
Among the following compounds nitrobenzene, benzene, aniline and phenol, the strongest basic behaviuor in acidic medium is exhibited by:
A. Phenol
B. Aniline
C. Nitrobenzene
D. Benzene
Answer
241.5k+ views
Hint: Basicity of species defines the basic character of the species. As the electron donating power of a species increases its basic character also increases. In acidic medium the basic character can be defined by electron donating power or hydrogen ion accepting power. It depends on several factors like- the groups attached, the resonance effect etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:Stability factor of base:
-As the tendency to participate in resonance increases the stability of the base also increases.
-A electron donating group attached to a species its basicity increases because the electron donating group donates its electron to benzene ring and hydrogen ion accepting tendency of the species increases.
-But an electron withdrawing group decreases the basicity of a species.
Stability comparison:
-Phenol or $C_6H_5OH$ can easily donate its hydrogen atom and acts as an acid.
-Aniline or $C_6H_5NH_2$ has electron donating $N$ atom attached with benzene and Nitrogen has a lone pair on it which it can donate to act as an base or accept protons to form ammonium ions.
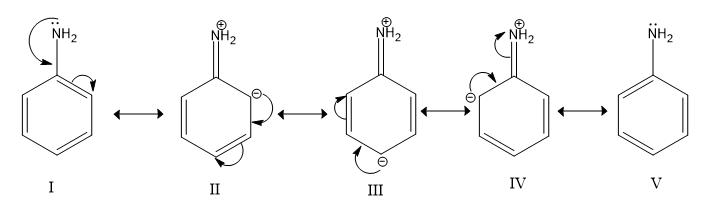
Image: Resonance of Aniline
-Nitrobenzene or $C_6H_5NO_2$ has an electron withdrawing nitro group attached with benzene which decreases its electron donating power and basic character decreases. The lone pair of electrons on N is not available for donation.
-Benzene can donate its electron pair and act as a moderately strong base.
Thus aniline is most basic in acidic solution.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: Basic character or basicity of a species defines the electron donating power. The acidic character or acidity of a species defines electron accepting power. Basicity increases with increase in ease of lone pair of electrons donation.
Complete step-by-step answer:Stability factor of base:
-As the tendency to participate in resonance increases the stability of the base also increases.
-A electron donating group attached to a species its basicity increases because the electron donating group donates its electron to benzene ring and hydrogen ion accepting tendency of the species increases.
-But an electron withdrawing group decreases the basicity of a species.
Stability comparison:
-Phenol or $C_6H_5OH$ can easily donate its hydrogen atom and acts as an acid.
-Aniline or $C_6H_5NH_2$ has electron donating $N$ atom attached with benzene and Nitrogen has a lone pair on it which it can donate to act as an base or accept protons to form ammonium ions.

Image: Resonance of Aniline
-Nitrobenzene or $C_6H_5NO_2$ has an electron withdrawing nitro group attached with benzene which decreases its electron donating power and basic character decreases. The lone pair of electrons on N is not available for donation.
-Benzene can donate its electron pair and act as a moderately strong base.
Thus aniline is most basic in acidic solution.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: Basic character or basicity of a species defines the electron donating power. The acidic character or acidity of a species defines electron accepting power. Basicity increases with increase in ease of lone pair of electrons donation.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




