
What are interstitial compounds? Why do these compounds have higher melting points than corresponding pure metals?
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: The melting point of an element or a compound can be stated as the temperature or the point when a solid changes its state to liquid.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Interstitial compounds are marked by the presence of some atoms like ${\rm{N,C}}$or ${\rm{H}}$. These atoms are trapped inside of the vacant interstitial spaces in the crystal lattice of the metals.${\rm{M}}{{\rm{n}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{H,F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{H,}}\,{\rm{Ti}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.73}}}}{\rm{,TiC}}$ are some common examples of interstitial compounds.
These interstitial compounds have higher melting points than corresponding pure metals. It is because these compounds are inert chemically, they are usually hard, and these compounds are stabilized due to the presence of foreign atoms.
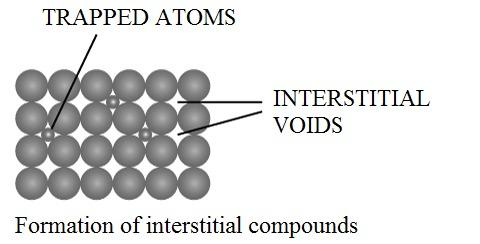
The above figure shows the presence of interstitial elements vacant interstitial spaces of the crystal lattice.
Additional information:
Transition metals form a lot of interstitial compounds. Transition metals react with elements like hydrogen, nitrogen, boron, carbon etc. forming interstitial compounds.
The various properties of the interstitial compounds are:
(a)Interstitial compounds are rigid and hard. It is because in the interstitial compound, the vacant spaces of the transition metals are filled up by the small atoms
(b) During the formation of interstitial compounds, the chemical properties of the parent transition metal do not get changed or altered. Various changes in the physical properties take place in the parent metals such as hardness, density, rigidity, ductility, malleability, electrical conductivity etc.
Note: Presence of some atoms like ${\rm{N,C}}$or ${\rm{H}}$ trapped in the vacant spaces in the crystal lattice gives rise to the interstitial compounds. The melting points of these compounds are higher than that of pure metals due to bonding between the metal and the non-metals, which is stronger than the metal-metal bonding.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Interstitial compounds are marked by the presence of some atoms like ${\rm{N,C}}$or ${\rm{H}}$. These atoms are trapped inside of the vacant interstitial spaces in the crystal lattice of the metals.${\rm{M}}{{\rm{n}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{H,F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{H,}}\,{\rm{Ti}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.73}}}}{\rm{,TiC}}$ are some common examples of interstitial compounds.
These interstitial compounds have higher melting points than corresponding pure metals. It is because these compounds are inert chemically, they are usually hard, and these compounds are stabilized due to the presence of foreign atoms.

The above figure shows the presence of interstitial elements vacant interstitial spaces of the crystal lattice.
Additional information:
Transition metals form a lot of interstitial compounds. Transition metals react with elements like hydrogen, nitrogen, boron, carbon etc. forming interstitial compounds.
The various properties of the interstitial compounds are:
(a)Interstitial compounds are rigid and hard. It is because in the interstitial compound, the vacant spaces of the transition metals are filled up by the small atoms
(b) During the formation of interstitial compounds, the chemical properties of the parent transition metal do not get changed or altered. Various changes in the physical properties take place in the parent metals such as hardness, density, rigidity, ductility, malleability, electrical conductivity etc.
Note: Presence of some atoms like ${\rm{N,C}}$or ${\rm{H}}$ trapped in the vacant spaces in the crystal lattice gives rise to the interstitial compounds. The melting points of these compounds are higher than that of pure metals due to bonding between the metal and the non-metals, which is stronger than the metal-metal bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




