
Aromatic primary amine when treated with cold \[HN{O_2}\] gives
(A) Benzyl Alcohol
(B) Nitro Benzene
(C) Benzene
(D) Diazonium salt
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: An amine is often a functional group with a lone pair on the nitrogen atom. Amines structurally mimic ammonia, where nitrogen can link with up to three hydrogen atoms. It is also defined by a number of carbon connectivity-based features.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In order to know that when an alkyl or aryl group replaces one of the hydrogen atoms in the ammonia molecule, the presence of the primary amines can be determined. For instance: Methylamine \[{\text{ }}C{H_3}N{H_2}\]and Aniline \[{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}\].
For the simple removal of a water molecule, nitrous acid \[(HN{O_2})\] is represented by the formula \[HO - N = O\]. As a result, a water molecule is created when the secondary amine's hydrogen ion joins with nitrous acid's \[O{H^ - }\]ion.
The reaction process that occurs when amine reacts with cold \[HN{O_2}\] will now be discussed below:
Using nitrous acid \[(HN{O_2})\]reagent to convert amine to diazonium ion,
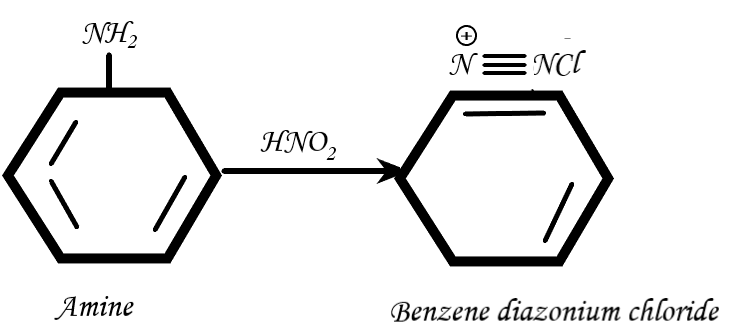
A primary aromatic amines react with cold \[HN{O_2}\]and dissolved in dilute \[HCl\]at \[0 - 5^\circ C\]will produced diazonium salt. The nitrogen gas will emerge when the cold salt is heated to the room temperature.
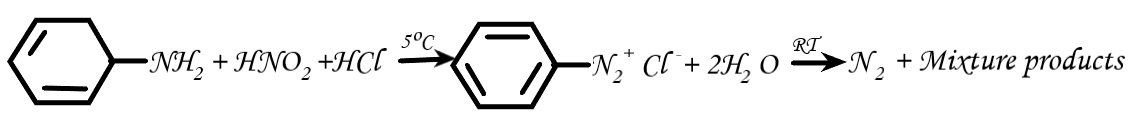
Therefore, the correct option is: (D) Diazonium salt.
Note: It is important to remember that the carbylamine reaction is utilised to find primary amines. Isocyanide, a substance that is produced and has a strong odour, is the end result. This reaction is not produced by secondary or tertiary amines. The reaction is as following: \[RN{H_2} + CHC{l_3} + 3KOH \to RNC + 3KCl + 3{H_2}O\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In order to know that when an alkyl or aryl group replaces one of the hydrogen atoms in the ammonia molecule, the presence of the primary amines can be determined. For instance: Methylamine \[{\text{ }}C{H_3}N{H_2}\]and Aniline \[{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}\].
For the simple removal of a water molecule, nitrous acid \[(HN{O_2})\] is represented by the formula \[HO - N = O\]. As a result, a water molecule is created when the secondary amine's hydrogen ion joins with nitrous acid's \[O{H^ - }\]ion.
The reaction process that occurs when amine reacts with cold \[HN{O_2}\] will now be discussed below:
Using nitrous acid \[(HN{O_2})\]reagent to convert amine to diazonium ion,

A primary aromatic amines react with cold \[HN{O_2}\]and dissolved in dilute \[HCl\]at \[0 - 5^\circ C\]will produced diazonium salt. The nitrogen gas will emerge when the cold salt is heated to the room temperature.

Therefore, the correct option is: (D) Diazonium salt.
Note: It is important to remember that the carbylamine reaction is utilised to find primary amines. Isocyanide, a substance that is produced and has a strong odour, is the end result. This reaction is not produced by secondary or tertiary amines. The reaction is as following: \[RN{H_2} + CHC{l_3} + 3KOH \to RNC + 3KCl + 3{H_2}O\]
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




