
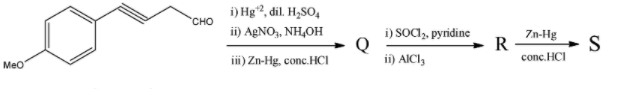
Choose the correct options for the following reaction sequence. Consider Q, R, and S to be major products.
(A) 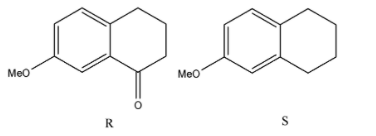
(B) 
(C) 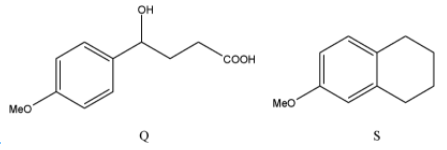
(D) 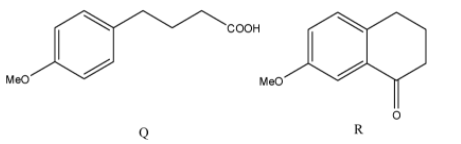
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Analyze the reactions of the reactants with each of the reagents separately. Think about what parts of the molecule will change after the reaction and which ones will not be affected. Almost all the reactions given in this question are name reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
To find the answer to this question, we will look at each of the reagents mentioned separately and then determine which molecule we will get as a product. According to this method, we will look at 3 reactions to obtain Q, 2 reactions to obtain R, and 1 reaction to obtain S.
- For Q
Here, we have three different reagents, we will look at each of the reagents and then determine the major product of the reaction.
i) $H{{g}^{2+}},dil.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
This reagent is mainly used to convert an alkyne into a ketone or in general, to convert a triple bond into a ketonic group. This reaction is called the Kucherov’s reaction and follows Markovnikov's rule. For the molecule given in the question, the reaction will be as follows:

ii) $AgN{{O}_{3}},N{{H}_{4}}OH$
We know that this is the Tollen’s reagent that is used to perform the silver mirror test that shows the presence of an aldehydic group in any molecule. The Tollen’s reagent is an oxidizing agent that oxidizes the aldehydic group to a carboxylic acid group. But it is not a strong enough oxidizing agent to oxidize a ketone so that group will remain unchanged. The reaction will continue as follows:
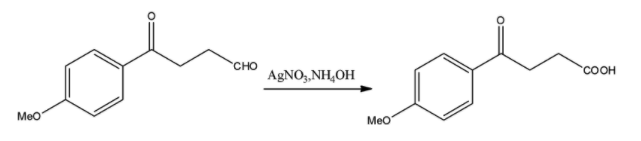
iii) $Zn-Hg,conc.HCl$
This reagent is used in the Clemmensen reduction reaction. In this reduction, any of the aldehyde or ketone groups present in the molecule are reduced to their corresponding alkyl groups. It does not have the capability to reduce a carboxylic acid group. The reaction will continue as follows:

Thus, we have the structure of Q. Similarly, we will find the structures of R and S.
- For R
Here, we have two different reagents, we will look at each of the reagents and then determine the major product of the reaction.
i) $SOC{{l}_{2}},pyridine$
This reagent is commonly used for Darzan's process. In this process, the chlorination of the acid group occurs, the $-OH$ group in the acid is replaced by the $-Cl$ group and no other changes occur. The reaction will continue as follows:
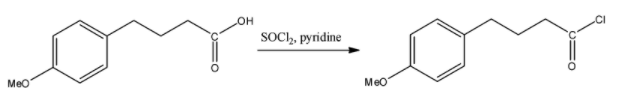
Here we have obtained the molecule that will replace the variable R in the reaction.
- For S
i) $Zn-Hg,conc.HCl$
This has only one reagent and even that is repeated. We saw this reagent when we were finding Q as the third reagent. This reagent is used for the Clemmensen reduction reaction and converts aldehydes and ketones to alkanes. Here, the sole ketonic group will be converted to an alkyl group. The reaction will be as follows:
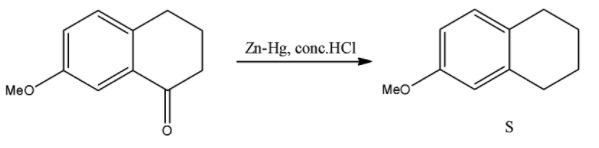
So now, looking at all the reactions and the structures of the molecules that we obtained for Q, R, and S.
The correct answers to this question are option A and option D.
Note: Remember that in the very first reaction that includes the Markovnikov’s rule some product that has the ketonic group at the other end of the triple bond will also be formed but we are only considering major products. Even if we do consider the minor product, we will eventually get the same structures for Q, R, and S.
Complete step by step solution:
To find the answer to this question, we will look at each of the reagents mentioned separately and then determine which molecule we will get as a product. According to this method, we will look at 3 reactions to obtain Q, 2 reactions to obtain R, and 1 reaction to obtain S.
- For Q
Here, we have three different reagents, we will look at each of the reagents and then determine the major product of the reaction.
i) $H{{g}^{2+}},dil.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
This reagent is mainly used to convert an alkyne into a ketone or in general, to convert a triple bond into a ketonic group. This reaction is called the Kucherov’s reaction and follows Markovnikov's rule. For the molecule given in the question, the reaction will be as follows:

ii) $AgN{{O}_{3}},N{{H}_{4}}OH$
We know that this is the Tollen’s reagent that is used to perform the silver mirror test that shows the presence of an aldehydic group in any molecule. The Tollen’s reagent is an oxidizing agent that oxidizes the aldehydic group to a carboxylic acid group. But it is not a strong enough oxidizing agent to oxidize a ketone so that group will remain unchanged. The reaction will continue as follows:

iii) $Zn-Hg,conc.HCl$
This reagent is used in the Clemmensen reduction reaction. In this reduction, any of the aldehyde or ketone groups present in the molecule are reduced to their corresponding alkyl groups. It does not have the capability to reduce a carboxylic acid group. The reaction will continue as follows:

Thus, we have the structure of Q. Similarly, we will find the structures of R and S.
- For R
Here, we have two different reagents, we will look at each of the reagents and then determine the major product of the reaction.
i) $SOC{{l}_{2}},pyridine$
This reagent is commonly used for Darzan's process. In this process, the chlorination of the acid group occurs, the $-OH$ group in the acid is replaced by the $-Cl$ group and no other changes occur. The reaction will continue as follows:

Here we have obtained the molecule that will replace the variable R in the reaction.
- For S
i) $Zn-Hg,conc.HCl$
This has only one reagent and even that is repeated. We saw this reagent when we were finding Q as the third reagent. This reagent is used for the Clemmensen reduction reaction and converts aldehydes and ketones to alkanes. Here, the sole ketonic group will be converted to an alkyl group. The reaction will be as follows:

So now, looking at all the reactions and the structures of the molecules that we obtained for Q, R, and S.
The correct answers to this question are option A and option D.
Note: Remember that in the very first reaction that includes the Markovnikov’s rule some product that has the ketonic group at the other end of the triple bond will also be formed but we are only considering major products. Even if we do consider the minor product, we will eventually get the same structures for Q, R, and S.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




