
$C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}A\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }}}B\xrightarrow[\vartriangle ]{{N{H_3}}}C\xrightarrow[{alkali}]{{B{r_2}}}D$ . D is:
A) $C{H_3}Br$
B) $C{H_3}CON{H_2}$
C) $C{H_2}N{H_2}$
D) $C{H_2}B{r_2}$
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Reagents used in the conversion are very important. The aqKOH use, carry out nucleophilic substitution reaction while $KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }$ is a very strong oxidizing agent. The ammonia $\left( {N{H_3}} \right)$ easily takes up protons in the reaction and $B{H_2}$ /alkali is a reagent used in Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
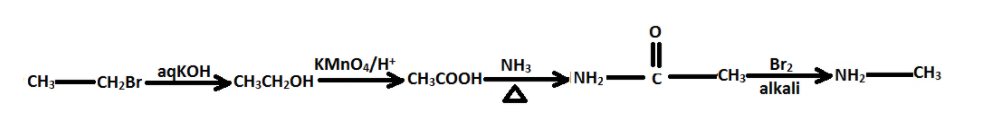
$C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}A\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }}}B\xrightarrow[\vartriangle ]{{N{H_3}}}C\xrightarrow[{alkali}]{{B{r_2}}}D$
First of all, let us break the sequential conversion, in order to make the conversion process easier for us.
Let us first look at this part of the reaction $C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}A$.
aqKOH acts a nucleophile here and the reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (${S_N}2$ reaction) as the ethyl bromide is a primary alkyl halide. Thus, we get
$C{H_3}C{H_2} - Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}C{H_3} - CH - OH$
The ethanol formed in the reaction is then oxidized by acidified potassium permanganate to give the corresponding carboxylic acid.
That is,
$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - OH\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }}}C{H_3} - COOH$
The $N{H_3}$ then takes up proton from the carboxylic forming ammonium ethanoate which when heated gives ethanamide.
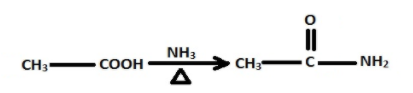
The ethanamide then reacts with $B{H_2}$ /alkali to form methylamine.
$C{H_3} - CON{H_2}\xrightarrow[{alkali}]{{B{H_2}}}C{H_3}N{H_2}$
This is Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide formed contains one carbon atom less than amide.
Thus, the sequential conversion can be written as –
Option (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Students should understand that associated colloids, also called micelles, are generally electrolytes. They exist as ions at low concentration. It is above a particular concentration called critical micelle concentration (CMC) and above a temperature called Kraft temperature; these get associated and exhibit colloidal behavior. It is very important to note that the primary distinguishing features between a true solution and a colloidal solution is fundamentally the dimension of the constituent part.
Complete step by step answer:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}A\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }}}B\xrightarrow[\vartriangle ]{{N{H_3}}}C\xrightarrow[{alkali}]{{B{r_2}}}D$
First of all, let us break the sequential conversion, in order to make the conversion process easier for us.
Let us first look at this part of the reaction $C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}A$.
aqKOH acts a nucleophile here and the reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (${S_N}2$ reaction) as the ethyl bromide is a primary alkyl halide. Thus, we get
$C{H_3}C{H_2} - Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}C{H_3} - CH - OH$
The ethanol formed in the reaction is then oxidized by acidified potassium permanganate to give the corresponding carboxylic acid.
That is,
$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - OH\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }}}C{H_3} - COOH$
The $N{H_3}$ then takes up proton from the carboxylic forming ammonium ethanoate which when heated gives ethanamide.

The ethanamide then reacts with $B{H_2}$ /alkali to form methylamine.
$C{H_3} - CON{H_2}\xrightarrow[{alkali}]{{B{H_2}}}C{H_3}N{H_2}$
This is Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide formed contains one carbon atom less than amide.
Thus, the sequential conversion can be written as –

Option (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Students should understand that associated colloids, also called micelles, are generally electrolytes. They exist as ions at low concentration. It is above a particular concentration called critical micelle concentration (CMC) and above a temperature called Kraft temperature; these get associated and exhibit colloidal behavior. It is very important to note that the primary distinguishing features between a true solution and a colloidal solution is fundamentally the dimension of the constituent part.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




