
An amine on reaction with benzene sulphonyl chloride produces a compound insoluble in an alkaline solution. This amine can be prepared by ammonolysis of Chloroethane. The correct structure of amine is
A.
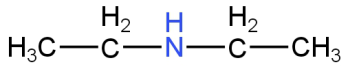
B.
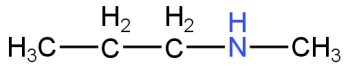
C.
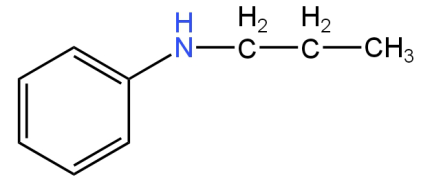
D.
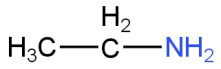
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: Benzenesulfonyl chloride reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulfonamides. Ammonolysis is the reaction of alkyl or benzyl halide with an ethanolic solution of ammonia.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When an alkyl or benzyl halide reacts with an ethanolic solution of ammonia, it undergoes a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The halogen atom is replaced by an amino group.
A.
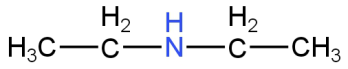
Image: Option A(N-ethylethanamine)
This is N-ethylethanamine.
This is a secondary amine.
It reacts with benzenesulfonamide to form
N, N-diethyl-benzenesulfonamide.
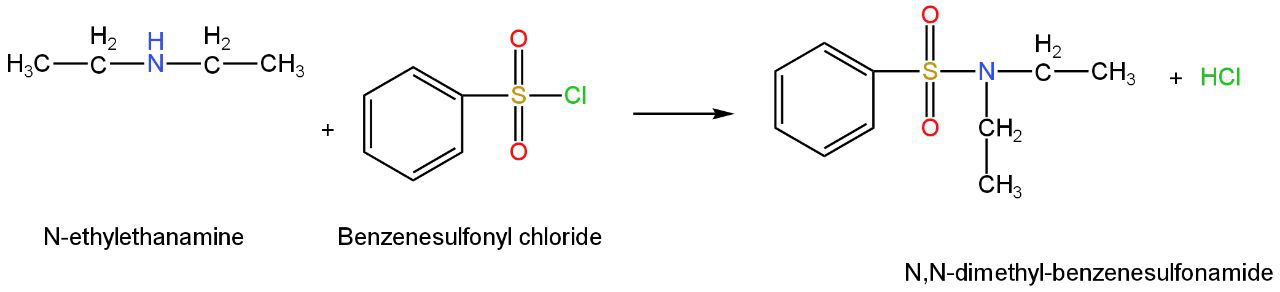
Image: reaction of N-ethylethanamine with benzenesulfonyl chloride.
We can see that N, N-diethyl-benzenesulfonamide does not include any acidic hydrogen atom next to the nitrogen atom.
So, it is not acidic and hence is insoluble in alkaline solution.
Chloroethane when treated with ammonia can give N-ethylethanamine as a product.
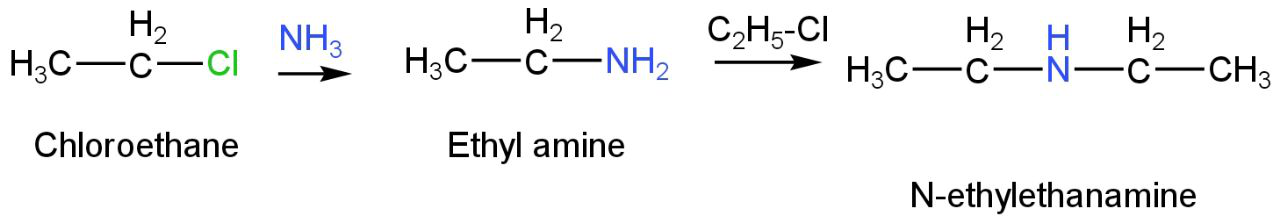
Image: Reaction of chloroethane with ammonia.
Thus, N-ethylethanamine is the correct amine compound as it can be made from Chloroethane through ammonolysis, it is not soluble in an alkaline solution.
B.
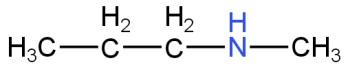
Image: Option B (N-methylpropanamine)
This is N-methylpropanamine.
This is a secondary amine.
It will react with Benzenesulfonyl chloride to form N-methyl-N-propyl benzenesulfonamide.
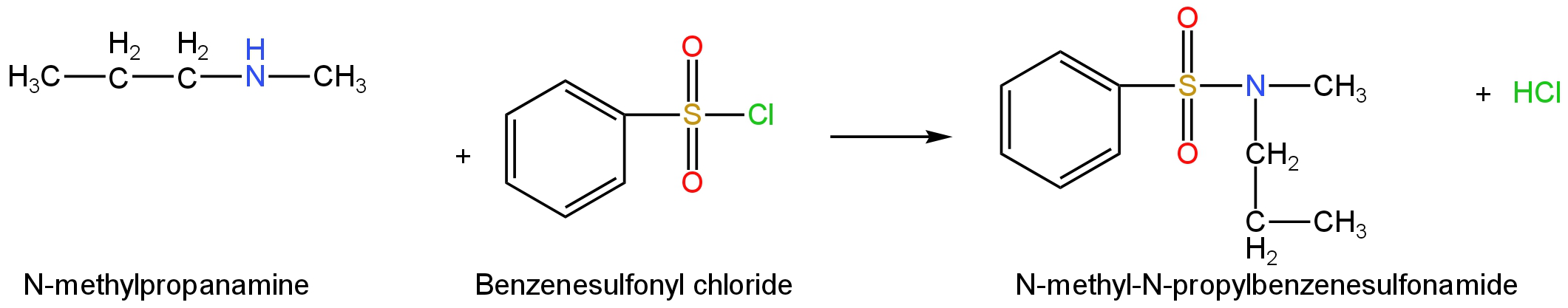
Image: Reaction of N-methylpropanamine with benzenesulfonyl chloride.
This compound in the absence of an acidic Hydrogen atom attached to the Nitrogen atom will not be soluble in an alkaline solution.
Hence, this is not the correct structure.
C.
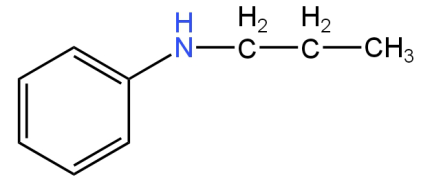
Image: Option C (N-phenyl-N-propylamine)
This is N-phenyl-N-propylamine.
This is a secondary amine.
It will react with Benzenesulfonamide to form N-phenyl-N-propylbenzenesulfonamide by the following reaction.
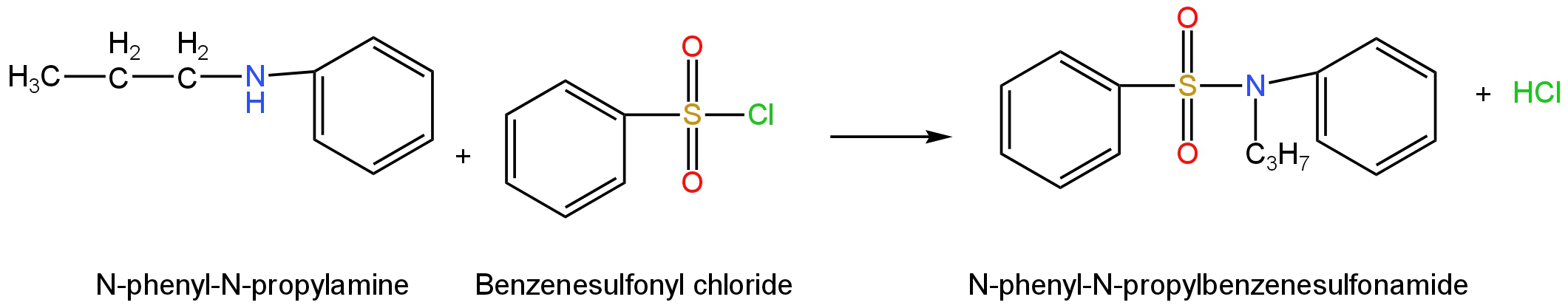
Image: Reaction of N-phenyl-N-propylamine
with benzenesulfonyl chloride
This compound in the absence of an acidic Hydrogen atom attached to the Nitrogen atom will not be soluble in an alkaline solution.
Hence, this is not the correct structure.
D.
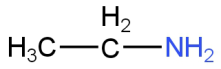
Image: Option D (Ethyl amine)
This is ethylamine.
Benzenesulfonyl chloride or Hinsberg's reagent reacts with an ethanamine to form
N-ethylbenzenesulfonamide.
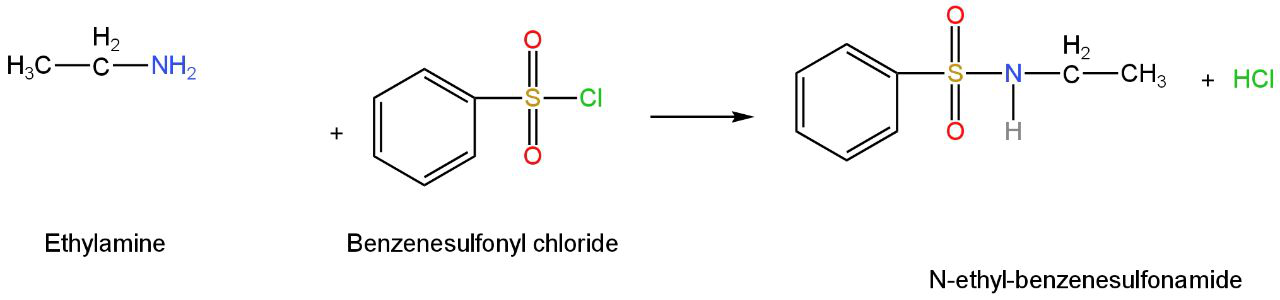
Image: Reaction of ethylamine with benzenesulfonyl chloride
The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulfonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of the electron-withdrawing sulfonyl group.
Due to this, it is soluble in alkali.
Chloroethane will undergo ammonolysis to give ethylamine.
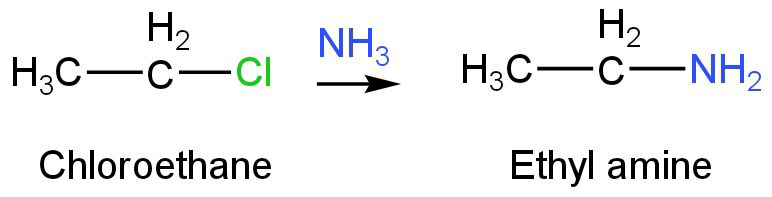
Image: Ammonolysis of chloroethane
So, it is not the correct structure of the amine as even though ammonolysis of chloroethane gives this compound it is soluble in an alkaline solution.
So, option A is correct.
Note: While attempting this question, it must be observed that after the given compound's reaction with the Hinsberg reagent, if the product has the presence of a hydrogen atom next to a nitrogen atom, or not. It must also be noted that both N-ethylethanamine and ethanamine can be formed from chloroethane, but only ethylamine is soluble in an alkaline solution.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When an alkyl or benzyl halide reacts with an ethanolic solution of ammonia, it undergoes a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The halogen atom is replaced by an amino group.
A.

Image: Option A(N-ethylethanamine)
This is N-ethylethanamine.
This is a secondary amine.
It reacts with benzenesulfonamide to form
N, N-diethyl-benzenesulfonamide.

Image: reaction of N-ethylethanamine with benzenesulfonyl chloride.
We can see that N, N-diethyl-benzenesulfonamide does not include any acidic hydrogen atom next to the nitrogen atom.
So, it is not acidic and hence is insoluble in alkaline solution.
Chloroethane when treated with ammonia can give N-ethylethanamine as a product.

Image: Reaction of chloroethane with ammonia.
Thus, N-ethylethanamine is the correct amine compound as it can be made from Chloroethane through ammonolysis, it is not soluble in an alkaline solution.
B.
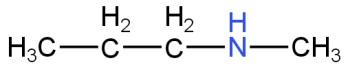
Image: Option B (N-methylpropanamine)
This is N-methylpropanamine.
This is a secondary amine.
It will react with Benzenesulfonyl chloride to form N-methyl-N-propyl benzenesulfonamide.

Image: Reaction of N-methylpropanamine with benzenesulfonyl chloride.
This compound in the absence of an acidic Hydrogen atom attached to the Nitrogen atom will not be soluble in an alkaline solution.
Hence, this is not the correct structure.
C.

Image: Option C (N-phenyl-N-propylamine)
This is N-phenyl-N-propylamine.
This is a secondary amine.
It will react with Benzenesulfonamide to form N-phenyl-N-propylbenzenesulfonamide by the following reaction.

Image: Reaction of N-phenyl-N-propylamine
with benzenesulfonyl chloride
This compound in the absence of an acidic Hydrogen atom attached to the Nitrogen atom will not be soluble in an alkaline solution.
Hence, this is not the correct structure.
D.

Image: Option D (Ethyl amine)
This is ethylamine.
Benzenesulfonyl chloride or Hinsberg's reagent reacts with an ethanamine to form
N-ethylbenzenesulfonamide.

Image: Reaction of ethylamine with benzenesulfonyl chloride
The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulfonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of the electron-withdrawing sulfonyl group.
Due to this, it is soluble in alkali.
Chloroethane will undergo ammonolysis to give ethylamine.

Image: Ammonolysis of chloroethane
So, it is not the correct structure of the amine as even though ammonolysis of chloroethane gives this compound it is soluble in an alkaline solution.
So, option A is correct.
Note: While attempting this question, it must be observed that after the given compound's reaction with the Hinsberg reagent, if the product has the presence of a hydrogen atom next to a nitrogen atom, or not. It must also be noted that both N-ethylethanamine and ethanamine can be formed from chloroethane, but only ethylamine is soluble in an alkaline solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

JEE Main Correction Window 2026 Session 1 Dates Announced - Edit Form Details, Dates and Link

Free Radical Substitution and Its Stepwise Mechanism

How Does Fusion Reaction Happen Inside the Sun?

JEE Main 2026 Helpline Numbers for Aspiring Candidates

Other Pages
Class 12 CBSE Chemistry Sample Paper - Set 6 Preparation

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry In Hindi Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium - 2025-26

Half Life of Zero Order Reaction for JEE

What Are Elastic Collisions in One Dimension?

Understanding Excess Pressure Inside a Liquid Drop

Understanding Geostationary and Geosynchronous Satellites




