
How is ethylamine prepared from methyl iodide?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept preparation of amines from haloalkanes. A primary amine is formed when alkyl halide reacts with ammonia. This can be used further to produce other substituted amines.
Complete Step by step solution:
Ethylamine is a colourless/light yellow liquid with a strong ammonia-like odour and is used in the preparation of various pharmaceutical products. It condenses just below the room temperature to a liquid miscible with mostly all solvents. It acts as a nucleophilic base. Let us discuss the easiest procedure to form ethylamine from methyl iodide
1.Methyl iodide is treated with \[NaCN\] to form acetonitrile
\[C{H_3} - I + NaCN \to C{H_3} - CN + NaI\]
This is an example of $S{N^2}$ a reaction
-$S{N^2}$ reactions are bimolecular reactions in which there are simultaneous bond-making and bond-breaking steps.
-$S{N^2}$ reactions do not proceed via an intermediate.
-$S{N^2}$ reactions result in inverted stereochemistry at the reaction centre.
-Steric effects are particularly important in $S{N^2}$reactions.
2.Acetonitrile is reduced with Na/ ethanol to form ethylamine. This reaction is called Mendius reduction
\[C{H_3} - CN \to C{H_3} - C{H_2} - N{H_2}\](in presence of Na/Ethanol)
Additional Note: Ethylamine can also be synthesised from the reaction of ethane and ammonia in the presence of a basic catalyst. Ethylamine is a weak base and undergoes reactions like acetylation and protonation. It can also be oxidised to form acetaldehyde.
Note: Another way of preparing ethyl amine prepared from methyl iodide is by using cyanohydrin reduction. Methyl iodide first is converted into methyl chloride using the ion-exchange method: \[C{H_3}I{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}NaCl{\text{ }} \to C{H_3}Cl\; + {\text{ }}NaI\].
Now the second reaction can be performed:
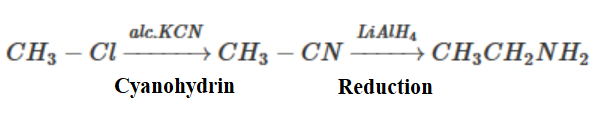
Complete Step by step solution:
Ethylamine is a colourless/light yellow liquid with a strong ammonia-like odour and is used in the preparation of various pharmaceutical products. It condenses just below the room temperature to a liquid miscible with mostly all solvents. It acts as a nucleophilic base. Let us discuss the easiest procedure to form ethylamine from methyl iodide
1.Methyl iodide is treated with \[NaCN\] to form acetonitrile
\[C{H_3} - I + NaCN \to C{H_3} - CN + NaI\]
This is an example of $S{N^2}$ a reaction
-$S{N^2}$ reactions are bimolecular reactions in which there are simultaneous bond-making and bond-breaking steps.
-$S{N^2}$ reactions do not proceed via an intermediate.
-$S{N^2}$ reactions result in inverted stereochemistry at the reaction centre.
-Steric effects are particularly important in $S{N^2}$reactions.
2.Acetonitrile is reduced with Na/ ethanol to form ethylamine. This reaction is called Mendius reduction
\[C{H_3} - CN \to C{H_3} - C{H_2} - N{H_2}\](in presence of Na/Ethanol)
Additional Note: Ethylamine can also be synthesised from the reaction of ethane and ammonia in the presence of a basic catalyst. Ethylamine is a weak base and undergoes reactions like acetylation and protonation. It can also be oxidised to form acetaldehyde.
Note: Another way of preparing ethyl amine prepared from methyl iodide is by using cyanohydrin reduction. Methyl iodide first is converted into methyl chloride using the ion-exchange method: \[C{H_3}I{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}NaCl{\text{ }} \to C{H_3}Cl\; + {\text{ }}NaI\].
Now the second reaction can be performed:
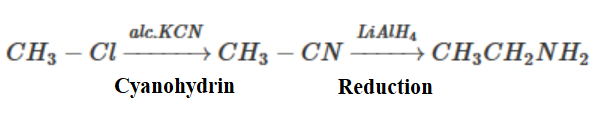
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




