
Find out the arrow or arrows which gives the direction of conventional current flow.
A) Arrow A only
B) Arrow B only
C) Arrow C only
D) Arrows A and D
E) Arrows B and E
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that generally, electrons flow from the negative end or terminal to a positive end or terminal. The definition of conventional current can be said as charge per unit time transported in a certain direction. The flow of conventional current is from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. The behaviour is like positive charge carriers will cause the current to flow. It can be assumed as a flow of protons in the opposite direction instead of flow of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
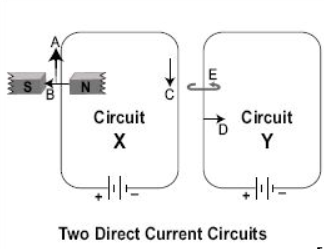
Arrow A shows the direction of magnetic force experienced by a current-carrying wire in a perpendicular magnetic field and Fleming's left-hand rule gives it.
Arrow B shows the direction of the magnetic field, from the north pole to south pole.
Arrow C shows the direction of conventional current from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery.
Arrow D shows the direction of repulsion force exerted by wire in circuit X to the wire of Y because the direction of current in both parallel wires is opposite.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Additional Information: Faraday’s law of EMI “electromagnetic induction”, is also called the law of electromagnetism. This law explains the operational principle of electric generators, electric inductors, electrical transformers, and electric motors. It helps in understanding important points that leads to the electromagnetic induction or production of electricity. Faraday’s law is conducted to see the way magnetic fields change due to the flow of current in wires.
Note: We all know that current is the flow of charges. The main difference between the conventional current and electric current is the direction of flow of charges changes. In the conventional current, it is from positive to negative terminal, whereas it is negative to the positive terminal in electric current.
Complete step by step answer:
Arrow A shows the direction of magnetic force experienced by a current-carrying wire in a perpendicular magnetic field and Fleming's left-hand rule gives it.
Arrow B shows the direction of the magnetic field, from the north pole to south pole.
Arrow C shows the direction of conventional current from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery.
Arrow D shows the direction of repulsion force exerted by wire in circuit X to the wire of Y because the direction of current in both parallel wires is opposite.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Additional Information: Faraday’s law of EMI “electromagnetic induction”, is also called the law of electromagnetism. This law explains the operational principle of electric generators, electric inductors, electrical transformers, and electric motors. It helps in understanding important points that leads to the electromagnetic induction or production of electricity. Faraday’s law is conducted to see the way magnetic fields change due to the flow of current in wires.
Note: We all know that current is the flow of charges. The main difference between the conventional current and electric current is the direction of flow of charges changes. In the conventional current, it is from positive to negative terminal, whereas it is negative to the positive terminal in electric current.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




