
$CH_{3}CH=CH_{2}\xrightarrow[H^{+}]{CO+H_{2}}CH_{3}CH(COOH)CH_{3}$ is known as
A. Wurtz reaction
B. Koch reaction
C. Clemmensen reaction
D. Kolbe's reaction
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alkenes on reaction with carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas in the presence of acid give rise to tertiary carboxylic acids.
Together, carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas are called synthesis gas, syn gas, or water gas.
Complete step-by-step answer: Alkenes or alcohols on treatment with synthesis gas in the presence of acids give rise to tertiary carboxylic acid.
This reaction is called the Koch reaction.
This reaction is an acid-catalyzed carbonylation reaction.
Carbonylation is the reaction in which carbon monoxide is treated with a substance.
This reaction happens at high pressure and temperature.
Generally, the reaction is conducted with powerful mineral acids like sulfuric acid, hydrogen fluoride etc.
The reaction occurs through a three-step mechanism.
The first step involves the addition of a proton to the propene or propylene.
Then the resulting carbocation is attacked by the incoming nucleophile which is carbon monoxide.
An acylium cation is formed as a result of this attack.
The acylium cation then undergoes hydrolysis to form 2-methyl propanoic acid or isobutyric acid.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
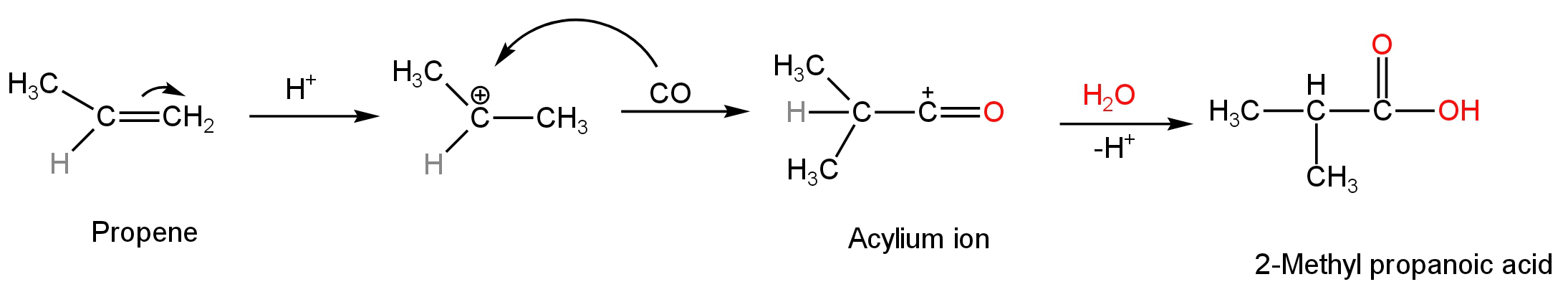
Image: Koch reaction mechanism
So, option B is correct.
Additional Information: Formic acid breaks down forming carbon monoxide in the presence of acids or deficient heat.
So, it is used in the reaction rather than carbon monoxide. This reaction is called Koch–Haaf reaction.
Note Propene on reaction with carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas gives rise to 2-methyl propanoic acid. This reaction is called the Koch reaction. In this reaction, an acid acts as a catalyst.
The mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen is called water gas. This mixture is used for the synthesis of methanol and other hydrocarbons.
Together, carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas are called synthesis gas, syn gas, or water gas.
Complete step-by-step answer: Alkenes or alcohols on treatment with synthesis gas in the presence of acids give rise to tertiary carboxylic acid.
This reaction is called the Koch reaction.
This reaction is an acid-catalyzed carbonylation reaction.
Carbonylation is the reaction in which carbon monoxide is treated with a substance.
This reaction happens at high pressure and temperature.
Generally, the reaction is conducted with powerful mineral acids like sulfuric acid, hydrogen fluoride etc.
The reaction occurs through a three-step mechanism.
The first step involves the addition of a proton to the propene or propylene.
Then the resulting carbocation is attacked by the incoming nucleophile which is carbon monoxide.
An acylium cation is formed as a result of this attack.
The acylium cation then undergoes hydrolysis to form 2-methyl propanoic acid or isobutyric acid.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:

Image: Koch reaction mechanism
So, option B is correct.
Additional Information: Formic acid breaks down forming carbon monoxide in the presence of acids or deficient heat.
So, it is used in the reaction rather than carbon monoxide. This reaction is called Koch–Haaf reaction.
Note Propene on reaction with carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas gives rise to 2-methyl propanoic acid. This reaction is called the Koch reaction. In this reaction, an acid acts as a catalyst.
The mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen is called water gas. This mixture is used for the synthesis of methanol and other hydrocarbons.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




