
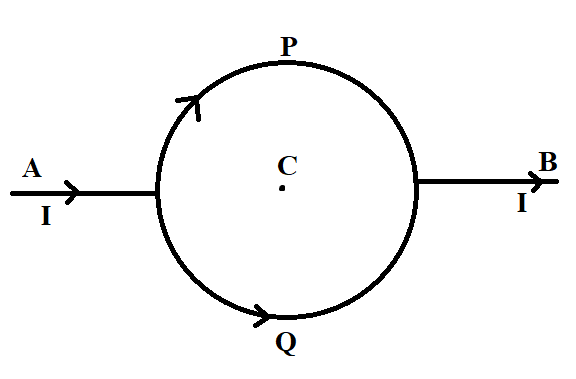
Consider the circuit shown where APB and AQB are semi-circles. What will be the magnetic field at the centre C of the loop?
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: C is the centre of the circle formed by joining the two semicircles APB and AQB. Since the two semicircles are equal and opposite the magnitude will be the same. But the direction will be opposite. The semicircles are said to have the same radius. Therefore it will have the same magnetic moment. We have to consider the direction of the magnetic field also.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that C is the centre of the circular loop formed by joining the two semi-circles APB and AQB. This means that the two semicircles have the same radius and length.
From the figure, we can see that the current flows in the opposite direction. In ABP the current flows in the clockwise direction, while current flows in the anticlockwise direction in AQB.
Since both semi-circles have the same radius and the same current is flowing through both semicircles, the magnitude of the magnetic field due to these two current elements at the centre C will be equal.But as the direction of current flow is opposite in direction, the magnetic field will also be opposite in direction.
Since the magnetic field at the centre of the circle is equal and opposite, the net effective magnetic field will be zero at the centre.
Note:The direction of the magnetic field can be given by Maxwell’s corkscrew rule. If a right-handed corkscrew is rotated so that the tip of the screw advances in the direction of the current, then the direction of rotation of the screw head gives the direction of the magnetic field.
Another method to find the direction of the magnetic field is the Right-hand grip rule. If a conductor is held in the right hand such that the thumb is in the direction of the current, then the direction of curled fingers will point the direction of the magnetic field.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that C is the centre of the circular loop formed by joining the two semi-circles APB and AQB. This means that the two semicircles have the same radius and length.
From the figure, we can see that the current flows in the opposite direction. In ABP the current flows in the clockwise direction, while current flows in the anticlockwise direction in AQB.
Since both semi-circles have the same radius and the same current is flowing through both semicircles, the magnitude of the magnetic field due to these two current elements at the centre C will be equal.But as the direction of current flow is opposite in direction, the magnetic field will also be opposite in direction.
Since the magnetic field at the centre of the circle is equal and opposite, the net effective magnetic field will be zero at the centre.
Note:The direction of the magnetic field can be given by Maxwell’s corkscrew rule. If a right-handed corkscrew is rotated so that the tip of the screw advances in the direction of the current, then the direction of rotation of the screw head gives the direction of the magnetic field.
Another method to find the direction of the magnetic field is the Right-hand grip rule. If a conductor is held in the right hand such that the thumb is in the direction of the current, then the direction of curled fingers will point the direction of the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




