
What is the dimensional formula of the moment of force?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The Moment of a force is a measure of its tendency to cause a body to rotate about a specific point or axis.
The expressions or formulae which tell us how and which of the fundamental quantities are present in a physical quantity are known as the Dimensional Formula of the Physical Quantity.
Theory:
Suppose there is a physical quantity X which depends on base dimensions M (Mass), L (Length), and T (Time) with respective powers a, b and c, then its dimensional formula is represented as: \[\left[ {{M^a}{L^b}{T^c}} \right]\]
Dimensional formula for basic physical quantities,
Mass = $\left[ M \right]$
Distance = \[\left[ L \right]\]
Time =$\left[ T \right]$
Complete solution:
Consider a freely rotating body It rotates about its center.
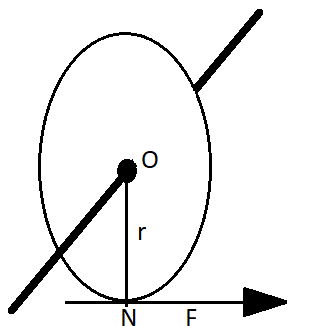
Now when force f is applied the body will start rotating about the fixed point, as long as the line of action of the force passes through O which is a fixed point. This rotating tendency or the turning effect of the force about that point is called the moment of force. We can also say that the moment of the force is the product of the magnitude of the force and the perpendicular distance of the line of action of the force from the axis of rotation.
Moment of a force about point O $ = \left( {F \times ON} \right)$
Here $\left( {ON} \right)$is the radius of the rotating body
Now calculation of dimensional formula of force
Velocity: It is the distance covered per unit time so $v = \left( {\dfrac{d}{t}} \right)$
From here we can say that is the ratio of distance and times so the dimensional formula will be
$\dfrac{L}{T}$ (Or) $\left[ {L{T^{ - 1}}} \right]$
Acceleration = it is the rate of change of velocity with time so,
We can say that $a = \dfrac{v}{t}$
Here velocity is divided by time again we will substitute the dimensional formulas of velocity band time to get the dimensional formula for acceleration
\[
\therefore a = \left[ {\dfrac{{L{T^{ - 1}}}}{T}} \right] \\
\to a = \left[ {L{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \\
\]
Force: It is defined as the mass time of acceleration so,
$F = M \times A$
Now we will be using the dimensional formula of acceleration and mass to find out the dimensional formula of force
$\because F = M \times A$
The dimensional formula of force will also be the product of the dimensional formula of the other two quantities
So,
$
\Rightarrow F = M \times L{T^{ - 2}} \\
\Rightarrow F = \left[ {ML{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \\
$
Now as $\left( {ON} \right)$is the radius of the disk so its dimension will be of a length so,
$r = \left[ {{M^0}{L^1}{T^0}} \right]$
AS Moment of Force = \[F \times r\]
$\therefore $ the dimensional formula for the moment of force will be
$
\Rightarrow \left[ {ML{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \times \left[ {{M^0}{L^1}{T^0}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow \left[ {{M^1}{L^2}{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \\
$
The dimensional formula for the moment of force is $\left[ {{M^1}{L^2}{T^{ - 2}}} \right].$
Note: Dimensional formula of any quantity can be derived for the fundamental quantities if the relation between them is known. Dimensional Formulas are used to check whether a given formula is dimensionally correct or not. Dimensional Formulae become not defined in the case of the trigonometric, logarithmic, and exponential functions as they are not physical quantities.
The expressions or formulae which tell us how and which of the fundamental quantities are present in a physical quantity are known as the Dimensional Formula of the Physical Quantity.
Theory:
Suppose there is a physical quantity X which depends on base dimensions M (Mass), L (Length), and T (Time) with respective powers a, b and c, then its dimensional formula is represented as: \[\left[ {{M^a}{L^b}{T^c}} \right]\]
Dimensional formula for basic physical quantities,
Mass = $\left[ M \right]$
Distance = \[\left[ L \right]\]
Time =$\left[ T \right]$
Complete solution:
Consider a freely rotating body It rotates about its center.

Now when force f is applied the body will start rotating about the fixed point, as long as the line of action of the force passes through O which is a fixed point. This rotating tendency or the turning effect of the force about that point is called the moment of force. We can also say that the moment of the force is the product of the magnitude of the force and the perpendicular distance of the line of action of the force from the axis of rotation.
Moment of a force about point O $ = \left( {F \times ON} \right)$
Here $\left( {ON} \right)$is the radius of the rotating body
Now calculation of dimensional formula of force
Velocity: It is the distance covered per unit time so $v = \left( {\dfrac{d}{t}} \right)$
From here we can say that is the ratio of distance and times so the dimensional formula will be
$\dfrac{L}{T}$ (Or) $\left[ {L{T^{ - 1}}} \right]$
Acceleration = it is the rate of change of velocity with time so,
We can say that $a = \dfrac{v}{t}$
Here velocity is divided by time again we will substitute the dimensional formulas of velocity band time to get the dimensional formula for acceleration
\[
\therefore a = \left[ {\dfrac{{L{T^{ - 1}}}}{T}} \right] \\
\to a = \left[ {L{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \\
\]
Force: It is defined as the mass time of acceleration so,
$F = M \times A$
Now we will be using the dimensional formula of acceleration and mass to find out the dimensional formula of force
$\because F = M \times A$
The dimensional formula of force will also be the product of the dimensional formula of the other two quantities
So,
$
\Rightarrow F = M \times L{T^{ - 2}} \\
\Rightarrow F = \left[ {ML{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \\
$
Now as $\left( {ON} \right)$is the radius of the disk so its dimension will be of a length so,
$r = \left[ {{M^0}{L^1}{T^0}} \right]$
AS Moment of Force = \[F \times r\]
$\therefore $ the dimensional formula for the moment of force will be
$
\Rightarrow \left[ {ML{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \times \left[ {{M^0}{L^1}{T^0}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow \left[ {{M^1}{L^2}{T^{ - 2}}} \right] \\
$
The dimensional formula for the moment of force is $\left[ {{M^1}{L^2}{T^{ - 2}}} \right].$
Note: Dimensional formula of any quantity can be derived for the fundamental quantities if the relation between them is known. Dimensional Formulas are used to check whether a given formula is dimensionally correct or not. Dimensional Formulae become not defined in the case of the trigonometric, logarithmic, and exponential functions as they are not physical quantities.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




