
Why is glucose called gluco-pyranose?
A. Glucose is an aldohexose
B. Glucose is a cyclic compound containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom
C. Glucose is ketohexose
D. Glucose is a cyclic compound containing six carbon atoms.
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: Think about the process of cyclization of glucose and what kind of ring is formed. Also, consider what exactly it means to be a pyranose molecule and what types of rings it includes.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we need to understand that although we may see that glucose is often represented as an open-chain molecule, that may not always be the case. The ring form or the cyclized form of glucose is found abundantly and chiefly in nature. Glucose is a six-carbon molecule with an aldehyde functional group, it is due to the intramolecular attraction between the hydroxyl groups on the carbons and the oxygen in the aldehyde functional group that these linear molecules cyclize into rings.
Now let us look at the cyclization reaction:
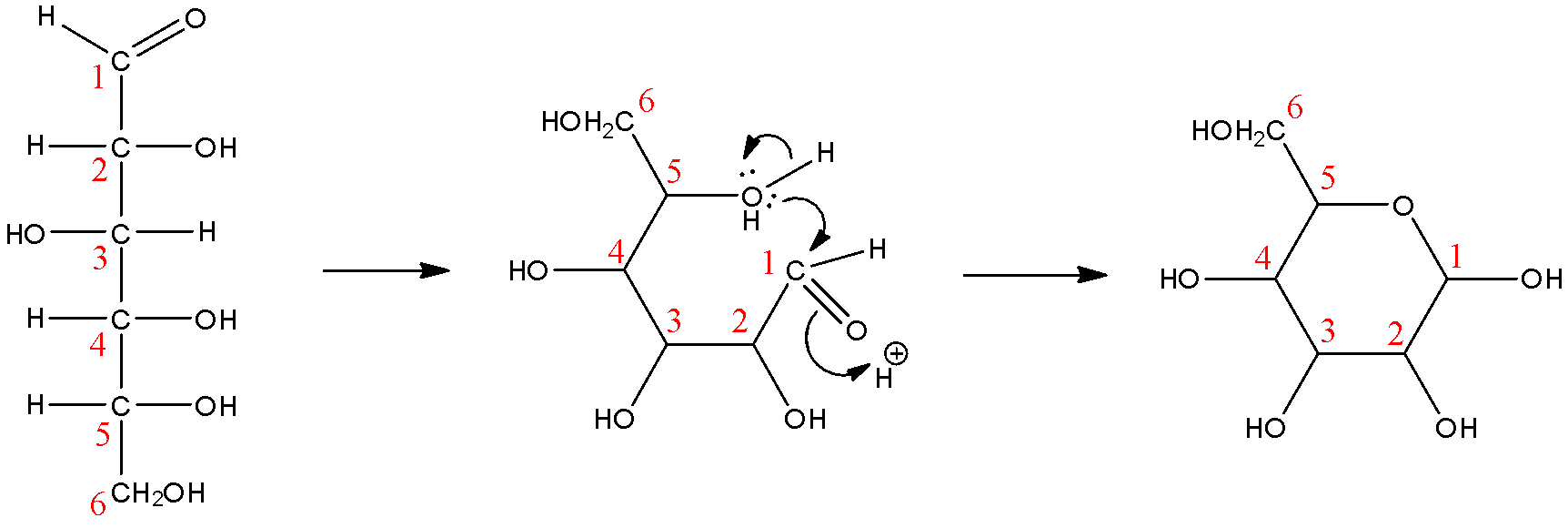
Here, we can see that while the ring form of glucose does have 6 carbon atoms, only 5 of them are involved in the cyclic ring. We will now see how the pyranose rings are defined before arriving at our answer. Pyranose rings are a defined class of saccharides that are six-membered rings that contain 5 carbon atoms and 1 oxygen atom. We can see that this is true in the reaction.
So, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is ‘B. Glucose is a cyclic compound containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom’
Note: Note that the options ‘A’ and ‘D’ are also true but they are not the right answer to this question. Let us consider option A first, glucose is an aldehydic sugar that contains 6 atoms of carbon, but this fact does not explain why glucose will be called gluco-pyranose, so this is not the correct answer. Now, let us consider option D, gluco-pyranose is a cyclic compound, it does contain 6 carbon atoms, but the oxygen atom that has to be present in pyranose rings is not mentioned here at all, it also indicates that all the 6 carbons are involved in the ring, which is not true, so this is not the correct answer either.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we need to understand that although we may see that glucose is often represented as an open-chain molecule, that may not always be the case. The ring form or the cyclized form of glucose is found abundantly and chiefly in nature. Glucose is a six-carbon molecule with an aldehyde functional group, it is due to the intramolecular attraction between the hydroxyl groups on the carbons and the oxygen in the aldehyde functional group that these linear molecules cyclize into rings.
Now let us look at the cyclization reaction:

Here, we can see that while the ring form of glucose does have 6 carbon atoms, only 5 of them are involved in the cyclic ring. We will now see how the pyranose rings are defined before arriving at our answer. Pyranose rings are a defined class of saccharides that are six-membered rings that contain 5 carbon atoms and 1 oxygen atom. We can see that this is true in the reaction.
So, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is ‘B. Glucose is a cyclic compound containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom’
Note: Note that the options ‘A’ and ‘D’ are also true but they are not the right answer to this question. Let us consider option A first, glucose is an aldehydic sugar that contains 6 atoms of carbon, but this fact does not explain why glucose will be called gluco-pyranose, so this is not the correct answer. Now, let us consider option D, gluco-pyranose is a cyclic compound, it does contain 6 carbon atoms, but the oxygen atom that has to be present in pyranose rings is not mentioned here at all, it also indicates that all the 6 carbons are involved in the ring, which is not true, so this is not the correct answer either.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




