
Amylopectin is a polymer of
(A) $\alpha -D$ glucose
(B) $\alpha -D$ fructose
(C) Lactose
(D) Amylose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Polymer is a substance consisting of a large number of molecules or macromolecules and composed of many repeating units.
Example. silk, wool, DNA, cellulose, proteins are all natural polymers.
Complete step by step answer:
Amylopectin is polysaccharide and a highly branched polymer. They are found in plants.
Amylopectin is one of the two important components of starch. It is water soluble.
The repeating unit in Amylopectin is $\alpha - D - $ glucose.
$\alpha - D - $glucose units are linked in a linear way with ${C_1} \to {C_4}$ glycosidic bonds.
A glycosidic linkage is a covalent bond that allows the linking of two monosaccharides together.
Amylopectin contributes about 80% of starch $\alpha - D - $ glucose linked ${C_1} - {C_4}$ atoms through glycosidic linkage branching occurs by the formation of glycosidic linkage between${C_1}$ of one$\alpha - D - $ glucose and ${C_6}$ of another $\alpha - D - $ glucose unit.
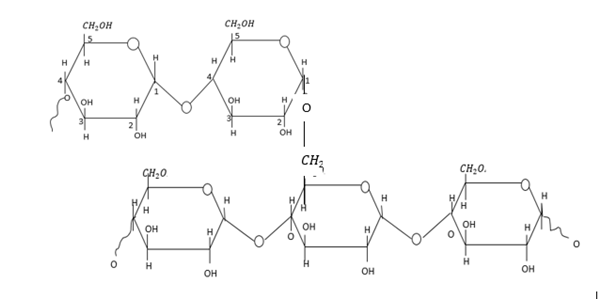
Linkage between two monosaccharide molecules through oxygen is called glycosidic linkage.
Therefore, by the above explanation, the correct option is [A]
Note: Polysaccharides have a large number of same or different monosaccharides, linked together by glycosidic linkage. They have molecular formula ${({C_6}{H_{10}}{O_5})_n}$
Another part of starch is Amylose. This is a water soluble part of starch.
Example. silk, wool, DNA, cellulose, proteins are all natural polymers.
Complete step by step answer:
Amylopectin is polysaccharide and a highly branched polymer. They are found in plants.
Amylopectin is one of the two important components of starch. It is water soluble.
The repeating unit in Amylopectin is $\alpha - D - $ glucose.
$\alpha - D - $glucose units are linked in a linear way with ${C_1} \to {C_4}$ glycosidic bonds.
A glycosidic linkage is a covalent bond that allows the linking of two monosaccharides together.
Amylopectin contributes about 80% of starch $\alpha - D - $ glucose linked ${C_1} - {C_4}$ atoms through glycosidic linkage branching occurs by the formation of glycosidic linkage between${C_1}$ of one$\alpha - D - $ glucose and ${C_6}$ of another $\alpha - D - $ glucose unit.

Linkage between two monosaccharide molecules through oxygen is called glycosidic linkage.
Therefore, by the above explanation, the correct option is [A]
Note: Polysaccharides have a large number of same or different monosaccharides, linked together by glycosidic linkage. They have molecular formula ${({C_6}{H_{10}}{O_5})_n}$
Another part of starch is Amylose. This is a water soluble part of starch.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




