
Alkene\[R - CH = C{H_2}\] reacts readily with\[{B_2}{H_6}\] and the product on oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxides produces
A.\[R - C{H_2} - CHO\]
B.\[R - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH\]
C.
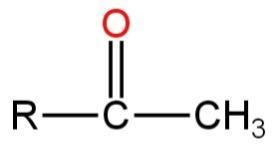
D.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: \[{B_2}{H_6}\] is called diborane which is one of the significant hydrides of boron. It is an electron-deficient compound thus when reacted with alkenes acts as an electrophile.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, we are given an alkene that reacts with diborane, and the resulting product will undergo oxidation.
Let us know about diborane.
Diborane has a bridge structure in which each boron atom is held by two hydrogen atoms by regular electron-pair bonds. These bonds are called terminal bonds.
Two bridging H-atoms construct bridge bonds with boron.
Alkenes react with diborane to give alkylboranes which on the oxidation with alkaline Hydrogen peroxide form alcohols.
This reaction is called hydroboration-oxidation.
Diborane forms two molecules of BH3.
In the first step,\[B{H_3}\] gets added to the double bond, replacing one of the hydrogen atoms with the carbon adjacent to the one which is bonded to the boron.
This hydroboration is done two more times making three alkenes add to each BH3.
The resulting trialkyl borane is reacted with hydrogen peroxide in the second step.
This procedure displaces the B-C bonds with HO-C bonds. The boron reagent is transformed into boric acid.
The Hydroxyl group gets connected to the less-substituted carbon. So, it is an anti-Markovnikov reaction.
The reaction happens as follows:-
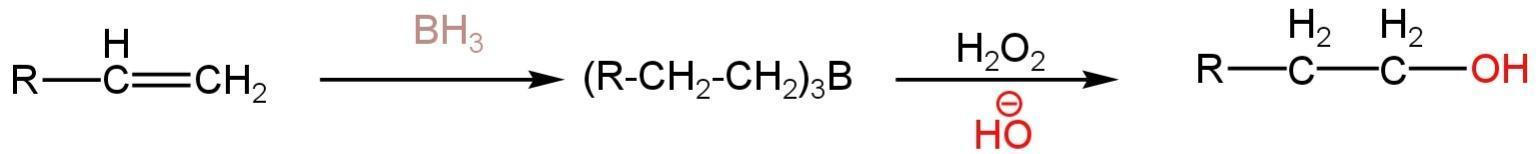
So, option B is correct.
Note: All hydrogens have to get connected to boron, until it happens, the boron group \[B{H_3}\]will continue to add to additional alkenes. This implies that one mole of hydroborane will encounter the reaction with three moles of alkene.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, we are given an alkene that reacts with diborane, and the resulting product will undergo oxidation.
Let us know about diborane.
Diborane has a bridge structure in which each boron atom is held by two hydrogen atoms by regular electron-pair bonds. These bonds are called terminal bonds.
Two bridging H-atoms construct bridge bonds with boron.
Alkenes react with diborane to give alkylboranes which on the oxidation with alkaline Hydrogen peroxide form alcohols.
This reaction is called hydroboration-oxidation.
Diborane forms two molecules of BH3.
In the first step,\[B{H_3}\] gets added to the double bond, replacing one of the hydrogen atoms with the carbon adjacent to the one which is bonded to the boron.
This hydroboration is done two more times making three alkenes add to each BH3.
The resulting trialkyl borane is reacted with hydrogen peroxide in the second step.
This procedure displaces the B-C bonds with HO-C bonds. The boron reagent is transformed into boric acid.
The Hydroxyl group gets connected to the less-substituted carbon. So, it is an anti-Markovnikov reaction.
The reaction happens as follows:-
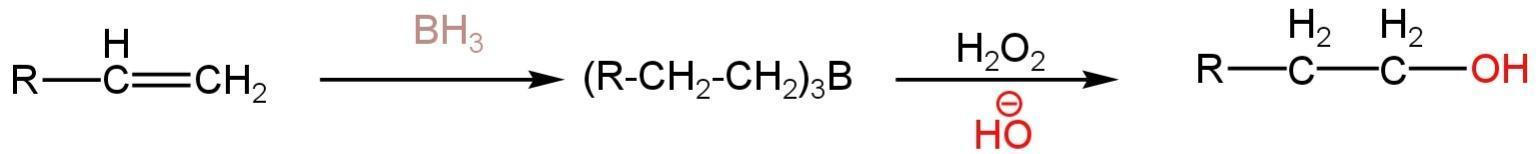
So, option B is correct.
Note: All hydrogens have to get connected to boron, until it happens, the boron group \[B{H_3}\]will continue to add to additional alkenes. This implies that one mole of hydroborane will encounter the reaction with three moles of alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




