
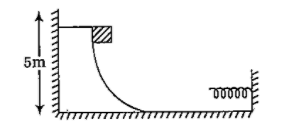
Consider the situation shown in the figure. A spring of spring constant \[400{\text{ }}Nm\]is attached at one end to a wedge fixed rigidly with the horizontal part. A \[40g\] mass is released from rest while situated at a height 5cm the curved track. The maximum deformation in the spring is nearly equal to (take \[g = 10m/{s^2}\]
(A) $9.8m$
(B) \[9.8cm\]
(C) $0.98m$
(D) $0.009km $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint In this situation energy from one form is converted into another form hence we can use the conservation of energy theorem with the given values to calculate the spring deformation
Formula Used:
\[{K_i} + {P_i} = {K_f} + {P_f}\]
Complete step by step answer
Since the block is released then initial velocity,$u = 0$and it will follow the curved path and compress the spring till the final velocity of block will be zero after that the spring will regain its position and the block will be thrown back.
Since it is a friction less path, no external force exists. Only conservative forces are present hence you can say that the mechanical energy is conserved between the point of drop till the point of maximum compression of spring.
\[{K_i} + {P_i} = {K_f} + {P_f}\] , where $K_i$ and $K_f$ are the initial and final kinetic energy ---(1)
And $P_i$ and $P_f$ are the initial and final potential energy
We know that potential energy at a height ‘h’ of mass ‘m’ is given by \[mgh\]where g is the acceleration due to gravity and the potential energy stored in the spring is $\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$ where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement.
\[{K_i} = 0\]and\[{K_f} = 0\]as the initial and final velocities are zero
As you can see that the final potential of block is also zero since its final velocity is zero, but the elastic potential energy will be acting thus
Substituting these in equation (1),
\[0 + mgh = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} \Rightarrow x = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2mgh}}{k}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 0.04 \times 10 \times 5}}{{400}}} = \dfrac{1}{{10}}m = 10cm \cong 9.8cm\]
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note
If a string is compressed or stretched then we see that work is done due to spring elasticity, this work done is stored in the spring in the form of elastic potential energy.
Formula Used:
\[{K_i} + {P_i} = {K_f} + {P_f}\]
Complete step by step answer
Since the block is released then initial velocity,$u = 0$and it will follow the curved path and compress the spring till the final velocity of block will be zero after that the spring will regain its position and the block will be thrown back.
Since it is a friction less path, no external force exists. Only conservative forces are present hence you can say that the mechanical energy is conserved between the point of drop till the point of maximum compression of spring.
\[{K_i} + {P_i} = {K_f} + {P_f}\] , where $K_i$ and $K_f$ are the initial and final kinetic energy ---(1)
And $P_i$ and $P_f$ are the initial and final potential energy
We know that potential energy at a height ‘h’ of mass ‘m’ is given by \[mgh\]where g is the acceleration due to gravity and the potential energy stored in the spring is $\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$ where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement.
\[{K_i} = 0\]and\[{K_f} = 0\]as the initial and final velocities are zero
As you can see that the final potential of block is also zero since its final velocity is zero, but the elastic potential energy will be acting thus
Substituting these in equation (1),
\[0 + mgh = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} \Rightarrow x = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2mgh}}{k}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 0.04 \times 10 \times 5}}{{400}}} = \dfrac{1}{{10}}m = 10cm \cong 9.8cm\]
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note
If a string is compressed or stretched then we see that work is done due to spring elasticity, this work done is stored in the spring in the form of elastic potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




