
Assertion: The position-Time graph of a stationary object is a straight line parallel to the time axis.
Reason: For a stationary object, the position does not change with time
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
C. Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D. Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: This question basically is a concept from Motion in one dimension. In the question given above, consider the graph of position vs time where the slope is zero and the object is stationary.
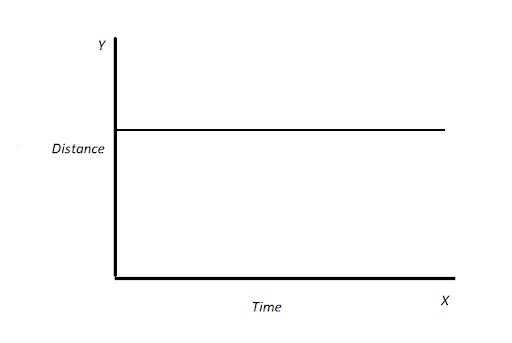
Given graph is position vs time which shows a straight line parallel to the time axis. In the concept of graph theory for different conditions of stationary objects, we basically calculate the slopes for the given graphs and watch the different aspects of the position of the objects with respect to the time.
Formula used:
\[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\] ,
Using the above formula, we can calculate the slopes for the graphs.
Complete step by step solution:
The given statement says that the position vs. time graph for a stationary object is basically a straight line parallel to the time axis. The stationary object is nothing but the simplest motion for any object to perform, basically, a stationary object does not move and the position of the object does not carry or change from its original location.
Therefore, the gradient m or the slope can be calculated for the given graph by dividing the change in the dependent variable y by the independent variable \[x\]. It’s given as:
\[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
Gradient or slope for the position vs time graph gives average velocity which comes out to be 0 m/s since the stationary object does not change its position.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note: Make sure you are calculating the slopes for the graph as per the required constraints and studying the different nature of the graphs and analysing it. When the object that is being considered is at rest, then its position will not change with time.

Given graph is position vs time which shows a straight line parallel to the time axis. In the concept of graph theory for different conditions of stationary objects, we basically calculate the slopes for the given graphs and watch the different aspects of the position of the objects with respect to the time.
Formula used:
\[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\] ,
Using the above formula, we can calculate the slopes for the graphs.
Complete step by step solution:
The given statement says that the position vs. time graph for a stationary object is basically a straight line parallel to the time axis. The stationary object is nothing but the simplest motion for any object to perform, basically, a stationary object does not move and the position of the object does not carry or change from its original location.
Therefore, the gradient m or the slope can be calculated for the given graph by dividing the change in the dependent variable y by the independent variable \[x\]. It’s given as:
\[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
Gradient or slope for the position vs time graph gives average velocity which comes out to be 0 m/s since the stationary object does not change its position.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note: Make sure you are calculating the slopes for the graph as per the required constraints and studying the different nature of the graphs and analysing it. When the object that is being considered is at rest, then its position will not change with time.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




