
Equation of a straight line on which length of the perpendicular from the origin is $4$ units and the line makes an angle of \[{120^ \circ }\] with the x-axis, is
(A) $x\sqrt 3 + y + 8 = 0$
(B) $x\sqrt 3 + y = 8$
(C) $x\sqrt 3 - y = 8$
(D) $x - \sqrt 3 y + 8 = 0$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, first we will make the appropriate figure according to the question. Then, we will find the required angles using the linear pair property and angle sum property of the triangle. Now, to get the required equation of a line, we will use the above values obtained in the general equation of a line.
Complete step by step Solution:
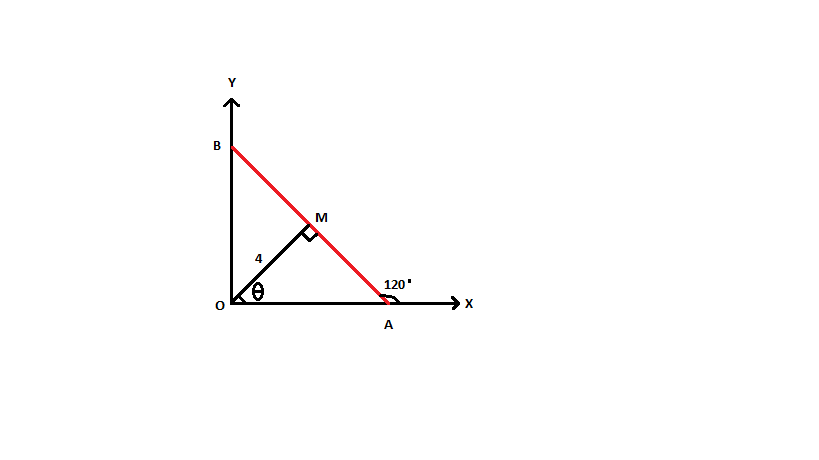
Given,
\[\angle MAX = {120^ \circ }\] ………………..equation $\left( 1 \right)$
First, we will find $\angle MAO,$
$\angle MAO + \angle MAX = {180^ \circ }$ $[\because $ Linear Pair$]$
Put the value of \[\angle MAX\] and solve it,
\[\angle MAO + {120^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\] $[\because $ Using equation $\left( 1 \right)]$
\[\angle MAO = {180^ \circ } - {120^ \circ }\]
\[\angle MAO = {60^ \circ }\] ………………..equation $\left( 2 \right)$
Now, let us find $\theta ,$
In $\vartriangle MOA,$
$\angle MOA + \angle MAO + \angle OMA = {180^ \circ }$ $[\because $ Angle Sum Property of Triangle$]$
\[\theta + {60^ \circ } + {90^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\] $[\because $ Using given an equation $\left( 2 \right)]$
Solving it further,
$\theta = {30^ \circ }$ ………………..equation $\left( 3 \right)$
Now, let us find the required equation of the line,
$x\;\cos \theta + y\;\sin \theta = p$
Substituting values from equation $\left( 3 \right)$
$x\;\cos {30^ \circ } + y\;\sin {30^ \circ } = 4$ $\left[ {\because p = OM = 4} \right]$
$x\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) + y\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 4$
Simplifying it further,
$x\sqrt 3 + y + 8 = 0$
This is the required equation of a line.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:The key concept to solve this type of question is to have a basic knowledge of properties (Angle sum property of triangle, Linear pair property) learned in previous classes. The figure should be made with proper attention and labeled correctly. The value of trigonometric angles should be known.
Complete step by step Solution:

Given,
\[\angle MAX = {120^ \circ }\] ………………..equation $\left( 1 \right)$
First, we will find $\angle MAO,$
$\angle MAO + \angle MAX = {180^ \circ }$ $[\because $ Linear Pair$]$
Put the value of \[\angle MAX\] and solve it,
\[\angle MAO + {120^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\] $[\because $ Using equation $\left( 1 \right)]$
\[\angle MAO = {180^ \circ } - {120^ \circ }\]
\[\angle MAO = {60^ \circ }\] ………………..equation $\left( 2 \right)$
Now, let us find $\theta ,$
In $\vartriangle MOA,$
$\angle MOA + \angle MAO + \angle OMA = {180^ \circ }$ $[\because $ Angle Sum Property of Triangle$]$
\[\theta + {60^ \circ } + {90^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\] $[\because $ Using given an equation $\left( 2 \right)]$
Solving it further,
$\theta = {30^ \circ }$ ………………..equation $\left( 3 \right)$
Now, let us find the required equation of the line,
$x\;\cos \theta + y\;\sin \theta = p$
Substituting values from equation $\left( 3 \right)$
$x\;\cos {30^ \circ } + y\;\sin {30^ \circ } = 4$ $\left[ {\because p = OM = 4} \right]$
$x\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) + y\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 4$
Simplifying it further,
$x\sqrt 3 + y + 8 = 0$
This is the required equation of a line.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:The key concept to solve this type of question is to have a basic knowledge of properties (Angle sum property of triangle, Linear pair property) learned in previous classes. The figure should be made with proper attention and labeled correctly. The value of trigonometric angles should be known.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




