
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The identification of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{i}}^{{\rm{2 + }}}}\] is carried out by dimethylglyoxime in the presence of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{OH}}\] .
Statement II: The dimethylglyoxime is a bidentate neutral ligand.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a. Both statement I and statement II are true
b. Both statement I and statement II are false
c. Statement I is false but statement II is true
d. Statement I is true but statement II is false
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: They are substances possessing chemical structures where a group of atoms or nonmetals surround a central metal. The surrounding atoms are termed ligands, joined to the metal by chemical bonds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let’s discuss the given statements one by one. First statement says, nickel ions (\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{i}}^{{\rm{2 + }}}}\] ) are identified by dimethylglyoxime in the presence of ammonium hydroxide (\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{OH}}\] ). The statement is correct. Let’s understand the statement. Neutral dimethylglyoxime (dmg) dot not behave as ligand. The reaction of nickel ions with dimethylglyoxime in the basic medium of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{OH}}\], results in the formation of rosy red coloured precipitate. The chemical reaction is,
\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{i}}^{{\rm{2 + }}}}\left( {aq} \right) + 2{\rm{dm}}{{\rm{g}}^ - } \to \left[ {{\rm{Ni(dmg}}{{\rm{)}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]{\rm{(Rosy}}\,{\rm{red}}\,{\rm{ppt}}{\rm{.}})\]
Let’s discuss the second statement which says that dimethylglyoxime is a bidentate ligand. Let’s understand what bidentate ligand. Bidentate ligands possess two donor atoms due to which bonds to the central metallic atom occur at two points. For example, ethylenediamine.
Let’s draw the structure of dimethylglyoxime.
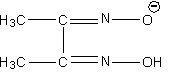
Image: Dimethylglyoxime
As we can see, dimethylglyoxime is a negative bidentate ligand. Therefore, 2nd statement is incorrect.
Hence, option (d) is right.
Note: Ligands are of different types, monodentate and polydentate. In monodentate ligand, only single donor atoms form a coordinate bond with the metal atom but in polydentate ligand, more than one atom forms bonds with the central metallic atom.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let’s discuss the given statements one by one. First statement says, nickel ions (\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{i}}^{{\rm{2 + }}}}\] ) are identified by dimethylglyoxime in the presence of ammonium hydroxide (\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{OH}}\] ). The statement is correct. Let’s understand the statement. Neutral dimethylglyoxime (dmg) dot not behave as ligand. The reaction of nickel ions with dimethylglyoxime in the basic medium of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{OH}}\], results in the formation of rosy red coloured precipitate. The chemical reaction is,
\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{i}}^{{\rm{2 + }}}}\left( {aq} \right) + 2{\rm{dm}}{{\rm{g}}^ - } \to \left[ {{\rm{Ni(dmg}}{{\rm{)}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]{\rm{(Rosy}}\,{\rm{red}}\,{\rm{ppt}}{\rm{.}})\]
Let’s discuss the second statement which says that dimethylglyoxime is a bidentate ligand. Let’s understand what bidentate ligand. Bidentate ligands possess two donor atoms due to which bonds to the central metallic atom occur at two points. For example, ethylenediamine.
Let’s draw the structure of dimethylglyoxime.

Image: Dimethylglyoxime
As we can see, dimethylglyoxime is a negative bidentate ligand. Therefore, 2nd statement is incorrect.
Hence, option (d) is right.
Note: Ligands are of different types, monodentate and polydentate. In monodentate ligand, only single donor atoms form a coordinate bond with the metal atom but in polydentate ligand, more than one atom forms bonds with the central metallic atom.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




