
For which of the following molecules is significant $\mu \ne 0$?
(A)  (B)
(B)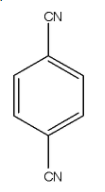 (C)
(C) 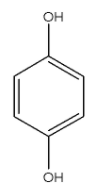 (D)
(D)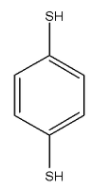
(A) Only (C)
(B) (C) and (D)
(C) Only (A)
(D) (A) and (B)
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The dipole moment can be defined as a negative or positive charge multiplied to the distance between the centres of positive and negative charges. The direction of dipole moment is always toward the more electronegative atom. The dipole moment cancels out when the direction of the dipole moment is in the opposite direction.
Complete step by step solution:
The dipole moment can be defined as a negative or positive charge multiplied to the distance between the centres of positive and negative charges. It is denoted by$\mu $. It is denoted by the arrow with its tail at the positive centre and head pointing towards the negative end:
$(+\mapsto -)$
The dipole moment is directed towards the more electronegative atom.
Let us see all the options:
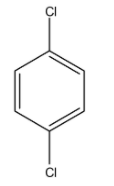
This compound is 1, 4-Dichlorobenzene. So, the chlorine is more electronegative atom than the carbon atom so the dipole moment will be towards the chlorine atom. So, both chlorines are in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be cancelled out. Hence, it will have $\mu $ will be 0.
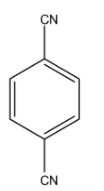
This compound is 1, 4-Dicyanobenzene. So, the carbon atom in the cyano group is more electronegative than the carbon atom of the benzene ring so the dipole moment will be towards the Cyano group. So, both Cyano is in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be cancelled out. Hence, it will have $\mu $ will be 0.
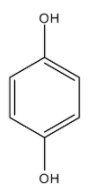
This compound is Benzene-1,4-diol. There are two conformers of this compound.

In these conformers both the groups are not in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be towards the oxygen atom but it will not cancel out each other. Hence they will have $\mu \ne 0$.
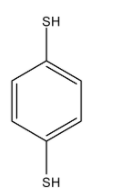
This compound is 1,4-Benzenedithiol. There are two conformers of this compound.
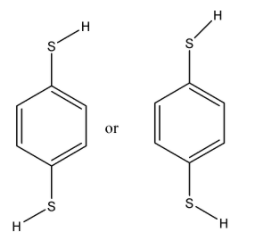
In these conformers both the groups are not in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be towards the carbon atom but it will not cancel out each other. Hence they will have $\mu \ne 0$.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (B)- (C) and (D).
Note: The determination of the dipole moment helps find the polarity of the molecule. The higher the dipole moment of the molecule, the higher is the polarity of the molecule. It can also be used in calculating the ionic character.
Complete step by step solution:
The dipole moment can be defined as a negative or positive charge multiplied to the distance between the centres of positive and negative charges. It is denoted by$\mu $. It is denoted by the arrow with its tail at the positive centre and head pointing towards the negative end:
$(+\mapsto -)$
The dipole moment is directed towards the more electronegative atom.
Let us see all the options:

This compound is 1, 4-Dichlorobenzene. So, the chlorine is more electronegative atom than the carbon atom so the dipole moment will be towards the chlorine atom. So, both chlorines are in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be cancelled out. Hence, it will have $\mu $ will be 0.

This compound is 1, 4-Dicyanobenzene. So, the carbon atom in the cyano group is more electronegative than the carbon atom of the benzene ring so the dipole moment will be towards the Cyano group. So, both Cyano is in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be cancelled out. Hence, it will have $\mu $ will be 0.

This compound is Benzene-1,4-diol. There are two conformers of this compound.

In these conformers both the groups are not in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be towards the oxygen atom but it will not cancel out each other. Hence they will have $\mu \ne 0$.

This compound is 1,4-Benzenedithiol. There are two conformers of this compound.

In these conformers both the groups are not in the opposite direction and the dipole moment will be towards the carbon atom but it will not cancel out each other. Hence they will have $\mu \ne 0$.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (B)- (C) and (D).
Note: The determination of the dipole moment helps find the polarity of the molecule. The higher the dipole moment of the molecule, the higher is the polarity of the molecule. It can also be used in calculating the ionic character.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




