
Fire is caught at the height of 125m from the fire brigade. To extinguish the fire, water is coming from the pipe of cross-section 6.4 cm with a rate of 950 litres/min. Find out the minimum velocity of water exiting from fire brigade tank ($g = 10 m/{s^2}$)
A) 5 m/s
B) 10 m/s
C) 25 m/s
D) 50 m/s
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this problem we need to first understand the concept of the volumetric flow rate of a fluid. The volume of fluid flowing per unit time through a particular section is now as volumetric flow rate. Volumetric flow rate is measured in m3/min or litres/min.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the problem that the diameter of the pipe through which the water is coming out is 6.4 cm, i.e. after conversion of the unit into meters we have, $d = 0.064m$
Also, the volumetric flow rate of water (Q) is given to be 950 litres/min,
i.e. $Q = 950l/\min = \dfrac{{950 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{60}}{m^3}/s$
$\Rightarrow Q = \dfrac{{95 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{6}{m^3}/s$
The volumetric flow rate of the water can be calculated by taking the product of the cross-sectional area of the pipe and the velocity of water in a direction perpendicular to this cross-section, as shown in the following figure.
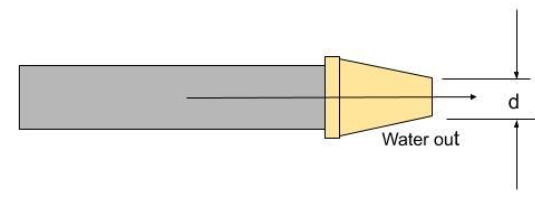
Therefore the volumetric flow rate is given by, $Q = A \times V$
Using the above equation the velocity of water is given by,
$V = \dfrac{Q}{A}$ ......... (1)
The cross-sectional area of the pipe is given by, $A = \dfrac{\pi }{4}{d^2} = \dfrac{\pi }{4}{0.064^2}$
Putting the values of area and discharge in equation (1) we get,
$V = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{95 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{6}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}{{0.064}^2}} \right)}}$
$\therefore V = 4.921m/s \approx 5m/s$
As the velocity of the fluid comes out to be 5 m/s, we can say that option (A) is the correct answer option.
Note: It is very important to use the term volumetric flow rate because just saying flow rate can create confusion. Flow rate can either be mass flow rate or volumetric flow rate. The mass flow rate is measured in kg/s. For kinematics of fluids (velocity and acceleration calculations), we use a volumetric flow rate.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the problem that the diameter of the pipe through which the water is coming out is 6.4 cm, i.e. after conversion of the unit into meters we have, $d = 0.064m$
Also, the volumetric flow rate of water (Q) is given to be 950 litres/min,
i.e. $Q = 950l/\min = \dfrac{{950 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{60}}{m^3}/s$
$\Rightarrow Q = \dfrac{{95 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{6}{m^3}/s$
The volumetric flow rate of the water can be calculated by taking the product of the cross-sectional area of the pipe and the velocity of water in a direction perpendicular to this cross-section, as shown in the following figure.

Therefore the volumetric flow rate is given by, $Q = A \times V$
Using the above equation the velocity of water is given by,
$V = \dfrac{Q}{A}$ ......... (1)
The cross-sectional area of the pipe is given by, $A = \dfrac{\pi }{4}{d^2} = \dfrac{\pi }{4}{0.064^2}$
Putting the values of area and discharge in equation (1) we get,
$V = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{95 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{6}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}{{0.064}^2}} \right)}}$
$\therefore V = 4.921m/s \approx 5m/s$
As the velocity of the fluid comes out to be 5 m/s, we can say that option (A) is the correct answer option.
Note: It is very important to use the term volumetric flow rate because just saying flow rate can create confusion. Flow rate can either be mass flow rate or volumetric flow rate. The mass flow rate is measured in kg/s. For kinematics of fluids (velocity and acceleration calculations), we use a volumetric flow rate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




