
An amusement park ride called "The spinning Terror" is a large vertical drum which spins so fast that everyone stays pinned against the wall when the floor drops away from, the minimum
A) Angular velocity is \[{\omega _{min}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{\mu R}}} \] for everyone to stay inside.
B) Linear velocity is \[{v_{min}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{\mu R}}} \] for everyone to stay Inside.
C) Angular velocity is \[{\omega _{min}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{gR}}{\mu }} \] for everyone to stay Inside.
D) Linear velocity is \[{v_{min}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{gR}}{\mu }} \] for everyone to stay Inside.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Linear velocity is defined as the rate of change of the displacement to the time, whenever the body is moving along a straight path. Angular velocity is defined as the rate of change of the angular position of a rotating body.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that it is a vertical drum.
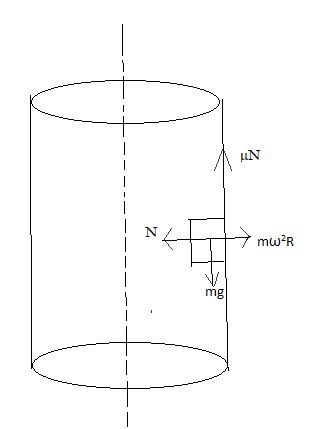
We know that $mg = \mu N\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 1 \right)$
From the diagram, $N = m{\omega ^2}_{min}R$
Substituting the value of N in equation 1, we get
$ \Rightarrow mg = \mu m{\omega ^2}_{min}R$
\[\therefore {\omega _{min}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{\mu R}}} \]
Also, we know that ${v_{min}} = R{\omega _{min}}$
Hence substituting the value of \[{\omega _{min}}\], we get
$ \Rightarrow {v_{min}} = R\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{\mu R}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{gR}}{\mu }} $
Hence the correct options are A and D.
Note: 1. Angular velocity is the change in angle over time whereas linear velocity is the speed in a straight line. The unit of linear velocity is m/s and the unit of angular velocity is rad/s.
2. When the object is coming in the same direction, in which the gravity is acting then the acceleration due to gravity is positive.
3. The rate of change of velocity is known as acceleration and the rate of change angular velocity is known as angular acceleration. Angular velocity and angular speed are both the same.
4. The acceleration gained by the body due to gravity is called acceleration due to gravity. The acceleration due to gravity depends on the mass of the earth and the radius of the earth. It is denoted by the symbol g. The acceleration due to gravity is maximum at the poles and is minimum at the equator. When a body is going up, the acceleration is negative as the speed is decreasing.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that it is a vertical drum.

We know that $mg = \mu N\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 1 \right)$
From the diagram, $N = m{\omega ^2}_{min}R$
Substituting the value of N in equation 1, we get
$ \Rightarrow mg = \mu m{\omega ^2}_{min}R$
\[\therefore {\omega _{min}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{\mu R}}} \]
Also, we know that ${v_{min}} = R{\omega _{min}}$
Hence substituting the value of \[{\omega _{min}}\], we get
$ \Rightarrow {v_{min}} = R\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{\mu R}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{gR}}{\mu }} $
Hence the correct options are A and D.
Note: 1. Angular velocity is the change in angle over time whereas linear velocity is the speed in a straight line. The unit of linear velocity is m/s and the unit of angular velocity is rad/s.
2. When the object is coming in the same direction, in which the gravity is acting then the acceleration due to gravity is positive.
3. The rate of change of velocity is known as acceleration and the rate of change angular velocity is known as angular acceleration. Angular velocity and angular speed are both the same.
4. The acceleration gained by the body due to gravity is called acceleration due to gravity. The acceleration due to gravity depends on the mass of the earth and the radius of the earth. It is denoted by the symbol g. The acceleration due to gravity is maximum at the poles and is minimum at the equator. When a body is going up, the acceleration is negative as the speed is decreasing.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




