
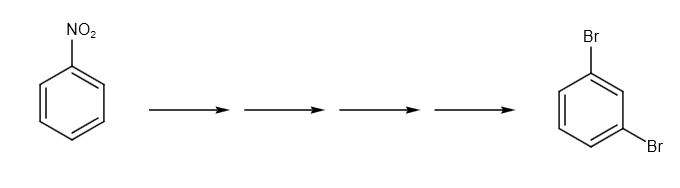
What is the correct sequence of reagent used for converting nitrobenzene into m-dinitrobenzene?
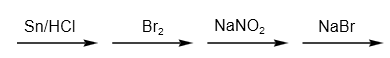
A.
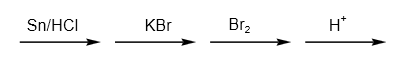
B.
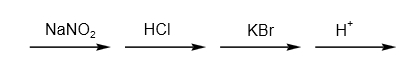
C.
D.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The aromatic chemical known as nitrobenzene contains a nitro group inside of a benzene ring. The Nitro group is meta-directing. Hence, any forward reaction will be taking place at the meta position of the ring.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
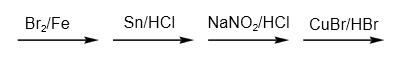
Firstly, we have to do bromination of the nitrobenzene. The reagent used for the reaction is \[B{r_2}/Fe\] reagent. Here, electrophilic substitution takes place. The reaction is as follows:
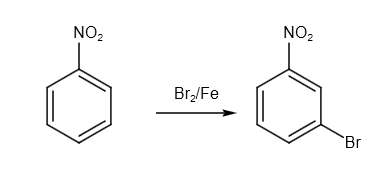
Image: Bromination of nitrobenzene
After that, we have to convert \[N{O_2}\] group to \[N{H_2}\] group. So, we can use \[Sn/HCl\] reagent. Tin (IV) chloride is created when tin interacts with HCl. Consequently, we may state that \[{H^ + }\] ions are released as a result of the aromatic compound's nitro functional group reaction. The reaction is as follows:
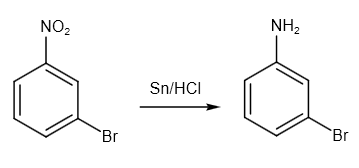
Image: Reduction by tin and HCl reagent
After that, we have to convert it into diazonium salt. The compound reacts with sodium nitrite and HCl in cold conditions to form diazonium salt. The reaction is as follows:
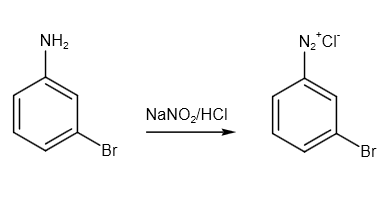
Image: Formation of diazonium salt
Finally, we have to use the Sandmeyer reaction to get the desired product dibromo benzene. A common substitution reaction is the Sandmeyer reaction, which is used to produce aryl halides from aryl diazonium ions. Catalysts for this process include copper salts like chloride, bromide, or iodide ions. The reaction is as follows:
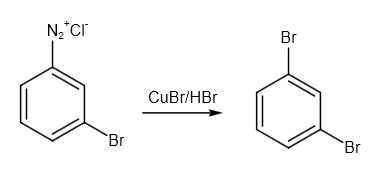
Image: Sandmeyer reaction
The complete reaction is written as follows:
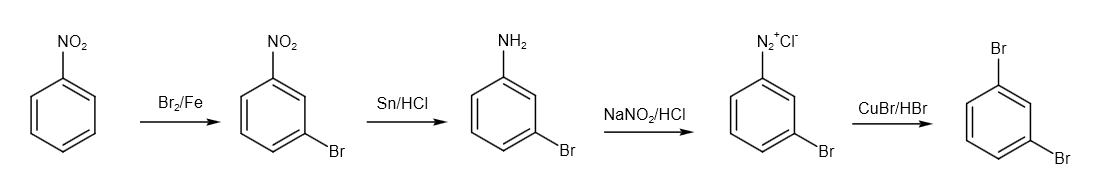
Image: Conversion of m-dinitrobenzene to dibromobenzene
As a result, the correct order of reagents used is option D.
Note: The two-step mechanism reaction is the Sandmeyer reaction. The free radical mechanism is used in the Sandmeyer reaction. The halogen linked to the copper enters the benzene ring during this process.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Firstly, we have to do bromination of the nitrobenzene. The reagent used for the reaction is \[B{r_2}/Fe\] reagent. Here, electrophilic substitution takes place. The reaction is as follows:

Image: Bromination of nitrobenzene
After that, we have to convert \[N{O_2}\] group to \[N{H_2}\] group. So, we can use \[Sn/HCl\] reagent. Tin (IV) chloride is created when tin interacts with HCl. Consequently, we may state that \[{H^ + }\] ions are released as a result of the aromatic compound's nitro functional group reaction. The reaction is as follows:

Image: Reduction by tin and HCl reagent
After that, we have to convert it into diazonium salt. The compound reacts with sodium nitrite and HCl in cold conditions to form diazonium salt. The reaction is as follows:

Image: Formation of diazonium salt
Finally, we have to use the Sandmeyer reaction to get the desired product dibromo benzene. A common substitution reaction is the Sandmeyer reaction, which is used to produce aryl halides from aryl diazonium ions. Catalysts for this process include copper salts like chloride, bromide, or iodide ions. The reaction is as follows:

Image: Sandmeyer reaction
The complete reaction is written as follows:

Image: Conversion of m-dinitrobenzene to dibromobenzene
As a result, the correct order of reagents used is option D.
Note: The two-step mechanism reaction is the Sandmeyer reaction. The free radical mechanism is used in the Sandmeyer reaction. The halogen linked to the copper enters the benzene ring during this process.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




