A.$\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2},1} \right]$
B. $[\dfrac{1}{2}, - 1)$
C. $[ - \dfrac{1}{2},1)$
D. $\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2}, - 1} \right]$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The domain of $f(x)$ is given, set $\sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2}$ to zero and obtain the values of x. Then obtain the common points between $ - 1 < x < 1$ and the obtained values of x to obtain the required answer.
Formula Used:
The quadratic formula of a quadratic equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ .
Domain of $(f + g)$=domain of $f(x) \cap $ domain of $g(x)$.
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation is $g(x) = \sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2}$.
So, set $\sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2}$to zero and obtain the values of x
$\sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2} = 0$
$4{x^2} - 4x - \sqrt 3 = 0$
Apply the quadratic formula to obtain the values of x.
$x = \dfrac{{4 \pm \sqrt {{{( - 4)}^2} - 4.4.\left( { - \sqrt 3 } \right)} }}{{2.4}}$
$ = \dfrac{{4 \pm \sqrt {16 + 16\sqrt 3 } }}{8}$
$ = \dfrac{{4 \pm 4\sqrt {1 + \sqrt 3 } }}{8}$
$ = \dfrac{{1 \pm \sqrt {1 + \sqrt 3 } }}{2}$
Therefore, $x \approx - \dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{3}{2}$
Now, let’s draw a number line to obtain the intersection of domain to given functions.
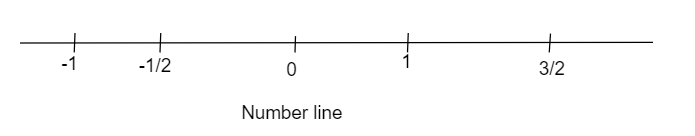
From the number line we have the intersection as $x \in [ - \dfrac{1}{2},1)$.
Option ‘C’ is correct
Note: Students are sometimes unable to factor the given quadratic equation because the equation lacks integer roots. So, to find the values of x, use the quadratic formula $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ and then find the intersection of two domains.
Formula Used:
The quadratic formula of a quadratic equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ .
Domain of $(f + g)$=domain of $f(x) \cap $ domain of $g(x)$.
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation is $g(x) = \sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2}$.
So, set $\sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2}$to zero and obtain the values of x
$\sqrt 3 + 4x - 4{x^2} = 0$
$4{x^2} - 4x - \sqrt 3 = 0$
Apply the quadratic formula to obtain the values of x.
$x = \dfrac{{4 \pm \sqrt {{{( - 4)}^2} - 4.4.\left( { - \sqrt 3 } \right)} }}{{2.4}}$
$ = \dfrac{{4 \pm \sqrt {16 + 16\sqrt 3 } }}{8}$
$ = \dfrac{{4 \pm 4\sqrt {1 + \sqrt 3 } }}{8}$
$ = \dfrac{{1 \pm \sqrt {1 + \sqrt 3 } }}{2}$
Therefore, $x \approx - \dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{3}{2}$
Now, let’s draw a number line to obtain the intersection of domain to given functions.

From the number line we have the intersection as $x \in [ - \dfrac{1}{2},1)$.
Option ‘C’ is correct
Note: Students are sometimes unable to factor the given quadratic equation because the equation lacks integer roots. So, to find the values of x, use the quadratic formula $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ and then find the intersection of two domains.
Recently Updated Pages
The area of an expanding rectangle is increasing at class 12 maths JEE_Main

If y xxx cdots infty then find dfracdydx A yxy 1 B class 12 maths JEE_Main

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Practical Organic Chemistry

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




