
An alkyl bromide produces a single alkene when it reacts with sodium ethoxide and ethanol. This alkene undergoes hydrogenation and produces 2-methyl butane. What is the identity of the alkyl bromide?
A. 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane
B. 1-bromobutane
C. 2-bromo-2-methylbutane
D. 1-bromo-2-methylbutane
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The conversion of an alkyl halide into an alkene happens in presence of potassium hydroxide. This reaction is termed the elimination reaction. This reaction is used in the laboratory to produce alcohol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, an alkyl halide undergoes an elimination reaction in the presence of ethanol. In an elimination reaction, there is the removal of several atoms from a molecule. The formed alkene when undergoing a hydrogenation reaction gives 2-methyl butane. So, the haloalkane is 1-bromo-2-methylbutane. So, the elimination reaction,
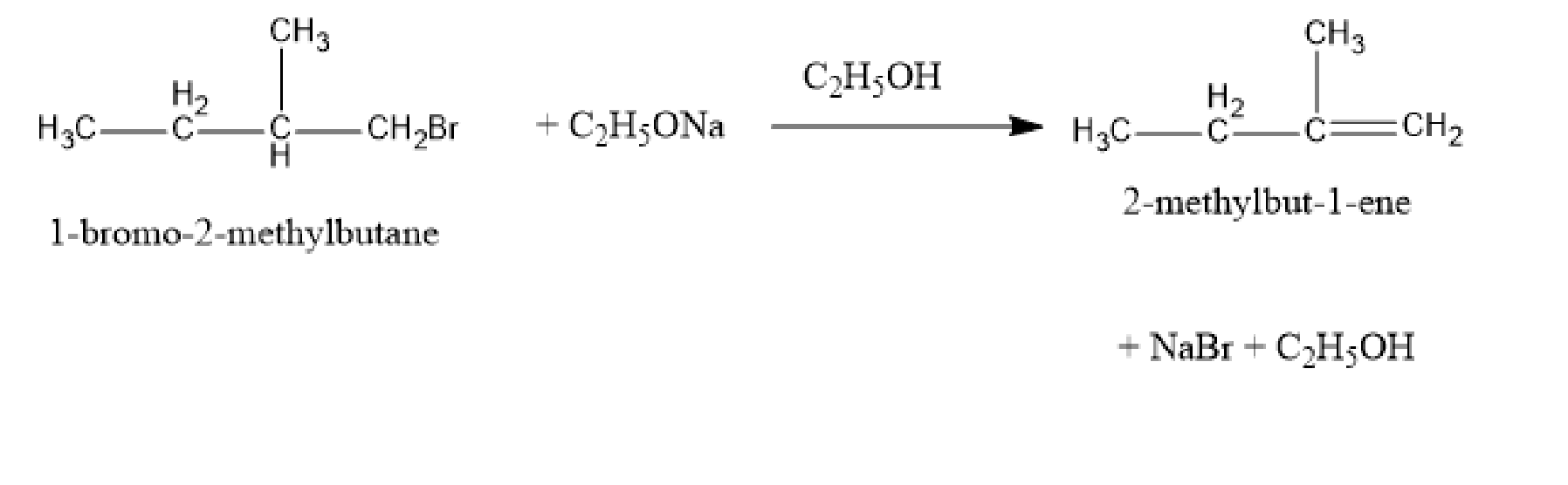
Fig: Elimination reaction of 1-bromo-2-methylbutane
In the above elimination reaction, one hydrogen atom and one bromine atom are removed from the 1-bromo-2-methylbutane. And the products formed are 2-methylbut-1-ene, sodium bromide, and ethanol.
In the second step, 2-methylbut-1-ene undergoes a hydrogenation reaction. In this reaction, hydrogen undergoes a reaction with a compound in presence of nickel (catalyst) to form an alkane. 2-methylbut-1-ene undergoes a hydrogenation reaction to form 2-methylbutane. The reaction is,
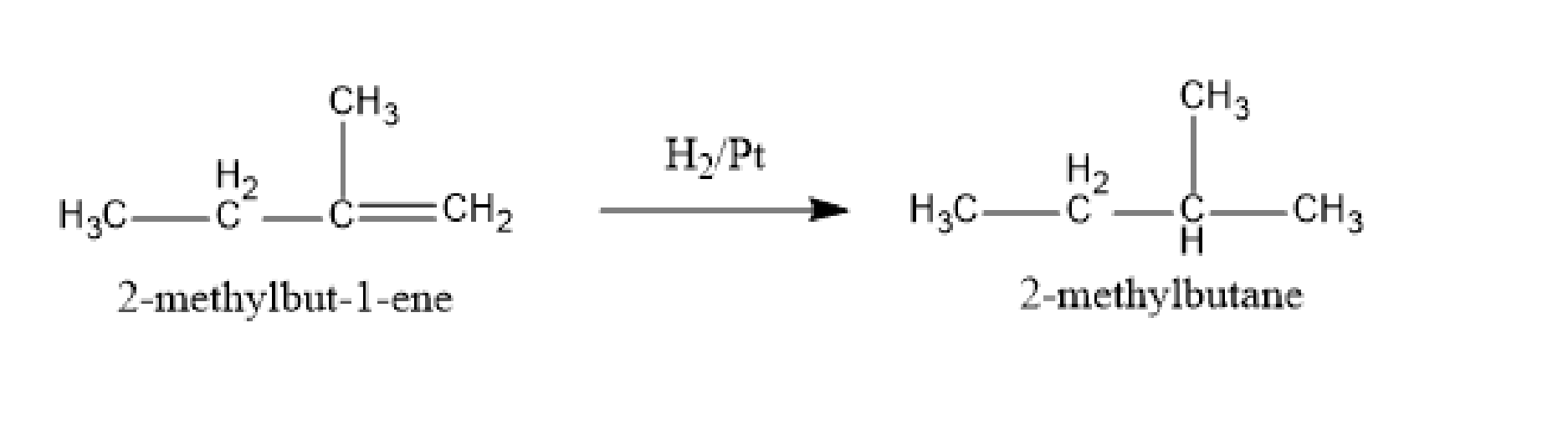
Fig: Hydrogenation reaction
Therefore, the alkyl halide used in the given reaction is 1-bromo-2-methylbutane.
Hence, option C is right.
Note: The elimination reaction is of three types, namely E1, E2, E1cb. The E1 reaction is a two-step removal process known by the name of unimolecular elimination. The E2 reaction is a one step removal process and known by the name of bimolecular elimination.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, an alkyl halide undergoes an elimination reaction in the presence of ethanol. In an elimination reaction, there is the removal of several atoms from a molecule. The formed alkene when undergoing a hydrogenation reaction gives 2-methyl butane. So, the haloalkane is 1-bromo-2-methylbutane. So, the elimination reaction,

Fig: Elimination reaction of 1-bromo-2-methylbutane
In the above elimination reaction, one hydrogen atom and one bromine atom are removed from the 1-bromo-2-methylbutane. And the products formed are 2-methylbut-1-ene, sodium bromide, and ethanol.
In the second step, 2-methylbut-1-ene undergoes a hydrogenation reaction. In this reaction, hydrogen undergoes a reaction with a compound in presence of nickel (catalyst) to form an alkane. 2-methylbut-1-ene undergoes a hydrogenation reaction to form 2-methylbutane. The reaction is,

Fig: Hydrogenation reaction
Therefore, the alkyl halide used in the given reaction is 1-bromo-2-methylbutane.
Hence, option C is right.
Note: The elimination reaction is of three types, namely E1, E2, E1cb. The E1 reaction is a two-step removal process known by the name of unimolecular elimination. The E2 reaction is a one step removal process and known by the name of bimolecular elimination.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




