
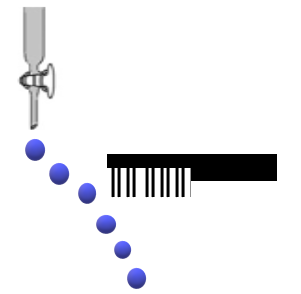
Consider the following compounds in the liquid form: \[{O_2},\,HF,\,{H_2}O,\,N{H_3},\,{H_2}{O_2},\,CC{l_4},\,CHC{l_3},\,{C_6}{H_6},\,{C_6}{H_5}Cl\]. When a charged comb is brought near their flowing stream, how many of them show deflection as per the following figure?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Electronegativity affects the molecules' polarity and nonpolarity. The more electronegative an atom is, it searches for electrons more actively. The concept of electronegativity is at play in the solution.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The list of substances in the question is provided by:
\[{O_2},\,HF,\,{H_2}O,\,N{H_3},\,{H_2}{O_2},\,CC{l_4},\,CHC{l_3},\,{C_6}{H_6},\,{C_6}{H_5}Cl\]
The polar liquid is the only substance that is affected by a comb's charging because it contains molecules that have a dipole moment or an uneven charge distribution. Because most of the molecule's electrons are clustered around the oxygen molecules, a water molecule, for instance, has a substantial concentration of negative charge on its oxygen atoms.
The charge in the comb attracts a positive charge and repels a negative charge. Since each molecule in nonpolar liquids has an equal distribution of positive and negative charges, the ensuing attracting and repelling forces balance one another. Due to the unbalanced attractive and repulsive forces in polar liquids, which result from the uneven charge distribution in the liquid's molecules, the liquid will deflect when it comes into contact with an electric field.
\[\therefore \] Polarity of the molecules are: \[HF,\,{H_2}O,\,N{H_3},\,{H_2}{O_2},\,CHC{l_3},\,{C_6}{H_5}Cl\]
And, the non-polarity of the molecules are: \[{O_2},\,CC{l_4},\,{C_6}{H_6}\]
Thus, when a charged comb is brought near their flowing stream, six compounds will show deflection as per the figure.
Note: It should be noted that the polarity of water molecules is frequently demonstrated by the way an electric charge deflects a stream of water. As we all know, unless the charged rod is sufficiently close to the point where the stream becomes discontinuous, no deflection happens if the water turns into a stream of individual drops. Even though mercury atoms are non-polar, a charged comb would deflect a continuous stream of mercury. A charged comb does not deflect a flow of non-polar molecules.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The list of substances in the question is provided by:
\[{O_2},\,HF,\,{H_2}O,\,N{H_3},\,{H_2}{O_2},\,CC{l_4},\,CHC{l_3},\,{C_6}{H_6},\,{C_6}{H_5}Cl\]
The polar liquid is the only substance that is affected by a comb's charging because it contains molecules that have a dipole moment or an uneven charge distribution. Because most of the molecule's electrons are clustered around the oxygen molecules, a water molecule, for instance, has a substantial concentration of negative charge on its oxygen atoms.
The charge in the comb attracts a positive charge and repels a negative charge. Since each molecule in nonpolar liquids has an equal distribution of positive and negative charges, the ensuing attracting and repelling forces balance one another. Due to the unbalanced attractive and repulsive forces in polar liquids, which result from the uneven charge distribution in the liquid's molecules, the liquid will deflect when it comes into contact with an electric field.
\[\therefore \] Polarity of the molecules are: \[HF,\,{H_2}O,\,N{H_3},\,{H_2}{O_2},\,CHC{l_3},\,{C_6}{H_5}Cl\]
And, the non-polarity of the molecules are: \[{O_2},\,CC{l_4},\,{C_6}{H_6}\]
Thus, when a charged comb is brought near their flowing stream, six compounds will show deflection as per the figure.
Note: It should be noted that the polarity of water molecules is frequently demonstrated by the way an electric charge deflects a stream of water. As we all know, unless the charged rod is sufficiently close to the point where the stream becomes discontinuous, no deflection happens if the water turns into a stream of individual drops. Even though mercury atoms are non-polar, a charged comb would deflect a continuous stream of mercury. A charged comb does not deflect a flow of non-polar molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




